Abstract
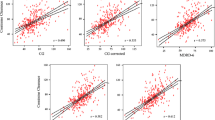
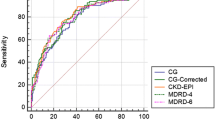
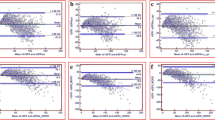
European as well as US guidelines recommend the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula to determine the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and, based on this, the staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The diagnosis of CKD is only established when a reduced eGFR has been observed for 3 months or longer. Because the MDRD equation is very complex, the calculation of eGFR is not possible without help from calculators or computers. Therefore, we converted this equation into simple, easy to use colour nomograms. These were drawn separately for men and women, on one hand, and for whites and blacks, on the other. These nomograms allow the determination of a patient’s eGFR in a quick and easy way and at any location.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjornsson TD (1979) Use of serum creatinine concentrations to determine renal function. Clin Pharmacokinet 4:200–222
Perrone RD, Madias NE, Levey AS (1992) Serum creatinine as an index of renal function: new insights into old concept. Clin Chem 38:1933–1953
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31–41
Gates GF (1985) Creatinine clearance estimation from serum creatinine values: an analysis of three mathematical models of glomerular function. Am J Kidney Dis 5:199–205
Jelliffe RW, Jelliffe SM (1972) A computer program for estimation of creatinine clearance from unstable serum creatinine levels, age, sex and weight. Math Biosc 14:17–24
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB et al (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of diet in renal disease study group. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Salazar DE, Corcoran GB (1988) Predicting creatinine clearance and renal drug clearance in obese patients from estimated fat-free body mass. Am J Med 84:1053–1060
Wright JG, Boddy AV, Highley M et al (2001) Estimation of glomerular filtration rate in cancer patients. Br J Cancer 84:452–459
European Best Practice guidelines (2002) Measurement of renal function, when to refer and when to start dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transpl 17:7–15
K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease (2002) Evaluation, classification and stratification: kidney disease outcome quality initiative. Am J Kidney Dis 39:S1–S266
Levey AS, Greene T, Kusek J et al (2000) A simplified equation to predict glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:A0828
Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T et al (2006) Chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration: using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 145:247–254
Agaba EI, Wigwe CM, Agaba PA, Tzamaloukas AH (2009) Performance of the Cockcroft-Gault and MDRD equations in adult Nigerians with chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 41(3):635–642
Wieczorowska-Tobis K, Niemir ZI, Guzik P et al (2006) Difference in estimated GFR with two different formulas in elderly individuals. Int Urol Nephrol 38(2):381–385
Acknowledgments
The first author is working as post-doctoral fellow for the Belgian Fund for Research Flanders (FWO Vlaanderen) and obtained funding from the FWO (Krediet aan Navorsers 1.5.115.06 N). The authors are indebted to Christel Beerens for her drawing assistance and John Patrick Garvey for his review.
Conflict of interest
The results presented in this paper have not been published previously in whole or part.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eloot, S., Van Vlem, B. & De Meester, J. Simple assessment of patient’s stage of chronic kidney disease using eGFR-MDRD nomograms. Int Urol Nephrol 44, 207–212 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-010-9849-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-010-9849-x