Abstract
Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) is the commonest cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) worldwide. Data scarcity on renal transplantation (RTx) outcome in diabetic nephropathy (DN) prompted us to review our experience. This retrospective single-center, 5-year study was undertaken to evaluate patient and graft survival and function, evaluated by serum creatinine (SCr), rejection episodes, and mortality in patients.
Patients and methods
One hundred type 2 DM-ESRD patients underwent RTx [80 living-related (LRD), 20 deceased donor (DD)] at our center following cardiac fitness of recipient. Post-transplant immunosuppression consisted of calcineurin inhibitor–based regimen. The mean donor age in the LRD group was 40.6 years and 52 years in the DD group. Male recipients constituted 95% in the LRD and 65% in the DD group.
Results
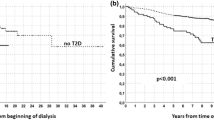
Over a mean follow-up of 2.47 years, 1- and 5-year patient/graft survival in LRDRTx was 85.1%/95.9% and 82.6%/95.9%, respectively, and mean SCr (in mg/dl) at 1 and 5 years was 1.38 and 1.58 mg/dl, respectively, with 20% of cases developing acute rejection (AR) episodes. Fifteen percent of patients died, mainly due to infections, and 1.3% died of coronary artery disease (CAD). In DDRTx, over a mean follow-up of 3.17 years, 1- and 4-year patient/graft survival was 72%/89.7% and 54%/89.7%, respectively; mean SCr at 1 and 4 years was 1.40 and 1.75 mg/dl, respectively, with 20% of cases developing AR episodes. Totally, 30% of patients were lost, mainly due to infections, and 10% of patients died from cerebrovascular events.
Conclusion
In our center, in patients with RTx for type 2 DM diabetic nephropathy, the 4- and 5-year patient and graft survival rates and graft function can be considered acceptable. The results are better in LRDRTx than in DDRTx patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Acute rejection
- AZA:
-
Azathioprine
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- CMV:
-
Cytomegalovirus
- CNI:
-
Calcineurin inhibitors
- CVA:
-
Cerebrovascular accidents
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular diseases
- DD:
-
Deceased donor
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DN:
-
Diabetic nephropathy
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- LRD:
-
Living-related
- MMF:
-
Mycophenolate mofetil
- MP:
-
Methylprednisolone
- r-ATG:
-
Rabbit-anti-thymocyte globulin
- RTx:
-
Renal transplantation
- SCr:
-
Serum creatinine
- TMP/SMX:
-
Trimethoprim/sulfamethaxazole
- UTI:
-
Urinary tract infections
References
International Diabetes Federation (IDF) (2009) Diabetes atlas, 4th edn. http://shop.idf.org/catalog/
Premlatha G, Shanthi Rani CS, Deepa E et al. (2000) Prevalence of diabetic complications in south Indians. Novo Nordisk, Diabetic Update 59–62
Victoria Rugg International Diabetes Federation and the International Society of Nephrology (2003) Diabetes and kidney disease: time to Act. http://www.isn-online.org/isn/society/publications/isn_20119.html
Modi GK, Jha V (2006) The incidence of end-stage renal disease in India: a population-based study. Kidney Int 70(12):2131–2133 Epub 2006 Oct 25. PMID: 17063176
Tobin GS, Tanenbaum ND, Brennanat DC et al (2009) Renal transplantation in diabetic nephropathy. http://www.uptodate.com/patients/content/topic
Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL et al (1999) Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med 341(23):1725–1730
Luan FL, Samaniego M (2010) Transplantation in diabetic kidney failure patients: modalities, outcomes, and clinical management. Semin Dial 23(2):198–205 Epub 2010 Mar 30
Davis CL, Delmonico FL (2005) Living-donor kidney transplantation: a review of the current practices for the live donor. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(7):2098–2110
Glannon W (2008) Underestimating the risk in living kidney donation. J Med Ethics 34(3):127–128
Benhamou PY, Marwah T, Balducci F et al (1992) Classification of diabetes in patients with end-stage renal disease: validation of clinical criteria according to fasting plasma C-peptide. Clin Nephrol 38:239–244
American Diabetes Association Expert Committee Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes mellitus (1997) Diabetes care. 20:1183–1197
Mieghem AV, Fonck C, Coosemans W et al (2001) Outcome of cadaver kidney transplantation in 23 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16(8):1686–1691
Reilly JB, Berns JS (2010) Selection and dosing of medications for management of diabetes in patients with advanced kidney disease. Semin Dial 23(2):163–168
Racusen LC, Colvin RB, Solez K et al (2003) Antibody-mediated rejection criteria–an addition to the Banff’97 classification of renal allograft rejection. Am J Transplant 3(6):708–714
Solez K, Colvin RB, Racusen LC et al (2007) Banff’05 meeting report: differential diagnosis of chronic allograft injury and elimination of chronic allograft nephropathy (‘CAN’). Am J Transplant 7(3):518–526
Evans RW, Manninen DL, Garrison LP Jr et al (1985) The quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease. N Engl J Med 312:553–559
