Abstract
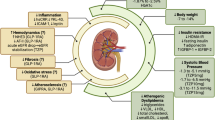
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is currently considered a modern global epidemic, and diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the most common cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Anemia is one of the most significant complications of CKD, and it is mainly attributed to insufficient erythropoietin (EPO) production. However, anemia develops earlier in the course of CKD among patients with DM, and the severity of anemia tends to be more marked in these patients compared to nondiabetic subjects, regardless of the stage of CKD. In this review, we focus on the “less known” complex interacting mechanisms which are involved in the pathophysiology of anemia associated with DN. Although the major cause of anemia in DN is considered to be an inappropriate response of the plasma EPO concentration to anemia, several other possible mechanisms have been suggested. Glomerular hyperfiltration, proteinuria, renal tubular dysfunction and interstitial fibrosis are among the main culprits. On the other hand, systemic effects such as chronic inflammation, autonomic neuropathy and the renin–angiotensin system are also involved. Finally, several medications are considered to aggravate anemia associated with DN. Since anemia is an important predictor of quality of life and is implicated in the increased burden of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, further research is required to elucidate its pathogenesis in diabetic patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harcourt BE, Penfold SA, Forbes JM (2013) Coming full circle in diabetes mellitus: from complications to initiation. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9:113–123
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmer PZ (2010) Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87:4–14
Forbes JM, Cooper ME (2013) Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev 93:137–188
Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, Keane WF, Mogensen CE, Parving HH et al (2004) Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 27:S79–S83
Mou S, Wang Q, Liu J, Che X, Zhang M, Cao L et al (2010) Prevalence of nondiabetic renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87:354–359
Parving HH, Smidt UM, Friisberg B, Bonnevie-Nielsen V, Andersen AR (1981) A prospective study of glomerular filtration rate and arterial blood pressure in insulin dependent diabetics with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 20:457–461
Gall M-A, Rossing P, Skøtt P, Damsbo P, Vaag A, Bech K et al (1991) Prevalence of micro- and macroalbuminuria, arterial hypertension, retinopathy and large vessel disease in European type 2 (non–insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 34:655–661
Parving HH, Lewis JB, Ravid M, Remuzzi G, Hunsicker LG, DEMAND investigators (2006) Prevalence and risk factors for microalbuminuria in a referred cohort of type II diabetic patients: a global perspective. Kidney Int 69(11):2057–2063
Rossing P, Hougaard P, Parving HH (2005) Progression of microalbuminuria in 15 type 1 diabetes: ten-year prospective observational study. Kidney Int 68(4):1446–1450
Foley RN, Collins AJ (2007) End-stage renal disease in the United States: an update from the United States Renal Data System. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2644–2648
Stengel B, Billon S, Van Dijk PC, Jager KJ, Dekker FW, Simpson K et al (2003) Trends in the incidence of renal replacement therapy for end-stage renal disease in Europe, 1990–1999. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:1824–1833
Villar E, Chang SH, McDonald SP (2007) Incidences, treatments, outcomes, and sex effect on survival in patients with end-stage renal disease by diabetes status in Australia and New Zealand (1991–2005). Diabetes Care 30:3070–3076
Dikow R, Schwenger V, Schömig M, Ritz E (2002) How should we manage anaemia in patients with diabetes? Nephrol Dial Transplant 17(Suppl 1):62–72
(2007) KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline and Clinical Practice Recommendations for anemia in chronic kidney disease: 2007 update of hemoglobin target. Am J Kidney Dis 50(3):471 530
