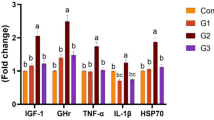
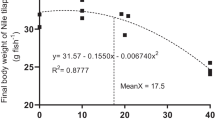
Abstract
The study aimed to verify the effect of water salinity and environmental temperature on the physiological variables (respiratory rate, heart rate, rectal temperature, and surface temperature) and ingestive behavior (rumination, feeding, drinking, and idle) of creole goats. Thirty-six males with an average age of 5.0 ± 0.6 months and an average weight of 20.0 ± 2.3 kg were housed in metabolic cages. The experimental design was a 2 × 3 type crossover (two temperatures and three levels of salinity). The two temperatures were: T1 = 26 ± 0.6 °C (thermoneutral) and T2 = 32 ± 1.2 °C (stress) and three levels salinity (1.0, 6.0, and 12.0 dS m−1). Between the temperatures, the respiratory rate (RR) and surface temperature (ST) present a difference (P < 0,05), being higher in the high temperature. Between temperatures, respiratory rate and surface temperature show a difference (P < 0.05), being higher at high temperature, keeping heart rate and rectal temperature similar at both temperatures. Among the different salinity levels in the behavioral activities, the feeding and urination activity presented a significant difference (P < 0.05), increasing with the water’s salinity level. Between temperatures, the rumination efficiency dray matter and neutral detergent fiber showed a significant difference (P < 0.05). With increasing air temperature, they decreased the rumination time—water salinity levels influence (P < 0.05) the feeding efficiency of dry matter. Therefore, water with up to 9.600 mg TDS L−1 can be used strategically in the desedentation of goats in semi-arid regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo, T.G.P., Furtado, D.A., Nascimento, J.W.B., Medeiros, A.N. and Lopes Neto, J.P., 2017. Thermoregulatory responses and adaptability of Anglo-nubiana goats maintained in a thermoneutral temperature and under heat stress. Journal of Behavior and Biometeorology, 5:106-111.
Bernabucci, U., Lacetera, N., Baumgard, L.H. and Rhoads, R.P., 2010. Metabolic and hormonal acclimation to heat stress in domesticated ruminants. Animal. 4:1167-1183.
Boyles, S. 2009. Livestock and water. The Ohio State University Extension. 18 p. Available at: <http:// www.ag.ohiostate.edu/~beef/library/water.html>. Accessed at: five may 2020.
Carvalho, G.G.P., Pires, A.J.V., Veloso, C.M., Silva, F.F. and Silva, R.R., 2006. Ruminal degradability of tropical forages hays. Revista Brasileira de Agrociência, 12:81-85.
Companhia de Pesquisa de Recursos Minerais-CPRM 2012. Eventos críticos. Brasília: [s.n]. Disponível em: <http://www.cprm.gov.br/publique/cgi/cgilua.exe/sys/start.htm?sid=35>. Acesso em: 10 jun. 2020.
Costa, R.G., Ribeiro, N.L., Nobre, P.T., Carvalho, F.F.R., Medeiros, A.N., Martins, F.E. 2019. Ingestive behavior and efficacy of male sheep housed in different stocking densities. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 46:e20180219
Digby, S.N., Blache, D., Masters, D.G., Revell, D.K. 2010. Responses to saline drinking water offspring born to ewes fed high salt during pregnancy. Small Ruminant Research, 91, 87-92.
Furtado, D.A., Leite, J.R.S., Nascimento, J.W.B., Leal, A.F. and Silva, A.S., 2012. Water consumption whem exposed sun and shade for native goats in the semiarid the state of Paraíba, Brazil. Engenharia Agrícola, 32:21-29.
Habibu, B., Kawu, M.U., Aluwong, T. and Makun, H.J., 2017. Influence of seasonal changes on physiological variables, hematology, and serum thyroid hormones profile in male Red Sokoto and Sahel goats. Journal of Applied Animal Research, 45:508-516.
Inbaraj, S., Kundu, A., A.K. Sunder, J. and Seijan, V., 2018. Seasonal changes in blood biochemical and endocrine responses of different indigenous goat breeds of tropical island agro-ecological environment. Biological Rhythm Research, 49:412-421.
Ítavo, L. C. V., Souza, S. R. M. B. O., Rimoli, J., Ítavo, C. C. B. F. and Dias, A. M., 2008. Diurnal intake behavior of bovines in continuous or rotational grazing. Archivos de Zootecnia 57:43-52.
Lucena, L.F.A., Furtado, D.A., Nascimento, J.W.B., Medeiros, A.N. and Souza, J.B., 2013. Physiological responses of native goats maintained in a thermoneutral temperature and thermal stress. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 17:672 – 679.
Marques, J.I., Lopes Neto, J.P., Nascimento, J.W.B., Talieri, I.C., Medeiros, G.R. and Furtado, D.A., 2018. Pupillary dilation as a thermal stress indicator in Boer crossbred goats maintained in a climate chamber. Small Ruminant Research, 158:26-29.
Marwick, G. 2007. Water requirements for sheep and cattle. Profitable and Sustainable primary industry. 3 th ed. Australian: Agriculture NSW, 5 p. Available at: <http://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au>. Accessed at: 14 mar. 2020.