Laupacis A, Keown P, Pus N et al (1996) A study of the quality of life and cost-utility of renal transplantation. Kidney Int 50:235–242
Abraham G, John GT, Shroff S et al (2010) Evolution of renal transplantation in India over the last four decades. NDT Plus 3(2):203–207
Atkins RC, Zimmet P (2010) Diabetic kidney disease: act now or pay later. Kidney Int 77(5):375–377
Locatelli F, Pozzoni P, Del Vecchio L (2004) Renal replacement therapy in patients with diabetes and end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 15 Suppl 1:S25–S29
Khauli RB, Steinmuller DR, Novick AC et al (1986) A critical look at survival of diabetics with end-stage renal disease. Transplantation versus dialysis therapy. Transplantation 41(5):598–602
Cosio FG, Hickson LJ, Griffin MD et al (2008) Patient survival and cardiovascular risk after kidney transplantation: the challenge of diabetes. Am J Transplant 8(3):593–599
Witczak BJ, Hartmann A, Jenssen T et al (2006) Routine coronary angiography in diabetic nephropathy patients before transplantation. Am J Transplant 6(10):2403–2408
Ramanathan V, Goral S, Tanriover B et al (2005) Screening asymptomatic diabetic patients for coronary artery disease prior to renal transplantation. Transplantation 79(10):1453–1458
Manske CL, Wang Y, Rector T et al (1992) Coronary revascularisation in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with chronic renal failure. Lancet 340(8826):998–1002
International Diabetes Federation (IDF) (2006) Diabetes atlas, 3rd edn. http://www.diabetesatlas.org/
Valera B, Gentil MA, Cabello V et al (2006) Epidemiology of urinary infections in renal transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 38(8):2414–2415
Alangaden GJ, Thyagarajan R, Gruber SA et al (2006) Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: current epidemiology and associated risk factors. Clin Transplant 20(4):401–409
Naqvi SA (2002) Immunosuppression strategies in developing countries. Transplant Proc 34(6):2083–2084
Masri MA, Haberal M, Rizvi M et al (2004) The pharmacokinetic of Equoral vs Neoral in stable renal transplant patients: a multi- national multi-center study. Transplant Proc 36:80
Bittar J, Cepeda P, de la Fuente J et al (2006) Renal transplantation in diabetic patients. Transplant Proc 38(3):895–898
Kronson JW, Gillingham KJ, Sutherland DE, Matas AJ (2000) Renal transplantation for type II diabetic patients compared with type I diabetic patients and patients over 50 years old: a single-center experience. Clin Transplant 14(3):226–234
Boucek P, Saudek F, Pokorna E et al (2002) Kidney transplantation in type 2 diabetic patients: a comparison with matched non-diabetic subjects. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17(9):1678–1683
Hirschl MM, Heinz G, Sunder-Plassmann G, Derfler K (1992) Renal replacement therapy in type 2 diabetic patients: 10 years’ experience. Am J Kidney Dis 20(6):564–568
Goldfarb-Rumyantzev A, Hurdle JF, Scandling J et al (2005) Duration of end-stage renal disease and kidney transplant outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(1):167–175
Shoskes DA, Cecka JM (1998) Deleterious effects of delayed graft function in cadaveric renal transplant recipients independent of acute rejection. Transplantation 66(12):1697–1701
Parekh J, Bostrom A, Feng S (2010) Diabetes mellitus: a risk factor for delayed graft function after deceased donor kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 10(2):298–303
Rao PS, Ojo A (2009) The alphabet soup of kidney transplantation: SCD, DCD, ECD–fundamentals for the practicing nephrologist. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4(11):1827–1831 Epub 2009 Sep 24
Keith DS, Demattos A, Golconda M et al (2004) Effect of donor recipient age match on survival after first deceased donor renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(4):1086–1091
Jha V, Chugh KS (2002) Posttransplant infections in the tropical countries. Artif Organs 26(9):770–777
Jha V, Chugh S, Chugh KS (2000) Infections in dialysis and transplant patients in tropical countries. Kidney Int 57(Suppl 74):S85–S93
Kher V (2002) End-stage renal disease in developing countries. Kidney Int 62(1):350–362
Sakhuja V, Jha V, Varma PP et al (1996) The high incidence of tuberculosis among renal transplant recipients in India. Transplantation 61(2):211–215
John GT (2003) Infections after renal transplantation in India. Indian J Nephrol 13:14–19
Shah BR, Hux JE (2003) Quantifying the risk of infectious diseases from people with diabetes. Diabetes Care 26(2):510–513
Ram R, Dakshina Murty KV, Prasad N (2005) Time table of infections after renal transplantation–South Indian experience. Indian J Nephrol 15: Supple2:S14–S21
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kute, V.B., Vanikar, A.V., Trivedi, H.L. et al. Outcome of renal transplantation in patients with diabetic nephropathy—a single-center experience. Int Urol Nephrol 43, 535–541 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-010-9852-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-010-9852-2