Abstract
Introduction
Cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality are greatly enhanced in patients with chronic kidney disease, partly due to increased arterial stiffness.
Material and method
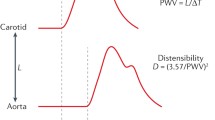
The study included 63 stable HD patients. Stiffness parameters were evaluated by applanation tonometry before the mid-week HD sessions. Pre-HD bioimpedance parameters were measured. A phase angle <six degrees was previously reported as abnormal, reflecting extracellular overhydration. Fluid status was evaluated echocardiographic by measuring the inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter. Endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent vascular reactivity were assessed by changes in Alx following sublingual nitroglycerin and inhaled salbutamol.
Results
PWV directly correlated with patients’ age and dialysis vintage. Patients with a phase angle <6°, were significantly overhydrated (larger IVC, increased ECW, and lower ICW), had stiffer arteries and greater left ventricle mass (LVM), compared with those with a phase angle >6°. Overhydration increases arterial stiffness, but has no influence on either EID or ED vascular reactivity.
Conclusion
In hemodialysis, volume overload is an important contributor to increased arterial stiffness and modifies cardiovascular status especially by LV hypertrophy. Achieving normohydration may significantly ameliorate cardiac abnormalities and arterial stiffness and may impact major clinical events and CV mortality.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY (2004) Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 35:1296–1305
Lin YP, Yu WC, Hsu TL, Ding PYA, Yang WC, Chen CH (2003) The extracellular fluid-to-intracellular fluid volume ratio is associated with large-artery structure and function in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 42(5):990–999
Sutton-Tyrrell K, Samer SN, Boudreau RM et al (2005) A Health ABC Study. Elevated aortic pulse wave velocity, a marker of arterial stiffness, predicts cardiovascular events in well-functioning older adults. Circulation 111(25):3384–3390
Konings C, Hermans M, Kooman JP et al (2004) Arterial stiffness and renal replacement therapy. Perit Dial Int 4(4):318–322
Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, London GM et al (2001) Arterial calcifications, arterial stiffness, and cardiovascular risk in end-stage renal disease. Hypertension 38(4):938–942
Guérin AP, Pannier B, Métivier F, Marchais SJ, London GM (2008) Assessment and significance of arterial stiffness in patients with chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens (6):635–641
Gusbeth-Tatomir P, Covic A (2007) Causes and consequences of increased arterial stiffness in chronic kidney disease patients. Kidney Blood Press Res 30:97–107
Chung A, Yang C, Kim JM et al (2010) Arterial stiffness and functional properties in chronic kidney disease patients on different dialysis modalities: an exploratory study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25(12):4031–4404
van Guldener C, Janssen MJ, Lambert J et al (1998) No change in impaired endothelial function after long-term folic acid therapy of hyperhomocysteinaemia in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13(1):106–112
Miyazaki H, Matsuoka H, Itabe H et al (2000) Hemodialysis impairs endothelial function via oxidative stress: effects of vitamin E-coated dialyzer. Circulation 101(9):1002–1006
Kanbay M, Afsar B, Gusbeth-Tatomir P, Covic A (2010) Arterial stiffness in dialysis patients: where are we now? Int Urol Nephrol 42(3):741–752
Voroneanu L, Cusai C, Hogas S et al (2010) The relationship between chronic volume overload and elevated blood pressure in hemodialysis patients: use of bioimpedance provides a different perspective from echocardiography and biomarker methodologies. Int Urol Nephrol 42:789–797
Pillon L, Piccoli A, Lowrie EG, Lazarus JM, Chertow GM (2004) Vector length as a proxy for the adequacy of ultrafiltration in hemodialysis. Kidney Int 66:1266–1271
Kuhlmann MK, Zhu F, Seibert E, Levin NW (2005) Bioimpedance, dry weight and blood pressure control: new methods and consequences. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 14(6):543–549
Segall L, Mardare NG, Ungureanu S et al (2009) Nutritional status evaluation and survival in haemodialysis patients in one centre from Romania. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:2536–2540
Ganau A, Devereux RB, Roman JM et al (1992) Patterns of left ventricular hypertrophy and geometry remodelling in essential hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 19:1550–1558
Covic A, Goldsmith DJ, Panaghiu L et al (2000) Analysis of the effect of haemodialysis on peripheral and central arterial pressure waveforms. Kidney Int 57:2634–2643
Wilkinson IB, Hall IR, MacCallum H et al (2002) Pulse-wave analysis: clinical evaluation of a noninvasive, widely applicable method for assessing endothelial function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:147–152
Wizemann V, Schilling M (1995) Dilemma of assessing volume state—the use and the limitations of a clinical score. Nephrol Dial Transplant 10(11):2114–2117
Annuk M, Zilmer M, Lind L, Linde T, Fellstrom B (2001) Oxidative stress and endothelial function in chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2747–2752
London GM, Guerin AP, Marchais SJ et al (1996) Cardiac and arterial interactions in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 50:600–608
Watabe D, Hashimoto J, Hatanaka R et al (2006) Electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy and arterial stiffness: the Ohasama study. Am J Hypertens 19(12):1199–1205
Gardin JM, Arnold A, Gottdiener JS et al (1997) Left ventricular mass in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Hypertension 29:1095–1103