Goldhaber A, Ness-Abramof R, Ellis MH (2009) Prevalence of anemia among unselected adults with diabetes mellitus and normal serum creatinine levels. Endocr Pract 15(7):714–719
Grossman C, Dovrish Z, Koren-Morag N, Bornstein G, Leibowitz A (2014) Diabetes mellitus with normal renal function is associated with anaemia. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 30(4):291–296
Bulum T, Prkacin I, Blaslov K, Zibar K, Duvnjak L (2013) Association between red blood cell count and renal function exist in type 1 diabetic patients in the absence of nephropathy. Coll Antropol 37(3):777–782
Ritz E, Haxsen V (2005) Diabetic nephropathy and anaemia. Eur J Clin Invest 35(Suppl 3):66–74
Astor BC, Muntner P, Levin A, Eustace JA, Coresh J (2002) Association of kidney function with anemia: the third National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (1988–1994). Arch Intern Med 162:1401–1408
El-Achkar TM, Ohmit SE, McCullough PA, Crook ED, Brown WW, Grimm R et al (2005) Higher prevalence of anemia with diabetes mellitus in moderate kidney insufficiency: the Kidney Early Evaluation Program. Kidney Int 67:1483–1488
Bosman DR, Winkler AS, Marsden JT, McDougall IC, Watkins PJ (2001) Anemia with erythropoietin deficiency occurs early in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 24:495–499
Thomas MC, Maclsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C, Molyneaux L, Goubina I, Fulcher G et al (2004) The burden of anemia in the type 2 diabetes and the role of nephropathy: a cross-sectional audit. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:1792–1797
Thomas MC, MacIsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C, Molyneaux L, Goubina I, Fulcher G et al (2004) Anemia in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:4359–4363
Thomas MC, MacIsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C, Power D, Jerums G (2003) Unrecognized anemia in patients with diabetes: a cross-sectional survey. Diabetes Care 26:1164–1169
Schuster SJ, Koury ST, Bohrer M, Salceda S, Caro J (1992) Cellular sites of extrarenal and renal erythropoietin production in anaemic rats. Br J Haematol 81:153–159
Maxwell PH, Osmond MK, Pugh CW, Heryet A, Nicholls LG, Tan CC et al (1993) Identification of the renal erythropoietin-producing cells using transgenic mice. Kidney Int 44:1149–1162
Jelkmann W (2011) Regulation of erythropoietin production. J Physiol 589:1251–1258
Middleton SA, Barbone FP, Johnson DL, Thurmond RL, You Y, McMahon FJ et al (1999) Shared and unique determinants of the erythropoietin (EPO) receptor are important for binding EPO and EPO mimetic peptide. J Biol Chem 274:14163–14169
Chasis JA, Mohandas N (2008) Erythroblastic islands: niches for erythropoiesis. Blood 112(3):470–478
Thomas M, Tsalamandris C, Maclsaac R, Jerums G (2005) Anaemia in diabetes: an emerging complication of microvascular disease. Curr Diabetes Rev 1:107–126
Haase VH (2010) Hypoxic regulation of erythropoiesis and iron metabolism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299(1):F1–F13
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basichelix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(12):5510–5514
Winkler AS, Marsden J, Chaudhuri KR, Hambley H, Watkins PJ (1999) Erythropoietin depletion and anaemia in diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 16:813–819
Ishimura E, Nishizawa Y, Okuno S, Matsumoto N, Emoto M, Inaba M et al (1998) Diabetes mellitus increases the severity of anemia in non-dialyzed patients with renal failure. J Nephrol 11:83–86
Inomata H, Itoh M, Imai H, Sato T (1997) Serum levels of erythropoietin as a novel marker reflecting the severity of diabetic nephropathy. Nephron 75:426–430
Jerums G, Premaratne E, Panagiotopoulos S, MacIsaac RJ (2010) The clinical significance of hyperfiltration in diabetes. Diabetologia 53:2093–2104
Sasson AN, Cherney DZ (2012) Renal hyperfiltration related to diabetes mellitus and obesity in human disease. World J Diabetes 3:1–6
Blantz RC, Singh P (2014) Glomerular and tubular function in the diabetic kidney. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 21(3):297–303
