Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to assess the effect of intralesional verapamil on the treatment of Peyronie’s disease.
Materials and methods
This randomized study involved 80 patients. First, they were divided into two groups. The first group (case: 40 patients) received intralesional verapamil and the second group (control: 40 patients) local saline injection. They were followed about 24 weeks and evaluated for the size of plaques, plaque softening, reduction of pain and amelioration of penile deformity and erectile dysfunction (estimated by the International Index of Erectile Function) before and after treatment.
Results
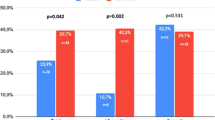
Reduction of plaque size was seen in 17.5% of the case group and 12.8% of the control group (P: 0.755). Pain was reduced in 30% of the case group and 28.2% of the control group (P: 0.99). Curvature was decreased in 17.5% of the case group and 23.1% the control group (P: 0.586). Plaque softening was seen in 30% of the case group compared with 25.6% improvement in the control group (P: 0.803).
Also we found 5% and 2.6% improvement in sexual dysfunction in the case and control groups, respectively. (P: 0.985).
Conclusion
Although in some studies verapamil has been found to be effective in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease, we did not find any improvement in comparison with the control group.
Furthermore, larger scale studies are warranted to assess the effect of this drug on the treatment of Peyronie’s disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith CJ, Mcmahon C, Shabsigh R (2005) Peyronie’s disease: the epidemiology, aetiology and clinical evaluation of deformity. BJU Int 95:729–732. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05391.x
Gelbard MK, Dorey F, James K (1990) The natural history of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 144:1376–1379
De la Peyronie F (1743) Sur quelques obstacle qui s opposent a l ejaculation naturelle de la semence. Mem Acad Chir (Paris) 1:318
Sommer F, Schwarzer U, Wassmer G et al (2002) Epidemiology of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res 14:379–383. doi:10.1038/sj.ijir.3900863
Schwarzer U, Sommer F, Klotz T, Braun M, Reifenrath B, Engelmann U (2001) The prevalence of Peyronie’s disease: results of a large survey. BJU Int 88:727–730. doi:10.1046/j.1464-4096.2001.02436.x
Fitkin J, Ho GT (1999) Peyronie’s disease: current management. Am Fam Physician 60:549–552
Tunuguntlas HS (2001) Management of Peyronie’s disease: a review. World J Urol 19:244–250. doi:10.1007/s003450100209
Anderson MS, Shankey TV, Lubrano T, Mulhall JP (2000) Inhibition of Peyronie’s plaque fibroblast proliferation by biologic agents. Int J Impot Res 12(suppl 3):s25–s31. doi:10.1038/sj.ijir.3900558
Lee RC, Ping J (1990) Calcium antagonists retard extracellular matrix production in connective tissue equivalent. J Surg Res 49:463–466. doi:10.1016/0022-4804(90)90197-A
Doong H, Dissanayaka S, Gowrishankar TR, La Barbera MC, Lee RC (1996) The 1996 Lindberg Award. Calcium antagonists alter cell shape and induce procollagenase synthesis in keloid and normal human dermal fibroblasts. J Burn Care Rehabil 17:497–514. doi:10.1097/00004630-199611000-00005
Roth M, Eickelberg O, Kohler E, Eme P, Block LH (1996) Ca channel blockers modulate metabolism of collagenase within the extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5478–5482. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.11.5478
Levine LA (1997) Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with intralesional verapamil injection. J Urol 158(4):1395–1399. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)64224-1
Rehman J, Benet A, Melman A (1998) Use of intralesional verapamil to dissolve Peyronie’s disease plaque: a long-term single blind study. Urology 51(4):620–626. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(97)00700-0
Levine LA, Merrick PF, Lee RC (1994) Intralesional verapamil injection for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 151(6):1522–1524
Devine CJ Jr, Somers KD, Jordan GH et al (1997) Proposal trauma as the cause of the Peyronie’s lesion. J Urol 157:285–290. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)65361-8
Greenfield JM, Levine LA (2005) Peyronie’s disease: etiology, epidemiology and medical treatment. Urol Clin North Am 32:469–478. doi:10.1016/j.ucl.2005.08.011
Scott WW, Scardino PL (1948) A new concept in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. South Med J 41:173–177
Akkus E, Carrier S, Rehman J et al (1994) Is colchicine effective in Peyronie’s disease? A pilot study. Urology 44(2):291–295. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(94)80155-X
Zarafonetis CJ, Horrax TM (1959) Treatment of Peyronie’s disease with potassium para-aminobenzoate (potaba). J Urol 81(6):770–772
Ralph DJ, Brooks MD, Bottazzo GF et al (1992) The treatment of Peyronie’s disease with tamoxifen. Br J Urol 70(6):648–651
Biagiotti G, Cavallini G (2001) Acetyl-L-carnitine vs tamoxifen in the oral therapy of Peyronie’s disease: a preliminary report. BJU Int 88(1):63–67. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02241.x
Ralph DJ, AL-Akraa M, Pryor JP (1995) The Nesbit operation for Peyronie’s disease: 16-year experience. J Urol 154:1362–1363. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66862-9
Devine CJ, Horton CE (1974) Surgical treatment of Peyronie’s disease with a dermal graft. J Urol 111:44
Lue TF, El-Sakka AI (1998) Venous patch graft for Peyronie’s disease. Part I. technique. J Urol 160:2047–2049. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01)62239-0
Wilson SK, Cleves MA, Delk JR (2001) Longterm follow-up of treatment for Peyronie’s disease: modelling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J Urol 165:825–829. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)66537-8
Carson CC (1998) Penile prosthesis implantation in the treatment of Peyronie’s disease. Int J Impot Res 10:125–128. doi:10.1038/sj.ijir.3900330
Levine LA, Sevier VL (2003) A double blind, placebo-controlled trial of electromotive drug administration (EMDA) using verapamil vs. saline for Peyronie’s disease: preliminary results. J Urol 169(4):274–275
Levine LA, Goldman KE, Greenfield JM (2002) Experience with intraplaque injection of verapamil for Peyronie’s disease. J Urol 168(2):621–625. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64691-5
Sahin M, Basar MM, Bozdogan O, Atan A (2001) Short-term histopatholoic effects of different intracavernosal agents on corpus cavernosum and antifibrotic activity of intracavernosal verapamil: an experimental study. Urology 58:487–492. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(01)01211-0
Bennett NE, Guhring P, Mulhall JP (2007) Intralesional verapamil prevents the progression of Peyronie’s disease. Urology 69:1181–1184. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2006.02.048
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirazi, M., Haghpanah, A.R., Badiee, M. et al. Effect of intralesional verapamil for treatment of Peyronie’s disease: a randomized single-blind, placebo-controlled study. Int Urol Nephrol 41, 467–471 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9522-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9522-4