Gosse P, Jullien V, Jarnier P, Lemetayer P, Clementy J (1999) Reduction in arterial distensibility in hypertensive patients as evaluated by ambulatory measurement of the QKD interval is correlated with concentric remodeling of the left ventricle. Am J Hypertens 12(1–2):1252–1255
Roman MJ, Ganau A, Saba PS, Pini R, Pickering TG, Devereux RB (2000) Impact of arterial stiffening on left ventricular structure. Hypertension 36:489–494
Aronson D, Burger AJ (2004) Relation between pulse pressure and survival in patients with decompensated heart failure. Am J Cardiol 93:785–788
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(13):1318–1327
London GM, Blacher J, Pannier B et al (2001) Arterial wave reflections and survival in end-stage renal failure. Hypertension 38:434–438
London GM, Pannier B (2010) Arterial functions: how to interpret the complex physiology. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:3815–3823
Goodman WG, London G, Amann K et al (2004) Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 43:572–579
Ozkahya M, Ok E, Toz H et al (2006) Long-term survival rates in haemodialysis patients treated with strict volume control. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:3506–3513
Santoro D, Bellinghieri G, Conti G et al (2010) Endothelial dysfunction in chronic renal failure. J Ren Nutr 20(5 Suppl):S103–S108
Duprez DA (2010) Is vascular stiffness a target for therapy? Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 24(4):305–310
Hornum M, Clausen P, Idorn T, Hansen JM, Mathiesen ER, Feldt-Rasmussen B (2010) Kidney transplantation improves arterial function measured by pulse wave analysis and endothelium-independent dilatation in uraemic patients despite deterioration of glucose metabolism. Nephrol Dial Transplant Nov 19 in press
Zoungas S, Kerr PG, Chadban S et al (2004) Arterial function after successful renal transplantation. Kidney Int 65:1882–1889
Covic A, Goldsmith DJ, Gusbeth-Tatomir P et al (2003) Successful renal transplantation decreases aortic stiffness and increases vascular reactivity in dialysis patients. Transplantation 76:1573–1577
Rizos EC, Agouridis AP, Elisaf MS (2010) The effect of statin therapy on arterial stiffness by measuring pulse wave velocity: a systematic review. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 8(5):638–644
Fassett RG, Robertson IK, Ball MJ, Geraghty DP, Sharman JE, Coombes JS (2010) Effects of atorvastatin on arterial stiffness in chronic kidney disease: a randomised controlled trial. J Atherosclerosis Thrombosis 17(3):235–241
Zhu F, Wystrychowski G, Kitzler T, Thijssen S, Kotanko P, Levin N (2006) Application of bioimpedance techniques to peritoneal dialysis. Contrib Nephrol 150:119–128
Crepaldi C, Soni S, Chionh CY, Wabel P, Cruz DN, Ronco C (2009) Application of body composition monitoring to peritoneal dialysis patients. Contrib Nephrol 163:1–6
Kuhlmann MK, Zhu F, Seibert E, Levin NW (2005) Bioimpedance, dry weight and blood pressure control: new methods and consequences. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 14(6):543–549
Levin N, Zhu F, Seibert E, Ronco C, Kuhlmann M (2005) Use of segmental multifrequency bioimpedance spectroscopy in hemodialysis. Contrib Nephrol 149:162–167
Mallamaci F, Benedetto FA, Tripepi R et al (2010) Detection of pulmonary congestion by chest ultrasound in dialysis patients. J Am Coll Cardiol Img 3:586–594
Charra B, Terrat JC, Vanel T et al (2004) Long thrice weekly hemodialysis: the Tassin experience. Int J Artif Organs 27(4):265–283
Kayikcioglu M, Tumuklu M, Ozkahya M et al (2009) The benefit of salt restriction in the treatment of end-stage renal disease by haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:956–962
Volker Wizemann W, Wabel P, Chamney P et al (2009) The mortality risk of overhydration in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:1574–1579
Diaz-Buxo JA, Woods HF (2006) Protecting the endothelium: a new focus for management of chronic kidney disease. Hemodial Int 10(1):42–48
Stenvinkel P, Carrero JJ, Axelsson J, Lindholm B, Heimburger Massy Z (2008) Emerging biomarkers for evaluating cardiovascular risk in the chronic kidney disease patient: how do new pieces fit into the uremic puzzle? Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:505–521
Zoccalli C (2006) Endothelial dysfunction and the kidney: emerging risk factors for renal insufficiency and cardiovascular outcomes in essential hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol 17(S6):1–3
Büssemaker E, Hillebrand U, Hausberg M, Pavenstädt H, Oberleithner H (2010) Pathogenesis of hypertension: interactions among sodium, potassium, and aldosterone. Am J Kidney Dis 55(6):1111–1120
Jablonski KL, Gates PE, Pierce GL, Seals DR (2009) Low dietary sodium intake is associated with enhanced vascular endothelial function in middle-aged and older adults with elevated systolic blood pressure. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 3(5):347–356
Reuter S, Büssemaker E, Hausberg M, Pavenstädt H, Hillebrand U (2009) Effect of excessive salt intake: role of plasma sodium. Curr Hypertens Rep 11(2):91–97
Kanbay M, Chen Y, Solak Y, Sanders PW (2011) Mechanisms and consequences of salt sensitivity and dietary salt intake. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20(1):37–43
Sanders PW (2009) Vascular consequences of dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(2):F237–F243
Acknowledgments
This work was supported from the Romanian state budget, by a research grant (PNCDI-II, program “IDEI”, code ID_1156), under the contractual authority of UEFISCSU (contract no. 392/2.10.2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hogas, S., Ardeleanu, S., Segall, L. et al. Changes in arterial stiffness following dialysis in relation to overhydration and to endothelial function. Int Urol Nephrol 44, 897–905 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-011-9933-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-011-9933-x