Abstract
Objectives
In this experimental study, our aim was to determine whether angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition and angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor blockade affect the apoptotic changes in contralateral testis following unilateral testicular torsion (UTT).
Methods
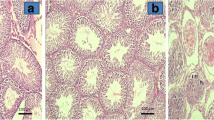
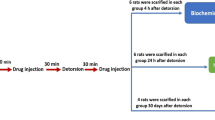
Study groups consisted of 30 adult male Wistar rats. The rats were randomly separated into five groups. Group 1 was maintained as control without manipulation. Group 2 underwent the sham operation. Torsion was created by rotating the left testis 720° clockwise for 4 h and maintained by fixing the testis to the scrotum in the other groups. Group 3 underwent torsion and detorsion, with saline administration after detorsion. In group 4, the same surgical procedure was done as in the detorsion group, but AT1 receptor blocker (losartan 30 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally for 60 min before detorsion. In group 5, the same surgical procedure was done as in the detorsion group, but ACE inhibitor (lisinopril 50 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally for 60 min before detorsion. Bilateral testes were removed from each rat 24 h after surgery. Apoptosis was assessed in paraffin-embedded sections stained for TUNEL method. Reticulum staining was performed to evaluate the extracellular changes semiquantitatively. Testicular biopsy score counts were performed on these sections according to Johnsen.
Results
The mean apoptotic scores of group 1, group 2 and group 3 were significantly higher than that of the other groups. There was no difference between the apoptotic scores of groups 1, 2, 4 and 5. Reticulum stain was increased in group 3 as compared to other groups. The mean Johnsen biopsy score of group 3 was significantly lower than that of the other groups.
Conclusion
ACE inhibition and AT1 receptor blockade reduced the tubular damage and apoptosis in the contralateral testes after UTT. The beneficial effect of these drugs may arise from inhibition of ischemic process resulting from increased sympathetic activity and elimination of insults subsequent to dysregulation of RAS. These results suggest that ACE inhibitors and AT1 receptor blockers may be of potential value in patients with UTT.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barada JH, Weingarten JL, Cromie WJ (1989) Testicular salvage and age-related delay in the presentation of testicular torsion. J Urol 142:746–748
Anderson JB, Williamson RC (1986) The fate of the human testes following unilateral torsion of the spermatic cord. Br J Urol 58:698–704
Williamson RC (1985) The continuing conundrum of testicular torsion. Br J Surg 72:509–510
Hadziselimovic F, Geneto R, Emmons LR (1998) Increased apoptosis in the contralateral testes of patients with testicular torsion as a factor for infertility. J Urol 160:1158–1160
Sarica K, Bakir K, Erbagci A, Yagci F, Uysal O, Ucak R (2001) Unilateral testicular torsion: evaluation of bcl-2, p-53 and PCNA expression in contralateral testes. Urol Int 66:94–99
Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL (2000) Signal transduction mechanisms mediating the physiological and pathophysiological actions of angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pharmacol Rev 52:639–672
Dzau VJ, Re R (1994) Tissue angiotensin system in cardiovascular medicine. A paradigm shift? Circulation 89:493–498
Bernstein KE, Shai SY, Howard T, Balogh R, Frenzel K, Langford K (1993) Structure and regulated expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme and the receptor for angiotensin II. Am J Kidney Dis 21:53–57
Ehlers MR, Riordan JF (1991) Angiotensin-converting enzyme: zinc- and inhibitor-binding stoichiometries of the somatic and testis isozymes. Biochemistry 30:7118–7126
Tanaka M, Ohnishi J, Ozawa Y, Sugimoto M, Usuki S, Naruse M, Murakami K, Miyazaki H (1995) Characterization of angiotensin receptor type 2 during differentiation and apoptosis of rat ovarian cultured granulosa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 207:593–598
Yamada T, Horiuchi M, Dzau VJ (1996) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor mediates programmed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:156–160
Horiuchi M, Yamada T, Hayashida W, Dzau VJ (1997) Interferon regulatory factor-1 up-regulates angiotensin II type 2 receptor and induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272:11952–11958
Cigola E, Kajstura J, Li B, Meggs LG, Anversa P (1997) Angiotensin II activates programmed myocyte cell death in vitro. Exp Cell Res 231:363–371
Dimmeler S, Rippmann V, Weiland U, Haendeler J, Zeiher AM (1997) Angiotensin II induces apoptosis of human endothelial cells. Protective effect of nitric oxide. Circ Res 81:970–976