Tomaszewski M, Charchar FJ, Maric C, McClure J, Crawford L, Grzeszczak W et al (2007) Glomerular hyperfiltration: a new marker of metabolic risk. Kidney Int 71:816–821
Vaziri ND, Kaupke CJ, Barton CH, Gonzales E (1992) Plasma concentration and urinary excretion of erythropoietin in adult nephrotic syndrome. Am J Med 92:35–40
Bays B, Serra A, Junc J, Lauzurica R (1988) Successful treatment of anaemia of nephritic syndrome with recombinant human erythropoietin. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:1894–1895
Ishimitsu T, Ono H, Sugiyama M, Asakawa H, Oka K, Numabe A et al (1996) Successful erythropoietin treatment for severe anemia in nephrotic syndrome without renal dysfunction. Nephron 74:607–610
Nowicki M, Kokot F, Kokot M, Bar A, Dulawa J (1994) Renal clearance of endogenous erythropoietin in patients with proteinuria. Int Urol Nephrol 26:691–699
Sasatomi Y, Ito K, Abe Y, Miyake K, Ogahara S, Nakashima H, Saito T (2012) Association of hypoalbuminemia with severe anemia in patients with diabetic nephrosclerosis. Ren Fail 34(2):189–193
Thomas MC, Tsalamandris C, MacIsaac R, Medley T, Kingwell B, Cooper ME et al (2004) Low-molecular-weight AGEs are associated with GFR and anemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int 66:1167–1172
Okon EB, Chung AW, Rauniyar P, Padilla E, Tejerina T, McManus BM et al (2005) Compromised arterial function in human type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 54:2415–2423
Téllez Gil L, Roselló AM, Collado Torres A, Moreno RL, Antonio Ferrón Orihuela J (2001) Modulation of soluble phases of endothelial/leukocyte adhesion molecule 1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 with interleukin-1 beta after experimental endotoxic challenge. Crit Care Med 29:776–781
Faquin WC, Schneider TJ, Goldberg MA (1992) Effect of inflammatory cytokines on hypoxia-induced erythropoietin production. Blood 79:1987–1994
Leng HM, Folb PI (1996) Erythropoiesis and erythropoietin synthesis during aseptic acute inflammation. Inflamm Res 45:541–545
Thomas MC, Tsalamandris C, Macisaac RJ, Jerums G (2006) Functional erythropoietin deficiency in patients with type 2 diabetes and anaemia. Diabet Med 23:502–509
Bhatia V, Chaudhuri A, Tomar R, Dhindsa S, Ghanim H, Dandona P (2006) Low testosterone and high C-reactive protein concentrations predict low hematocrit in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 29:2289–2294
Johnson CS, Keckler DJ, Topper MI, Braunscweiger PG, Furmanski P (1989) In vivo hematopoietic effects of recombinant interleukin-1 alpha in mice: stimulation of granulocytic, monocytic, megakaryocytic, and early erythroid progenitors, suppression of late-stage erythropoiesis, and reversal of erythroid suppression with erythropoietin. Blood 73:678–683
Maciejewski JP, Selleri C, Sato T, Anderson S, Young NS (1995) Fas antigen expression on CD34+ human marrow cells is induced by interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha and potentiates cytokine-mediated hematopoietic suppression in vitro. Blood 85:3183–3190
Van Der Putten K, Braam B, Jie KE, Gaillard CA (2008) Mechanisms of disease: erythropoietin resistance in patients with both heart and kidney failure. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 4:47–57
Shuvaev VV, Fujii J, Kawasaki Y, Iton H, Hamaoka R, Barbier A et al (1999) Glycation of apolipoprotein E impairs its binding to heparin: identification of the major glycation site. Biochem Biophys Acta 1454:296–308
Brito PL, Fioretto P, Drummond K, Kim Y, Steffes MW, Basgen JM et al (1998) Proximal tubular basement membrane width in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 53:754–761
Mise K, Hoshino J, Ueno T, Imafuku A, Kawada M, Sumida K, et al (2014) Impact of tubulointerstitial lesions on anaemia in patients with biopsy proven diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Med. doi:10.1111/dme.12633 (Epub ahead of print)
Bosman DR, Osborne CA, Marsden JT, McDougall IC, Gardner WN, Watkins PJ (2002) Erythropoietin response to hypoxia in patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy and non-diabetic chronic renal failure. Diabet Med 19:65–69
