Abstract
Purpose
To assess whether there is an association between the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value and the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer.
Methods
The study cohort consisted of 29 consecutive patients with prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. All patients underwent diffusion-weighted MRI before the prostate biopsy. In 42 tumor foci, the associations of the ADC values with the clinicopathological characteristics and Ki-67 labeling index (LI) were analyzed.
Results
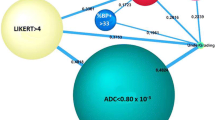
High-grade cancers (Gleason score [GS] ≥ 4 + 3), larger cancers (maximum diameter (MD) ≥ 16 mm), and highly proliferating cancers (Ki-67 LI ≥ 4.43 %) had significantly lower ADC values, respectively (P < .001, P = .008, and P = .044, respectively). There was no significant difference in ADC value according to age, prostate-specific antigen, presence of extra-prostatic extension, and intra-tumoral stroma proportion. Multivariate analysis showed that GS, Ki-67 LI, and MD had independent and significant correlations with ADC value (P < .001, P = .006, and P = .002, respectively). Low ADC tumors (<0.52 × 10−3 mm2/s) are likely to be high-grade cancer foci compared with high ADC tumors (relative risk: 65.2). The sensitivity and specificity of the ADC value to predict high-grade cancer foci are 81.8 and 93.5 %, respectively.
Conclusions
A low ADC value reflects the morphological and biological features of prostate cancer. Analyzing the ADC value may make it possible to more precisely predict the cancer aggressiveness of each focus before treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed HU, Hindley RG, Dickinson L, Freeman A, Kirkham AP, Sahu M, Scott R, Allen C, Van der Meulen J, Emberton M (2012) Focal therapy for localised unifocal and multifocal prostate cancer: a prospective development study. Lancet Oncol 13(6):622–632. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70121-3
Smith DW, Stoimenova D, Eid K, Barqawi A (2012) The role of targeted focal therapy in the management of low-risk prostate cancer: update on current challenges. Prostate Cancer 2012:587139. doi:10.1155/2012/587139
Matsuoka Y, Numao N, Saito K, Tanaka H, Kumagai J, Yoshida S, Koga F, Masuda H, Kawakami S, Fujii Y, Kihara K (2012) Combination of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and extended prostate biopsy predicts lobes without significant cancer: application in patient selection for hemiablative focal therapy. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.10.010
Numao N, Yoshida S, Komai Y, Ishii C, Kagawa M, Kijima T, Yokoyama M, Ishioka J, Matsuoka Y, Koga F, Saito K, Masuda H, Fujii Y, Kawakami S, Kihara K (2013) Usefulness of prebiopsy multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and clinical variables to reduce initial prostate biopsy in men with suspected clinically localized prostate cancer. J Urol. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.3197
Tan CH, Wang J, Kundra V (2011) Diffusion weighted imaging in prostate cancer. Eur Radiol 21(3):593–603. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-1960-y
Koh DM, Collins DJ (2007) Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188(6):1622–1635. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.1403
Wu LM, Xu JR, Ye YQ, Lu Q, Hu JN (2012) The clinical value of diffusion-weighted imaging in combination with T2-weighted imaging in diagnosing prostate carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199(1):103–110. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7634
Hambrock T, Somford DM, Huisman HJ, van Oort IM, Witjes JA, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, Scheenen T, Barentsz JO (2011) Relationship between apparent diffusion coefficients at 3.0-T MR imaging and Gleason grade in peripheral zone prostate cancer. Radiology 259(2):453–461. doi:10.1148/radiol.11091409
Kitajima K, Takahashi S, Ueno Y, Miyake H, Fujisawa M, Kawakami F, Sugimura K (2013) Do apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values obtained using high b-values with a 3-T MRI correlate better than a transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided biopsy with true Gleason scores obtained from radical prostatectomy specimens for patients with prostate cancer? Eur J Radiol 82(8):1219–1226. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.02.021
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM, Chenevert TL, Thoeny HC, Takahara T, Dzik-Jurasz A, Ross BD, Van Cauteren M, Collins D, Hammoud DA, Rustin GJ, Taouli B, Choyke PL (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 11(2):102–125