Siragy HM (2000) AT(1) and AT(2) receptors in the kidney: role in disease and treatment. Am J Kidney Dis 36:4–9
Wu L, Iwai M, Nakagami H, Li Z, Chen R, Suzuki J, Akishita M, de Gasparo M, Horiuchi M (2001) Roles of angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation associated with selective angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade with valsartan in the improvement of inflammation-induced vascular injury. Circulation 104:2716–2721
Libby P (2001) Current concepts of the pathogenesis of the acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 104:365–372
Hornig B, Landmesser U, Kohler C, Ahlersmann D, Spiekermann S, Christoph A, Tatge H, Drexler H (2001) Comparative effect of ACE inhibition and angiotensin II type I receptor antagonism on bioavailability of nitric oxide in patients with coronary artery disease: role of superoxide dismutase. Circulation 103:799–805
Johnsen SG (1970) Testicular biopsy score count-a method for registration of spermatogenesis in human testes: normal values and results in 335 hypogonadal males. Hormones 1:2–5
Wallace DM, Gunter PA, Landon GV, Pugh RC, Hendry WF (1982) Sympathetic orchiopathia-an experimental and clinical study. Br J Urol 54:765–768
Sarica K, Kupeli B, Budak M, Kosar A, Kavukcu M, Durak I, Gogus O (1997) Influence of experimental spermatic cord torsion on the contralateral testis in rats. Urol Int 58:208–212
Dominguez C, Martinez Verduch M, Estornell F, Garcia F, Hernandez M, Garcia-Ibarra F (1994) Histological study in contralateral testis of prepubertal children following unilateral testicular torsion. Eur Urol 26:160–163
Shai SY, Fishel RS, Martin BM, Berk BC, Bernstein KE (1992) Bovine angiotensin converting enzyme cDNA cloning and regulation. Increased expression during endothelial cell growth arrest. Circ Res 70:1274–1281
Cesarano TS, Nachtsheim DA, Otero F, Parsons CL (1984) The effect of testicular torsion on contralateral testis and the production of antisperm antibodies in rabbits. J Urol 132:577–579
Merimsky E, Orni-Wasserlauf R, Yust I (1984) Assessment of immunological mechanism in infertility of the rat after experimental testicular torsion. Urol Res 12:179–184
Kolettis PN, Stowe NT, Inman RS, Thomas AJ (1996) Acute spermatic cord torsion alters the microcirculation of the contralateral testis. J Urol 155:350–354
Tanyel FC, Buyukpamukçu N, Hicsonmez A (1989) Contralateral testicular blood flow during unilateral testicular torsion. Br J Urol 63:522–524
Cosentino MJ, Nishida M, Rabinowitz R, Cockett ATK (1985) Histological changes occurring in the contralateral testes of prepubertal rats subjected to various durations of unilateral spermatic cord torsion. J Urol 133:906–911
York JP, Drago JR (1985) Torsion and contralateral testicle. J Urol 133:294–297
Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O, Suzuki Y, Ruperez M, Egido J (2001) Proinflammatory actions of angiotensins. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 10:321–329
Mezzano SA, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J (2001) Angiotensin II and renal fibrosis. Hypertension 38:635–638
Roberts AB, Mc Cune BK, Sporn MB (1992) TGF-B: regulation of extracellular matrix. Kidney Int 41:557–579
Ayan S, Roth JA, Freeman MR, Bride SH, Peters CA (2001) Partial ureteral obstruction dysregulates the renal renin-angiotensin system in the fetal sheep kidney. Urology 58:301–306
Fukuzawa M, Satoh J, Sagara M, Muto G, Muto Y, Nishimura S, Miyaguchi S, Qiang XL, Sakata Y, Nakazawa T, Ikehata F, Ohta S, Toyota T (1997) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors suppress production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in vitro and in vivo. Immunopharmacology 36:49–55
Guo G, Morrissey J, McCracken R, Tolley T, Klahr S (1999) Role of TNFR1 and TNFR2 receptors in tubulointerstitial fibrosis of obstructive nephropathy. Am J Physiol 277:766–772
Nakamura A, Johns EJ, Imaizumi A, Yanagawa Y, Kohsaka T (1999) Effect of beta(2)-adrenoceptor activation and angiotensin II on tumour necrosis factor and interleukin 6 gene transcription in the rat renal resident macrophage cells. Cytokine 11:759–765
Wang ZQ, Todani T, Watanabe Y, Toki A, Ogura K, Miyamoto O, Toyoshima T, Itano T (1998) Germ-cell degeneration in experimental unilateral cryptorchidism: role of apoptosis. Pediatr Surg Int 14:9–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gokce, G., Karboga, H., Yildiz, E. et al. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on apoptotic changes in contralateral testis following unilateral testicular torsion. Int Urol Nephrol 40, 989–995 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9348-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9348-5