Matthews MR (1992) Autonomic ganglia in multiple system atrophy and pure autonomic failure. In: Bannister R, Mathias CJ (eds) Autonomic failure: a textbook of disorders of the autonomic nervous system, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 592–621
Van Ingelghem E, Van Zandijcke M, Lammens M (1994) Pure autonomic failure: a new case with clinical, biochemical, and necropsy data. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57:745–747
Biaggioni I, Robertson D, Krantz S, Jones M, Haile V (1994) The anemia of primary autonomic failure and its reversal with recombinant erythropoietin. Ann Intern Med 121:181–186
Finne PH, Skoglund RW (1970) Erythropoietin production in the rat following splanchnic neurectomy. J Lab Clin Med 76:103–106
Mayaudon H, Dupuy O, Dolz M, Bordier L, Belmejdoub G, Garcin JM et al (2002) Influence of blood pressure profile on erythropoietin levels in diabetics. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss 95:743–746
Jeffrey RF, Kendall RG, Prabhu P, Norfolk DR, Will EJ, Davison AM (1995) Reestablishment of erythropoietin responsiveness in end-stage renal failure following renal transplantation. Clin Nephrol 44:241–247
Kim MK, Baek KH, Lim DJ, Kim YK, Kang MI, Lee KW, Song KH (2010) Erythropoetin response to anemia and its association with autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients without advanced renal failure. J Diabetes Complic 24(2):90–95
Kim YC, Mungunsukh O, McCart EA, Roehrich PJ, Yee DK, Day RM (2014) Mechanism of erythropoietin regulation by angiotensin II. Mol Pharmacol 85(6):898–908
Vlachakos DV, Marathias KP, Madias NE (2010) The role of the rennin angiotensin system in the regulation of erythropoiesis. Am J Kidney Dis 56:558–565
Donnelly S (2001) Why is erythropoietin made in the kidney? The kidney functions as a critmeter. Am J Kidney Dis 38:415–425
Christlieb AR (1976) Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 25(Suppl 2):820–825
Donnelly S, Shah BR (1999) Erythropoietin deficiency in hyporeninemia. Am J Kidney Dis 33:947–953
Christlieb AR, Munichoodappa C, Braaten JT (1974) Decreased response of plasma renin activity to orthostasis in diabetic patients with orthostatic hypotension. Diabetes 23:835–840
Christlieb AR, Kaldany A, D’elia JA (1976) Plasma renin activity and hypertension in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 25:969–974
Azizi M, Rousseau A, Ezan E, Guyene TT, Michelet S, Grognet JM et al (1996) Acute angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition increases the plasma level of the natural steam cell regulator N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline. J Clin Investig 97:839–844
Hayashi T, Suzuki A, Shoji T, Togawa M, Okada N, Tsubakihara Y et al (2000) Cardiovascular effects of normalizing the hematocrit level during erythropoietin therapy in predialysis patients with chronic renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis 35:250–256
Inoue A, Babazono T, Iwamoto Y (2008) Effects of the renin–angiotensin system blockade on hemoglobin levels in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Am J Hypertens 21:317–322
Saito A, Kaseda R, Hosojima M, Sato H (2010) Proximal tubule cell hypothesis for cardiorenal syndrome in diabetes. Int J Nephrol 2011:957164. doi:10.4061/2011/957164
Wang S, Denichilo M, Brubaker C, Hirschberg R (2001) Connective tissue growth factor in tubulointerstitial injury of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 60:96–105
Thomas MC, Burns WC, Cooper ME (2005) Tubular changes in early diabetic nephropathy. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 12:177–186
Vallon V, Thomson SC (2012) Renal function in diabetic disease models: the tubular system in the pathophysiology of the diabetic kidney. Annu Rev Physiol 74:351–375
Thomson SC, Vallon V, Blantz RC (2004) Kidney function in early diabetes: the tubular hypothesis of glomerular filtration. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F8–F15
Eckardt KU, Kurtz A, Bauer C (1989) Regulation of erythropoietin production is related to proximal tubular function. Am J Physiol 256:F942–F947
Kurtz A, Eckardt KU (1990) Erythropoietin production in chronic renal disease before and after transplantation. Contrib Nephrol 87:15–25
