Abstract
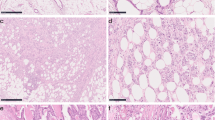
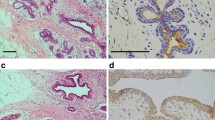
Objective: We investigated the expression of thymidine phosphorylase (TP) in bladder carcinomas and assessed its prognostic significance in superficial bladder cancer samples. Patients and methods: We studied 142 primary bladder cancer samples immunohistochemically for nuclear thymidine phosphorylase (TPN), cytoplasmic (TPC) and stromal (TPSTR) expression. We correlated them with standard clinicopathological features (grade, stage, concurrent in situ, multiplicity, primary or recurrent status), as well with recurrence and progression. We examined also the relationship between TP and tumor microvessel density. Results: The level of all types of TP correlated well with stage, while grade correlated well only with TPSTR and the presence of carcinoma in situ only with TPN. Patients with low levels of TPN had a longer tumor free interval, during a 38.6 months mean follow up time. Regarding the association between TP count and microvessel density we found the strongest association with TPSTR (p=0.003), a borderline statistical significance with TPC (p=0.049) and no relationship with TPN (p=0.072). Conclusions: We suggest that the assessment of TPN might be useful for predicting recurrence in superficial bladder cancer. We propose also that TP may stimulate angiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F Ishikawa K Miyazono U Hellman et al. (1989) ArticleTitleIdentification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of the platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor Nature 338 557–562 Occurrence Handle10.1038/338557a0 Occurrence Handle2467210
EH Streeter AL. Harris (2002) ArticleTitleAngiogenesis in bladder cancer-prognostic marker and target for future therapy Sur Oncol 11 85–100 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0960-7404(02)00013-0
T O’Brien D Cranston S Fuggle et al. (1995) ArticleTitleDifferent angiogenic pathways characterize superficial and invasive bladder cancer Cancer Res 55 IssueID3 510–513 Occurrence Handle7530595
Y Takebayashi S Akiyama S Akiba et al. (1989) ArticleTitleClinicopathologic and prognostic significance of an angiogenic factor, thymidine phosphorylase, in human colorectal carcinoma J Natl Cancer Inst 88 110–117
Y Takebayashi S Natsugoe M Baba et al. (1999) ArticleTitleThymidine phosphorylase in human esophageal suamous cell carcinoma Cancer 85 282–289 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990115)85:2<282::AID-CNCR3>3.0.CO;2-T Occurrence Handle10023693
S Takao Y Takebayashi C Xiangming et al. (1998) ArticleTitleExpression of thymidine phosphorylase is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas Clin Cancer Res 4 1619–1624 Occurrence Handle9676835
T Ueda M Tawaki O Ogawa N. Yoshimura (2002) ArticleTitleOverexpression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in patients with interstitial cystitis and bladder carcinoma J Urol 167 347–351 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00005392-200201000-00099 Occurrence Handle11743354
TS O’Brien SB Fox AJ Dickinson et al. (1996) ArticleTitleExpression of the angiogenic factor thymidine phosphorylase/platelet derived endothelial cell growth factor in primary bladder cancers Cancer Res 56 IssueID20 4799–4804 Occurrence Handle8841001
Y Mizutani Y Okada O. Yoshida (1997) ArticleTitleExpression of platelet derived endothelial cell growth factor in bladder carcinoma Cancer 79 1190–1194 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19970315)79:6<1190::AID-CNCR18>3.0.CO;2-V Occurrence Handle9070497
S Li K Nomata K Sawase et al. (2001) ArticleTitlePrognostic significance of platelet derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase expression in stage pT1G3 bladder cancer Int J Urol 8 IssueID9 478–482 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1442-2042.2001.00354.x Occurrence Handle11683966
M Toi S Hoshina T Tanipuchi et al. (1995) ArticleTitleExpression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in human breast cancer Int J Cancer 64 IssueID2 79–82 Occurrence Handle7542228
S Tsukagoshi Y Saga N Suzuki et al. (2003) ArticleTitleThymidine phosphorylase-mediated angiogenesis is regulated thymidine phosphorylase inhibitor in human ovarian cancer cells in vitro Int J Oncol 22 IssueID5 961–967 Occurrence Handle12684660
Y Imazono Y Takebayashi K Nishiyama et al. (1997) ArticleTitleCorrelation between thymidine phosphorylase expression and prognosis in human renal cell carcinoma J Clin Oncol 15 2570–2578 Occurrence Handle9215827
M Haraguchi K Miyadera K Uemma et al. (1994) ArticleTitleAngiogenic activity of enzymes Nature 368 198 Occurrence Handle10.1038/368198a0 Occurrence Handle7511797
K Sawase K Nomata H Kanetake Y. Saito (1998) ArticleTitleThe expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor in human bladder cancer Cancer Lett 130 IssueID1–2 35–441 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3835(98)00097-4 Occurrence Handle9751254
Y Kubota T Miura M Moriyama et al. (1997) ArticleTitleThymidine phosphorylase activity in human bladder cancer difference between superficial and invasive cancer Clin Cancer Res 3 IssueID6 973–976 Occurrence Handle9815773
J Arima Y Imazono Y Takebayashi et al. (2000) ArticleTitleExpression of thymidine phosphorylase as an indicator of poor prognosis for patient with transitional ceel carcinoma of the bladder Cancer 88 1131–1138 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(20000301)88:5<1131::AID-CNCR25>3.0.CO;2-P Occurrence Handle10699904
Y Takebayashi K Yamada k Miyadera et al. (1996) ArticleTitleThe activity and expression of thymidine phosphorylase in hyman solid tumors Eur J Cancer 32A IssueID7 1227–1232 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0959-8049(96)00061-5 Occurrence Handle8758258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stavropoulos, N.E., Bouropoulos, C., Ioachim, E. et al. Prognostic Significance of Thymidine Phosphorylase in Superficial Bladder Carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol 37, 55–60 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-004-6079-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-004-6079-0