Abstract
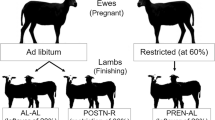
This study evaluated the effects of prenatal nutrition on body weight (BW), average daily gain (ADG), rump fat thickness (RFT), backfat thickness (BFT), ribeye area (REA), muscle cell area (MCA), and the number of cells in REA (NCREA) of young Nellore bulls during the rearing period. After pregnancy confirmation (30 days of pregnancy), 126 Nellore cows were separated into three prenatal nutritional treatments (NP (control; 0.03% of BW), only mineral supplementation; PP (0.3% of BW), protein-energy supplementation in the final third; and FP (0.3% of BW) protein-energy supplementation during the entire pregnancy). After calving, all animals were submitted to the same environmental conditions (sanitary and nutritional) and the different supplementation protocols ceased. The males (63 bulls) were evaluated during the entire rearing phase (210 ± 28 days to 540 ± 28 days of age) to weight gain (BW and ADG), carcass characteristics (RFT, BFT, and REA), and for histological assessments (MCA and NCREA; 7 animals per treatment randomly selected). All phenotypes were subjected to an analysis of variance. The different prenatal stimuli had no effect on BFT, RFT, MCA, and NCREA (P > 0.05); however, prenatal nutrition influenced BW of the animals during the rearing phase (P < 0.01) and showed a tendency on ADG (P = 0.09) and REA (P = 0.08). In conclusion, the offspring from FP treatment showed greater BW during the rearing phase in comparison to the NP group. This is related to a greater protein offered in prenatal nutrition, increasing muscle development during the gestational period.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Belkacemi, L., Nelson, D.M., Desai, M. and Ross, M.G., 2010. Maternal undernutrition influences placental-fetal development, Biology of Reproduction, 83, 325–331
Bell, A.W. and Greenwood, P.L., 2016. Prenatal origins of postnatal variation in growth, development and productivity of ruminants, Animal Production Science, 56, 1217-1232.
Bergen, R.D., McKinnon, J.J., Christensen, D.A. and Kohle, N., 1996. Prediction of lean yield in yearling bulls using real-time ultrasound, Canadian Journal of Animal Science, 76, 305–311.
Bianchini, W., Silveira, A.C., Jorge, A.M., Arrigoni, M.D.B., Martins, C.L., Rodrigues, É., Hadlich, J.C. and Andrighetto, C., 2007. Effect of genetic group on carcass traits and fresh and aged beef tenderness from young cattle, Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 36, 2109–2117.
Bonin, M.N., Ferraz, J.B.S., Pedrosa, V.B., Silva, S.L., Gomes, R.C., Cucco, D.C., Santana, M.H.A., Campos, J.H.A., Barbosa, V.N., Castro, F.S.F., Novais, F.J. and Oliveira, E.C.M., 2015. Visual body-scores selection and its influence on body size and ultrasound carcass traits in Nellore cattle, Journal of Animal Science, 93, 5597–5606.
Bonnet, M., Cassar-Malek, I., Chilliard, Y. and Picard, B., 2010. Ontogenesis of muscle and adipose tissues and their interactions in ruminants and other species, Animal, 4, 1093–1109.
Castro-Rodríguez, D.C., Rodríguez-González, G.L., Menjivar, M. and Zambrano, E., 2020. Maternal interventions to prevent adverse fetal programming outcomes due to maternal malnutrition: evidence in animal models, Placenta, 102, 49-54.
Caton, J.S., Crouse, M.S., McLean, K.J., Dahlen, C.R., Ward, A.K., Cushman, R.A., Grazul-Bilska, A.T., Neville, B.W., Borowicz, P.P. and Reynolds, L.P., 2020. Maternal periconceptual nutrition, early pregnancy, and developmental outcomes in beef cattle, Journal of Animal Science, 98.
Chavatte-Palmer, P., Velazquez, M.A., Jammes, H. and Duranthon, V., 2018. Review: epigenetics, developmental programming and nutrition in herbivores, animal, 12, s363–s371.
