Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to investigate the prevalence and risk factors for hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation in HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy for glomerulonephritis.
Methods
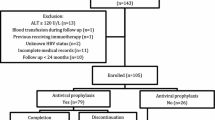
We performed a retrospective study of 745 HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy for glomerulonephritis from years 2003 to 2012 at the department of nephrology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China. The patients were divided into HBV reactivation group (n = 27) and non-HBV reactivation group (n = 718).
Results
The prevalence of HBV reactivation in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy for glomerulonephritis was up to 3.62% in serological status of HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive. HBV reactivation was associated with several findings: greater proportion of lupus nephritis (25.93 vs. 9.61%, p = 0.014), much higher percentage of HBsAb-negative (74.07 vs. 23.82%, p < 0.001), longer duration of immunosuppressive treatment (100 vs. 70.06%, p < 0.001), as well as more cases of combined immunosuppressant (92.59 vs. 61.56%, p = 0.001). After univariate and multivariate analysis, three variables remained as independent risk factors for HBV reactivation: serological status of HBsAb-negative (OR 8.375, 95% CI 3.674–19.776, p = 0.001), length of immunosuppressive treatment more than 1 year (OR 1.308, 95% CI 1.121–1.358, p = 0.024), and combined immunosuppressant (OR 6.342, 95% CI 1.675–30.166, p = 0.003).
Conclusions
HBV reactivation is not uncommon in HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive glomerulonephritis patients treated with immunosuppressant, and the prevalence was up to 3.62%. Patients with serological status of HBsAb-negative, more than 1 year of immunosuppressive therapy, and combined immunosuppressant are independent risk factors for HBV reactivation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yi Z, Jie YW, Nan Z (2011) The efficacy of anti-viral therapy on hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hepatol 10:165–173
Raimondo G, Pollicino T, Cacciola I, Squadrito G (2007) Occult hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 46:160–170
López-Serrano P, Pérez-Calle JL, Sánchez-Tembleque MD (2013) Hepatitis B and inflammatory bowel disease: role of antiviral prophylaxis. World J Gastroenterol 19:1342–1348
Rahier JF, Magro F, Abreu C, Armuzzi A, Ben-Horin S, Chowers Y, Cottone M, de Ridder L, Doherty G, Ehehalt R, Esteve M, Katsanos K, Lees CW, Macmahon E, Moreels T, Reinisch W, Tilg H, Tremblay L, Veereman-Wauters G, Viget N, Yazdanpanah Y, Eliakim R, Colombel JF (2014) Second European evidence-based consensus on the prevention, diagnosis and management of opportunistic infections in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohn’s Colitis 8:443–468
Beaugerie L, Gerbes AL (2010) Liver dysfunction in patients with IBD under immunosuppressive treatment: Do we need to fear? Gut 59:1310–1311
Manzano-Alonso ML, Castellano-Tortajada G (2011) Reactivation of hepatitis B virus infection after cytotoxic chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy. World J Gastroenterol 17:1531–1537
Shen LP, Zhang Y, Wang F, Zhang S, Yang JY, Fang KX, Yu T, Wang XY, Zhang WY, Bi SL (2011) Epidemiological changes in hepatitis B prevalence in an entire population after 20 years of the universal HBV vaccination programme. Epidemiol Infect 139:1159–1165
Zhang H, Li Q, Sun J, Wang C, Gu Q, Feng X, Du B, Wang W, Shi X, Zhang S, Li W, Jiang Y, Feng J, He S, Niu J (2011) Seroprevalence and risk factors for hepatitis B infection in an adult population in Northeast China. Int J Med Sci 8:321–331
Sung-Nan SN, Chen CH, Lee CM et al (2010) Reactivation of hepatitis B virus following rituximab-based regimens: a serious complication in both HBsAg-positive and HBsAg-negative patients. Ann Hematol 89:255–262
Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis G, Burroughs A (2010) Liver grafts from anti-hepatitis B core positive donors: a systematic review. J Hepatol 52:272–279
López-Serrano P, Pérez-Calle JL, Sánchez-Tembleque MD (2013) Hepatitis B and inflammatory bowel disease: role of antiviral prophylaxis. World J Gastroenterol 19:1342–1348
Yuen MF, Wong DK, Fung J, Ip P, But D, Hung I, Lau K, Yuen JC, Lai CL (2008) HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B in Asian patients: replicative level and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 135:1192–1199
Matsue K, Kimura S, Takanashi Y, Iwama K, Fujiwara H, Yamakura M, Takeuchi M (2010) Reactivation of hepatitis B virus after rituximab-containing treatment in patients with CD20-positive B-cell lymphoma. Cancer 116:4769–4776
Kim SJ, Hsu C, Song YQ, Tay K, Hong XN, Cao J, Kim JS, Eom HS, Lee JH, Zhu J, Chang KM, Reksodiputro AH, Tan D, Goh YT, Lee J, Intragumtornchai T, Chng WJ, Cheng AL, Lim ST, Suh C, Kwong YL, Kim WS (2013) Hepatitis B virus reactivation in B-cell lymphoma patients treated with rituximab: analysis from the Asia Lymphoma Study Group. Eur J Cancer 49:3486–3496
