Abstract
Objective
To investigate the influence of serum albumin on the prognosis of elderly patients with stage 3–4 chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods
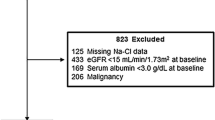
From July 2013 to November 2015, elderly CKD patients (≥60 years), with eGFR ≥15 mL/min/1.73 m2 and <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, with CKD stage 3–4 in the geriatric nephrology clinic were enrolled. General information and underlying diseases were recorded. Laboratory indices were evaluated. Composite endpoint events (CEE) including renal endpoint events, cardiocerebral vascular endpoint events, and death were elucidated. Based on the ROC curves, the patients were divided into lower and higher serum albumin groups (<42.5 and ≥42.5 g/L).
Results
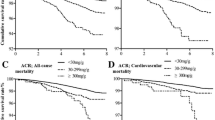
The occurrence of CEEs was significantly higher in lower serum albumin group than those in the higher group. Also, the patients in the higher group were significantly younger with lower urinary protein, blood urea, brain natriuretic peptide, and cystatin C than those in the lower serum albumin group. Contrastingly, hemoglobin, total serum protein, serum calcium, and superoxide dismutase were remarkably higher. The composite endpoints of multifactor logistic regression analysis indicated that as the serum albumin is increased by every 1 g/L, the probability of CEEs would reduce 14.8%, and the risk occurrence rate of the lower serum albumin group was 4.739 fold than the higher group.
Conclusion
The results suggest that patients with higher serum albumin had a better prognosis than those with lower serum albumin. The low level was an independent risk factor influencing the prognosis of elderly patients in stage 3–4 CKD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang L, Zhang P, Wang F et al (2008) Prevalence and factors associated with CKD: a population study from Beijing. Am J Kidney Dis 51(3):373–384
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L et al (2012) Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet 379(9818):815–822
Menon V, Greene T, Wang X et al (2005) C-reactive protein and albumin as predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 68(2):766–772
Kato A, Takita T, Furuhashi M et al (2010) Comparison of serum albumin, C-reactive protein and carotid atherosclerosis as predictors of 10-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int 14(2):226–232
Ni Z, Yuan Y, Wang Q et al (2014) Time-averaged albumin predicts the long-term prognosis of IgA nephropathy patients who achieved remission. J Transl Med 12:194
Shah NR, Dumler F (2008) Hypoalbuminaemia–a marker of cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease stages II–IV. Int J 5(6):366–370
Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Elsayed EF et al (2008) The relationship between nontraditional risk factors and outcomes in individuals with stage 3 to 4 CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 51(2):212–223
Muntner P, He J, Astor BC et al (2005) Traditional and nontraditional risk factors predict coronary heart disease in chronic kidney disease: results from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(2):529–538
Oh KH, Park SK, Park HC et al (2014) KNOW-CKD (KoreaN cohort study for Outcome in patients With Chronic Kidney Disease): design and methods. BMC Nephrol 15(1):901–910
Pifer TB, McCullough KP, Port FK et al (2002) Mortality risk in hemodialysis patients and changes in nutritional indicators: DOPPS. Kidney Int 62(6):2238–2245
Gama-Axelsson T, Heimburger O, Stenvinkel P et al (2012) Serum albumin as predictor of nutritional status in patients with ESRD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7(9):1446–1453
Kovesdy CP, George SM, Anderson JE et al (2009) Outcome predictability of biomarkers of protein-energy wasting and inflammation in moderate and advanced chronic kidney disease. Am J Clin Nutr 90(2):407–414
Chiu PF, Tsai CC, Wu CL et al (2016) Trajectories of serum albumin predict survival of peritoneal dialysis patients: a 15-year follow-up study. Medicine 95(12):e3202
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kilpatrick RD, Kuwae N et al (2005) Revisiting mortality predictability of serum albumin in the dialysis population: time dependency, longitudinal changes and population-attributable fraction. Nephro Dial Transplant 20(9):1880–1888
Yuvaraj A, Vijayan M, Alex M et al (2016) Effect of high-protein supplemental therapy on subjective global assessment of CKD-5D patients. Hemodial Int 20(1):56–62
Trifiro G, Fatuzzo PM, Ientile V et al (2014) Expert opinion of nephrologists about the effectiveness of low-protein diet in different stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Int J Food Sci Nutr 65(8):1027–1032
Lai S, Molfino A, Coppola B et al (2015) Effect of personalized dietary intervention on nutritional, metabolic and vascular indices in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19(18):3351–3359
Brunori G, Viola BF, Parrinello G et al (2007) Efficacy and safety of a very-low-protein diet when postponing dialysis in the elderly: a prospective randomized multicenter controlled study. Am J Kidney Dis 49(5):569–580
Carrero J (2009) Identification of patients with eating disorders: clinical and biochemical signs of appetite loss in dialysis patients. J Ren Nutr 19(1):10–15
Tucker PS, Dalbo VJ, Han T et al (2013) Clinical and research markers of oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Biomarkers 18(2):103–115
Krishnamoorthy V, Sunder S, Mahapatra HS et al (2015) Evaluation of protein-energy wasting and inflammation on patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and its correlations. Nephrourol 7(6):e33143
Kaysen GA, Dubin JA, Muller HG et al (2004) Inflammation and reduced albumin synthesis associated with stable decline in serum albumin in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 65(4):1408–1415
Locatelli F, Canaud B, Eckardt KU et al (2003) Oxidative stress in end-stage renal disease: an emerging threat to patient outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18(7):1272–1280
Kaysen GA, Greene T, Daugirdas JT et al (2003) Longitudinal and cross-sectional effects of C-reactive protein, equilibrated normalized protein catabolic rate, and serum bicarbonate on creatinine and albumin levels in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 42(6):1200–1211
Gupta KL, Sahni N (2012) Dietary antioxidents and oxidative stress in predialysis chronic kidney disease patients. J Nephropathol 1(3):134–142
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by the Capital Health Project Beijing Science Committee (Grant No: Z131100004013042) and Ministry of Human Resource of China (Grant No. bj201335) both to Dr. Jihong Yang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, H., Yang, J., Liu, L. et al. Effect of serum albumin on the prognosis of elderly patients with stage 3–4 chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 859–865 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1542-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1542-x