Copping, K.J., Callaghan, M.J., Geesink, G.H., Gugusheff, J.R., McMillen, I.C., Rodgers, R.J., Muhlhausler, B.S., Vithayathil, M.A. and Perry, V.E.A., 2021. Periconception and first Trimester diet modifies appetite, hypothalamic gene expression, and carcass traits in bulls, Frontiers in Genetics, 12, 1591.
Copping, K.J., Hernandez-Medrano, J., Hoare, A., Hummitzsch, K., McMillen, I.C., Morrison, J.L., Rodgers, R.J., Perry, V.E.A., Copping, K.J., Hernandez-Medrano, J., Hoare, A., Hummitzsch, K., McMillen, I.C., Morrison, J.L., Rodgers, R.J. and Perry, V.E.A., 2020. Maternal periconceptional and first trimester protein restriction in beef heifers: effects on placental parameters and fetal and neonatal calf development, Reproduction, Fertility and Development, 32, 495–507.
Costa, T.C., Du, M., Nascimento, K.B., Galvão, M.C., Meneses, J.A.M., Schultz, E.B., Gionbelli, M.P. and Duarte, M. de S., 2021. Skeletal muscle development in postnatal beef cattle resulting from maternal protein restriction during mid-gestation, Animals, 11, 860.
Coutinho, C., Mercadante, M., Jorge, A., Paz, C., El Faro, L. and Monteiro, F., 2015. Growth curves of carcass traits obtained by ultrasonography in three lines of Nellore cattle selected for body weight, Genetics and Molecular Research, 14, 14076–14087.
Detmann, E., Paulino, M.F., De Campos Valadares Filho, S. and Huhtanen, P., 2014. Nutritional aspects applied to grazing cattle in the tropics: a review based on brazilian results, Semina:Ciencias Agrarias, 35, 2829–2854.
Dickinson, H., Moss, T.J., Gatford, K.L., Moritz, K.M., Akison, L., Fullston, T., Hryciw, D.H., Maloney, C.A., Morris, M.J., Wooldridge, A.L., Schjenken, J.E., Robertson, S.A., Waddell, B.J., Mark, P.J., Wyrwoll, C.S., Ellery, S.J., Thornburg, K.L., Muhlhausler, B.S. and Morrison, J.L., 2016. A review of fundamental principles for animal models of DOHaD research: an australian perspective, Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease, 7, 449-472.
Diniz, W.J.S., Crouse, M.S., Cushman, R.A., McLean, K.J., Caton, J.S., Dahlen, C.R., Reynolds, L.P. and Ward, A.K., 2021. Cerebrum, liver, and muscle regulatory networks uncover maternal nutrition effects in developmental programming of beef cattle during early pregnancy, Scientific Reports, 11, 1–14.
Du, M., Huang, Y., Das, A.K., Yang, Q., Duarte, M.S., Dodson, M. V. and Zhu, M.J., 2013. Meat science and muscle biology symposium: manipulating mesenchymal progenitor cell differentiation to optimize performance and carcass value of beef cattle, Journal of Animal Science, 91, 1419–1427.
Du, M., Tong, J., Zhao, J., Underwood, K.R., Zhu, M., Ford, S.P. and Nathanielsz, P.W., 2010. Fetal programming of skeletal muscle development in ruminant animals, Journal of animal science, 88, E51–E60.
Duarte, M.S., Gionbelli, M.P., Paulino, P.V.R., Serão, N.V.L., Martins, T.S., Tótaro, P.I.S., Neves, C.A., Valadares Filho, S.C., Dodson, M. V., Zhu, M. and Du, M., 2013. Effects of maternal nutrition on development of gastrointestinal tract of bovine fetus at different stages of gestation, Livestock Science, 153, 60–65.