Ceneli O, Ozkurt ZN, Acar K, Rota S, Aki SZ, Yeğin ZA, Yağci M, Ozenirler S, Sucak GT (2010) Hepatitis B-related events in autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients. World J Gastroenterol 16:1765–1771
Viganò M, Vener C, Lampertico P, Annaloro C, Pichoud C, Zoulim F, Facchetti F, Poli F, Scalamogna M, Deliliers GL, Colombo M (2011) Risk of hepatitis B surface antigen seroreversion after allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 46:125–131
Perrillo RP, Gish R, Falck-Ytter YT (2015) American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on prevention and treatment of hepatitis B virus reactivation during immunosuppressive drug therapy. Gastroenterology 148:221–244
Pei SN, Chen CH, Lee CM, Wang MC, Ma MC, Hu TH, Kuo CY (2010) Reactivation of hepatitis B virus following rituximab-based regimens: a serious complication in both HBsAg-positive and HBsAg-negative patients. Ann Hematol 89:255–262
Hsu C, Tsou HH, Lin SJ, Wang MC, Yao M, Hwang WL, Kao WY, Chiu CF, Lin SF, Lin J, Chang CS, Tien HF, Liu TW, Chen PJ, Cheng AL (2014) Chemotherapy-induced hepatitis B reactivation in lymphoma patients with resolved HBV infection: a prospective study. Hepatology 59:2092–2100
Yeo W, Chan PK, Zhong S et al (2000) Frequency of hepatitis B virus reactivation in cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy: a prospective study of 626 patients with identification of risk factors. J Med Virol 62:299–307
Kanaan N, Kabamba B, Marechal C et al (2012) Significant rate of hepatitis B reactivation following kidney transplantation in patients with resolved infection. J Clin Virol 55:233–238
Pei SN, Ma MC, Wang MC, Kuo CY, Rau KM, Su CY, Chen CH (2012) Analysis of hepatitis B surface antibody titers in B cell lymphoma patients after rituximab therapy. Ann Hematol 91:1007–1012
Mikulska M, Nicolini L, Signori A, Rivoli G, Del Bono V, Raiola AM, Di Grazia C, Dominietto A, Varaldo R, Ghiso A, Bacigalupo A, Viscoli C (2014) Hepatitis B reactivation in HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: risk factors and outcome. Clin Microbiol Infect 20:O694–O701
Seto WK, Chan TS, Hwang YY, Wong DK, Fung J, Liu KS, Gill H, Lam YF, Lie AK, Lai CL, Kwong YL, Yuen MF (2014) Hepatitis B reactivation in patients with previous hepatitis B virus exposure undergoing rituximab-containing chemotherapy for lymphoma: a prospective study. J Clin Oncol 32:3736–3743
Du W, Zheng Z, Han S et al (2013) HBV reactivation in an occult HBV infection patient treated with prednisone for nephrotic syndrome: case report and literature review. BMC Infect Dis 13:394
Campos-Outcalt D (2014) Immunization update: the latest ACIP recommendations. J Fam Pract 63:137–140
Dixon WG, Kezouh A, Bernatsky S, Suissa S (2011) The influence of systemic glucocorticoid therapy upon the risk of non-serious infection in older patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nested case–control study. Ann Rheum Dis 70:956–960
Morisco F, Castiglione F, Rispo A, Stroffolini T, Vitale R, Sansone S, Granata R, Orlando A, Marmo R, Riegler G, Vecchi M, Biancone L, Caporaso N (2011) Hepatitis B virus infection and immunosuppressive therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Liver Dis 43(Suppl 1):S40–S48
Moses SE, Lim Z, Zuckerman MA (2011) Hepatitis B virus infection: pathogenesis, reactivation and management in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 9:891–899
Serradori T, Germain A, Scherrer ML, Ayav C, Perez M, Romain B, Palot JP, Rohr S, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Bresler L (2013) The effect of immune therapy on surgical site infection following Crohn’s disease resection. Br J Surg 100:1089–1093
Sansone S, Guarino M, Castiglione F, Rispo A, Auriemma F, Loperto I, Rea M, Caporaso N, Morisco F (2014) Hepatitis B and C virus reactivation in immunosuppressed patients with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 20:3516–3524
European Association For The Study Of The Liver (2012) EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 57:167–185
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the many physicians who cared for the patients described in this report, including Drs. Yun Jiang, Wen Chen, Yanfang Yang, Duo Li, Li Zhuo, Yali Cao, and the nursing staff of nephrology department.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare no financial support or relationships that may pose conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, J., Li, W., Peng, X. et al. Hepatitis B reactivation in HBsAg-negative/HBcAb-positive patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy for glomerulonephritis: a retrospective analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 475–482 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1487-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1487-5