Maurya, V.P., Sejian, V., Kumar, D. and Naqvi, M.K., 2018. Biological ability of Malpura rams to counter heat stress challenges and consequences on production performance in a semi-arid tropical environment. Biological Rhythm Research, 49:479-493.
Mdletshe, Z.M., Chimonyo, M., Marufu, M.C. and Msahlai, I.V., 2017. Effects of saline water consumption on physiological responses in Nguni goats. Small Ruminant Research, 153:209-211.
Mendonça, S. S., Campos, J. M. S., Valadares Filho, S. C., Valadares, R. F. D., Soares, C. A., Lana, R. P., Queiroz, A. C., Assis, A. J., Pereira, M. L. A. 2004. Comportamento ingestivo de vacas leiteiras alimentadas com dietas à base de cana-de-açúcar ou silagem de milho. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 33: 7 23-728.
Miranda, J. R., Furtado, D. A., Lopes Neto, J.P., Silva, V.C. and Ribeiro, N. L., 2018. Physiological parameters and cortisol hormon as thermal stress indicators in goats submitted to climate chamber. Energia na Agricultura, 33:133-137.
Moura, J.H.A., Araújo, G.G.L., Saraiva, E.P., Albuquerque, I.R.R., Turco, S. and Costa, S.A.P., 2016. Ingestive behavior of crossbred Santa Inês shep fed water with different salinity levels. Semina Ciências Agrárias, 37:1057-1068.
National Research Council – NRC 2007. Nutrient requeriments of small ruminants : sheep, goats, cervids, and new world camelids. Washington, DC.
Paiva, G.N., Araújo, G.G.L., Henriques, L.T., Medeiros, A.N., Beltrão Filho, E.M., Costa, R.G.; Albuquerque, I.R.R., Gois, G.C., Campos, F.S. and Freire, R.N.B., 2017. Water with different salinity levels for lactating goats. Semina: Ciências Agrárias, 38:2065-2074.
Piccione, G. and Refinetti, R., 2003. Thermal chronobiology of domestic animals. Frontiers in Bioscience, 8:258-264.
Ribeiro, N.L., Costa, R.G., Pimenta Filho, E.C., Ribeiro, M.N., Crovetti, A., Saraiva, E.P. and Bozzi, R., 2016. Adaptive profile of Garfagnina goat breed assessed through physiological, haematological, biochemical and hormonal parameters. Small Ruminant Research, 144:236-241.
Ribeiro, N. L., Costa, R.G., Pimenta Filho, E.C., Ribeiro, M.N. and Bozzi, R., 2018a. Effects of the dry and the rainy season on endocrine and physiologic profiles goats in the Brazilian semi-arid region. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 17:454-461.
Ribeiro, M.N., Ribeiro, N.L., Bozzi, R. and Costa, R.G., 2018b. Physiological and biochemical blood variables of goats subjected to heat stress – a review. Journal of Applied Animal Research, 46:1036-1041.
Sas Institute, 2010. SAS system for Windows. Version 9.1. Cary: SAS Institute Inc.
Silva, C.M., Araújo, G.G.L., Oliveira, B.Y.S., Azevedo, J.A.G. and Furtado, D.A., 2016. Performance and economic viability of feedlot sheep fed different levels of roughage, concentrate, and water. Semina: Ciências Agrárias, 37:1595-1606.
Swenson, M.J. and Reece, W.O., 2006. Dukes – Fisiologia dos Animais Domésticos. Guanabara Koogan S.A., Rio de Janeiro. 12 ed.
Wilson, A.D. 1966. The tolerance of sheep to sodium chloride in food or drinking water. Australasian Journal of Agricultural Research, 17, 503-514.
Yirga, H., Puchala, R., Tsukahara, Y., Tesfai, K., Sahlu, T., Mengistu, U.L. and Goetsch, A.L., 2018. Effects of level of brackish water and salinity on feed intake, digestion, heat, energy, ruminal fluid characteristics, and blood constituent levels in growing Boer goat wethers and mature Boer goat and Katahdin sheep wethers. Small Ruminant Research, 164:70-81.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable for that section.
Code availability
Not applicable for that section.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Federal University of Campina Grande and the Federal University of Paraíba for their technical assistance. CNPq and CAPES supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Evaldo de A. Cardoso: Data curation, formal analyses, investigation, writing–original draft
Dermeval A. Furtado: Conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, methodology
Neila L. Ribeiro: Formal analyses, methodology, writing–original draft, writing–review
Edilson Paes Saraiva: Supervision, formal analyses, investigation, methodology
José W. Barbosa do Nascimento: Supervision, investigation, methodology
Ariosvaldo Nunes de Medeiros: Supervision, investigation, methodology
Francinilda A. de Sousa: Data curation, formal analyses, investigation
Pedro H. Borba Pereira: Data curation, formal analyses, investigation
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The Animal Ethics Committee approved this study of the Federal University of Paraiba (UFPB), Brazil (protocol no. 6167/18).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cardoso, E.d.A., Furtado, D.A., Ribeiro, N.L. et al. Intake salinity water by creole goats in a controlled environment: ingestive behavior and physiological variables. Trop Anim Health Prod 53, 333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-021-02754-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-021-02754-8