Schultze RG, Weisser F, Bricker NS (1972) The influence of uremia on fractional sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of rats. Kidney Int 2:59–65
Brezis M, Rosen S (1995) Hypoxia of the renal medulla—its implications for disease. N Engl J Med 332:647–655
Donnelly S, Shah BR (1996) Erythropoietin deficiency in type I diabetic patients is associated with decrease in fractional sodium reabsorption. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:1356
Nagai T, Yasuoka Y, Izumi Y, Horikawa K, Kimura M, Nakayama Y et al (2014) Revealuation of erythropoietin production by the nephron. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 449(2):222–228
Baldini P, Incerpi S, Lambert-Gardini S, Spinedi A, Luly P (1989) Membrane lipid alterations and Na+-pumping activity in erythrocytes from IDDM and NIDDM subjects. Diabetes 38:825–831
Kowluru R, Bitensky MW, Kowluru A, Dembo M, Keaton PA, Buican T (1989) Reversible sodium pump defect and swelling in the diabetic rat erythrocyte: effect on filterability and implications for microangiopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:3327–3331
Brown CD, Ghali HS, Zhao Z, Thomas LL, Friedman EA (2005) Association of reduced red blood cell deformability and diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 67:295–300
Elishkevitz K, Fusman R, Koffler M, Shapira I, Avitzour D, Arber N et al (2002) Rheological determinants of red blood cell aggregation in diabetic patients in relation to their metabolic control. Diabet Med 19:152–156
Resmi H, Akhunlar H, Temiz Artmann A, Güner G (2005) In vitro effects of high glucose concentrations on membrane protein oxidation, G-actin and deformability of 23 human erythrocytes. Cell Biochem Funct 23:163–168
Vlassara H, Valinsky J, Brownlee M, Cerami C, Nishimoto S, Cerami A (1987) Advanced glycation endproducts on erythrocyte cell surface induce receptor-mediated phagocytosis by macrophages. A model for turnover of aging cells. J Exp Med 166:539–549
Manodori AB, Kuypers FA (2002) Altered red cell turnover in diabetic mice. J Lab Clin Med 140:161–165
Rigal D, Monestier M, Baboin-Jaubert M, Chabaud-Sassulas D, Marseglia GL, Ville D et al (1985) Evaluation of erythrocyte survival by the determination of glycosylated haemoglobin. Clinical value. Presse Med 14:521–523
Wagstaff AJ, Goa KL (2002) Rosiglitazone: a review of its use in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 62:1805–1837
Nesto RW, Bell D, Bonow RO, Fonseca V, Grundy SM, Horton ES et al (2003) Thiazolidinedion use, fluid retention, and congestive heart failure: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. October 7, 2003. Circulation 108:2941–2948
Maarani Y, Stessman J (2005) Mild reversible pancytopenia induced by rosiglitazone. Diabetes Care 28:1536
Raptis AE, Bacharaki D, Mazioti M, Marathias KP, Markakis KP, Raptis SA et al (2012) Anemia due to coadministration of renin–angiotensin-system inhibitors and PPARγ agonists in uncomplicated diabetic patients. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 120:416–419
Kouroumichakis I, Papanas N, Zarogoulidis P, Liakopoulos V, Maltezos E, Mikhailidis DP (2012) Fibrates: therapeutic potential for diabetic nephropathy? Eur J Intern Med 23:309–316
Poyart C, Marden MC, Kister J (1994) Bezafibrate derivatives as potent effectors of hemoglobin. Methods Enzymol 232:496–513
Fazio S, Linton MF (2010) High-density lipoprotein therapeutics and cardiovascular prevention. J Clin Lipidiol 4:411–419
Perutz MF, Poyart C (1983) Bezafibrate lowers oxygen affinity of hemoglobin. Lancet 2(8355):881–882
Balakumar P, Kadian S, Mahadevan N (2012) Are PPAR alpha agonists a rational therapeutic strategy for preventing abnormalities of the diabetic kidney? Pharmacol Res 65:430–436
Florentin M, Liberopoulos EN, Mikhailidis DP, Elisaf MS (2008) Fibrate associated adverse effects beyond muscle and livertoxicity. Curr Pharm Des 14:574–587
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pappa, M., Dounousi, E., Duni, A. et al. Less known pathophysiological mechanisms of anemia in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 1365–1372 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1012-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1012-2