Oto A, Yang C, Kayhan A, Tretiakova M, Antic T, Schmid-Tannwald C, Eggener S, Karczmar GS, Stadler WM (2011) Diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of prostate cancer: correlation of quantitative MR parameters with Gleason score and tumor angiogenesis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197(6):1382–1390. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.6861
Woodfield CA, Tung GA, Grand DJ, Pezzullo JA, Machan JT, Renzulli JF 2nd (2010) Diffusion-weighted MRI of peripheral zone prostate cancer: comparison of tumor apparent diffusion coefficient with Gleason score and percentage of tumor on core biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194(4):W316–W322. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.2651
Kobayashi S, Koga F, Kajino K, Yoshita S, Ishii C, Tanaka H, Saito K, Masuda H, Fujii Y, Yamada T, Kihara K (2013) Apparent diffusion coefficient value reflects invasive and proliferative potential of bladder cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. doi:10.1002/jmri.24148
Yoshida S, Kobayashi S, Koga F, Ishioka J, Ishii C, Tanaka H, Nakanishi Y, Matsuoka Y, Numao N, Saito K, Masuda H, Fujii Y, Kihara K (2013) Apparent diffusion coefficient as a prognostic biomarker of upper urinary tract cancer: a preliminary report. Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-2805-2
Zelhof B, Pickles M, Liney G, Gibbs P, Rodrigues G, Kraus S, Turnbull L (2009) Correlation of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance data with cellularity in prostate cancer. BJU Int 103(7):883–888. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08130.x
Kasivisvanathan V, Dufour R, Moore CM, Ahmed HU, Abd-Alazeez M, Charman SC, Freeman A, Allen C, Kirkham A, van der Meulen J, Emberton M (2013) Transperineal magnetic resonance image targeted prostate biopsy versus transperineal template prostate biopsy in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. J Urol 189(3):860–866. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.10.009
Moore CM, Robertson NL, Arsanious N, Middleton T, Villers A, Klotz L, Taneja SS, Emberton M (2013) Image-guided prostate biopsy using magnetic resonance imaging-derived targets: a systematic review. Eur Urol 63(1):125–140. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.06.004
Higano S, Yun X, Kumabe T, Watanabe M, Mugikura S, Umetsu A, Sato A, Yamada T, Takahashi S (2006) Malignant astrocytic tumors: clinical importance of apparent diffusion coefficient in prediction of grade and prognosis. Radiology 241(3):839–846. doi:10.1148/radiol.2413051276
Kang Y, Choi SH, Kim YJ, Kim KG, Sohn CH, Kim JH, Yun TJ, Chang KH (2011) Gliomas: histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient maps with standard- or high-b-value diffusion-weighted MR imaging-correlation with tumor grade. Radiology 261(3):882–890. doi:10.1148/radiol.11110686
Wieduwilt MJ, Valles F, Issa S, Behler CM, Hwang J, McDermott M, Treseler P, O’Brien J, Shuman MA, Cha S, Damon LE, Rubenstein JL (2012) Immunochemotherapy with intensive consolidation for primary CNS lymphoma: a pilot study and prognostic assessment by diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin Cancer Res 18(4):1146–1155. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-0625
Kobayashi S, Koga F, Yoshida S, Masuda H, Ishii C, Tanaka H, Komai Y, Yokoyama M, Saito K, Fujii Y, Kawakami S, Kihara K (2011) Diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in bladder cancer: potential utility of apparent diffusion coefficient values as a biomarker to predict clinical aggressiveness. Eur Radiol 21(10):2178–2186. doi:10.1007/s00330-011-2174-7
Yamamoto S, Yonese J, Kawakami S, Ohkubo Y, Tatokoro M, Komai Y, Takeshita H, Ishikawa Y, Fukui I (2007) Preoperative serum testosterone level as an independent predictor of treatment failure following radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 52(3):696–701. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2007.03.052
Yoshida S, Koga F, Kobayashi S, Ishii C, Tanaka H, Komai Y, Saito K, Masuda H, Fujii Y, Kawakami S, Kihara K (2012) Role of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in predicting sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83(1):e21–e27. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.11.065
Yoshida S, Masuda H, Ishii C, Tanaka H, Fujii Y, Kawakami S, Kihara K (2011) Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI in diagnosis of upper urinary tract cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196(1):110–116. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.4632
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, H., Yoshida, S., Matsuoka, Y. et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient value as a biomarker reflecting morphological and biological features of prostate cancer. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 555–561 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0557-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0557-1