Ferreira, M.F., Rennó, L.N., Detmann, E., Paulino, M.F., De Campos Valadares Filho, S., Moreira, S.S., Martins, H.C., De Oliveira, B.I.C., Marquez, J.A. and De Paula Cidrine, I., 2020. Performance, metabolic and hormonal responses of grazing Nellore cows to an energy-protein supplementation during the pre-partum phase, BMC Veterinary Research, 16, 1–13.
Greenwood, P.L. and Cafe, L.M., 2007. Prenatal and pre-weaning growth and nutrition of cattle: long-term consequences for beef production, Animal, 1, 1283–1296.
Hammond, J., 1944. Physiological factors affecting birth weight, Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 2, 8–14.
Hoffman, M.L., Reed, S.A., Pillai, S.M., Jones, A.K., McFadden, K.K., Zinn, S.A. and Govoni, K.E., 2017. Physiology and endocrinology symposium: the effects of poor maternal nutrition during gestation on offspring postnatal growth and metabolism, Journal of Animal Science, 95, 2222–2232.
Jennings, T.D., Gonda, M.G., Underwood, K.R., Wertz-Lutz, A.E. and Blair, A.D., 2016. The influence of maternal nutrition on expression of genes responsible for adipogenesis and myogenesis in the bovine fetus, Animal, 10, 1697–1705.
Laporta, J., Dado-Senn, B. and Skibiel, A.L., 2021. Late gestation hyperthermia: epigenetic programming of daughter’s mammary development and function, Domestic Animal Endocrinology, 106681.
Long, J.M., Trubenbach, L.A., Pryor, J.H., Long, C.R., Wickersham, T.A., Sawyer, J.E. and Satterfield, M.C., 2021. Maternal nutrient restriction alters endocrine pancreas development in fetal heifers, Domestic Animal Endocrinology, 74, 106580.
Long, N.M., Prado-Cooper, M.J., Krehbiel, C.R., DeSilva, U. and Wettemann, R.P., 2010. Effects of nutrient restriction of bovine dams during early gestation on postnatal growth, carcass and organ characteristics, and gene expression in adipose tissue and muscle, Journal of Animal Science, 88, 3251–3261.
Lopes, L.S., Ladeira, M.M., Neto, O.R.M., Paulino, P.V.R., Chizzotti, M.L., Ramos, E.M. and de Oliveira, D.M., 2012. Características de carcaça e cortes comerciais de tourinhos Red Norte e Nelore terminados em confinamento, Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 41, 970–977.
Maresca, S., Valiente, S.L., Rodriguez, A.M., Testa, L.M., Long, N.M., Quintans, G.I. and Pavan, E., 2019. The influence of protein restriction during mid- to late gestation on beef offspring growth, carcass characteristic and meat quality, Meat Science, 153, 103–108.
Marquez, D.C., Paulino, M.F., Rennó, L.N., Villadiego, F.C., Ortega, R.M., Moreno, D.S., Martins, L.S., De Almeida, D.M., Gionbelli, M.P., Manso, M.R., Melo, L.P., Moura, F.H. and Duarte, M.S., 2017. Supplementation of grazing beef cows during gestation as a strategy to improve skeletal muscle development of the offspring, Animal, 11, 2184–2192.
McCoski, S., Bradbery, A., Marques, R. da S., Posbergh, C. and Sanford, C., 2021. Maternal nutrition and developmental programming of male progeny, Animals, 11, 2216.
Meyer, A.M., Reed, J.J., Vonnahme, K.A., Soto-Navarro, S.A., Reynolds, L.P., Ford, S.P., Hess, B.W. and Caton, J.S., 2010. Effects of stage of gestation and nutrient restriction during early to mid-gestation on maternal and fetal visceral organ mass and indices of jejunal growth and vascularity in beef cows, Journal of Animal Science, 88, 2410–2424.
Paradis, F., Wood, K.M., Swanson, K.C., Miller, S.P., McBride, B.W. and Fitzsimmons, C., 2017. Maternal nutrient restriction in mid-to-late gestation influences fetal mRNA expression in muscle tissues in beef cattle, BMC Genomics, 18, 632.
