Abstract
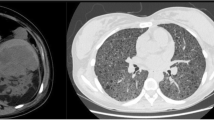
Current management strategies of renal angiomyolipomas (AMLs) include observation, embolization and partial or total nephrectomy. Selective arterial embolization is an effective and safe treatment of large angiomyolipomas with low complication rates. Percutaneous drainage was the recommended treatment for renal abscess formation following the embolization. Herein we describe two cases which we performed percutaneous drainage of the liquefaction of entire tumors after embolization. Open surgery was needed for one of the patients who showed recurrence after percutaneous drainage and alcohol irrigation of the cavity, whereas percutaneous drainage was the sufficient treatment for the other patient as recommended.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eble JN (1998). Angiomyolipoma of kidney. Semin Diagn Pathol 15: 21–40
Mourikis D, Chatziioannou A and Antoniou A (1999). Selective arterial embolization in the management of symptomatic renal angiomyolipomas. Eur J Radiol 32: 153–159
Nelson CP and Sanda MG (2002). Contemporary diagnosis and management of renal angiomyolipoma. J Urol 168: 1315–1325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkara, H., Özkan, B. & Solok, V. Management of renal abscess formation after embolization due to renal angiomyolipomas in two cases. Int Urol Nephrol 38, 427–429 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-005-0253-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-005-0253-x