Picard, B., Lefaucheur, L., Berri, C. and Duclos, M.J., 2002. Muscle fibre ontogenesis in farm animal species, Reproduction Nutrition Development, 42, 415-431.
Polizel, G.H.G., Fantinato-Neto, P., Rangel, R.B., Grigoletto, L., Bussiman, F. de O., Cracco, R.C., Garcia, N.P., Ruy, I.M., Ferraz, J.B.S. and Santana, M.H. de A., 2021. Evaluation of reproductive traits and the effect of nutrigenetics on bulls submitted to fetal programming, Livestock Science, 247, 104487.
Prophet, E., Mills, B., Arrington, J.B. and Sobin, L.H., 1992. Laboratory methods in histotechnology, (Armer Registry of Pathology).
Reynolds, L.P., Borowicz, P.P., Caton, J.S., Crouse, M.S., Dahlen, C.R. and Ward, A.K., 2019. Developmental programming of fetal growth and development, Veterinary Clinics of North America - Food Animal Practice, 35, 229-247.
Robinson, D.L., Café, L.M. and Greenwood, P.L., 2013. Meat science and muscle biology symposium: Developmental programming in cattle: consequences for growth, efficiency, carcass, muscle, and beef quality characteristics, Journal of Animal Science, 91, 1428–1442.
Robinson, J.J., McDonald, I., Fraser, C. and Gordon, J.G., 1977. Studies on reproduction in prolific ewes, The Journal of Agricultural Science, 94, 331–338.
Silva, S. and Nascimento Júnior, D., 2007. Avanços na pesquisa com plantas forrageiras tropicais em pastagens : características morfofisiológicas e manejo do pastejo, Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 36, 121–138.
Underwood, K.R., Tong, J.F., Price, P.L., Roberts, A.J., Grings, E.E., Hess, B.W., Means, W.J. and Du, M., 2010. Nutrition during mid to late gestation affects growth, adipose tissue deposition, and tenderness in cross-bred beef steers, Meat Science, 86, 588–593.
Wu, G., Bazer, F.W., Cudd, T.A., Meininger, C.J. and Spencer, T.E., 2004. Maternal nutrition and fetal development, Journal of Nutrition, 134, 2169-2172.
Zago, D., Canozzi, M.E.A. and Barcellos, J.O.J., 2019. Pregnant cow nutrition and its effects on foetal weight - A meta-analysis, Journal of Agricultural Science, 157, 83–95.
Zhu, M.-J., Ford, S.P., Nathanielsz, P.W. and Du, M., 2004. Effect of maternal nutrient restriction in sheep on the development of fetal skeletal muscle, Biology of Reproduction, 71, 1968–1973.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (grant’s numbers 2019/02310–3, 2017/12105–2), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (grant’s number 432270/2018–3), and the College of Animal Science and Food Engineering (FZEA-USP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: G.H.G.P.; data curation: G.H.G.P. and R.F.S.; formal analysis: G.H.G.P.; funding acquisition: M.H.A.S. and G.H.G.P.; investigation: G.H.G.P., C.B.Z., H.H.C., and G.C.B.; methodology: R.F.S., M.H.A.S., R.C.C., and A.C.F.; project administration: M.H.A.S., G.H.G.P., A.C.F., and R.C.C.; writing—original draft: G.H.G.P.; writing—review and editing: M.H.A.S., R.F.S., C.B.Z., H.H.C., G.C.B., R.C.C., and A.C.F.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Research Ethics Committee of the College of Animal Science and Food Engineering from São Paulo University approved this study, under protocol No. 1843241117, according to the guidelines of the National Council for the Control of Animal Experimentation (CONCEA).
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polizel, G.H.G., de Francisco Strefezzi, R., Cracco, R.C. et al. Effects of different maternal nutrition approaches on weight gain and on adipose and muscle tissue development of young bulls in the rearing phase. Trop Anim Health Prod 53, 536 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-021-02982-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-021-02982-y