Abstract
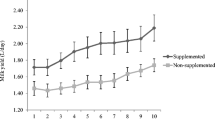
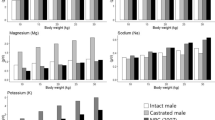
The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of different levels of dietary supplementation and reproductive stages on dry matter intake, digestibility, milk production, and mineral metabolism in Santa Inês hair ewes. Two dietary supplement levels of 0.5 and 1.5%, based on body weight, were used. A total of 12 hair ewes (six subjected to 0.5 and six subjected to 1.5% of concentrate supplementation based on body weight—BW) of the Santa Inês breed were evaluated in a completely randomized design with fixed effects of supplementation level, period, and its interactions. Dry matter intake, digestibility, milk production, and mineral metabolism (calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I), parathyroid hormone (PTH), and osteocalcin (OC)) were assessed. Dry matter digestibility was affected by the supplementation level (during both pregnancy and lactation), with higher values in ewes fed at a level of 1.5% of BW. A significant interaction between treatment × reproductive stages was found for the Mg concentration. A period effect (P < 0.05) on serum concentrations of P, Ca/P, Mg, and IGF-I was observed. Serum P concentrations were influenced (P < 0.05) by treatments and reproductive stages. There were significant differences in the Ca/P ratio among the reproductive stages. The enzymatic activity of ALP and serum IGFI differed among reproductive stages. Ewes supplemented at a level of 1.5% of BW produced 18.5% more milk than ewes supplemented at a level of 0.5% of BW. The use of 0.5% of body weight in concentrate supplementation is recommended for the reduction of production costs, without having an effect on the mineral metabolism of Santa Inês hair ewes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agenäs, S., Burstedt, E., Holtenius, K. 2003 Effects of feeding intensity during the dry period. 1. Feed intake, body weight, and milk production. Journal of Dairy Science, 86, 870–82.
Araujo, R.C., Pires, A.V., Susin, I., Mendes, C.Q., Rodrigues, G.H., Packer, I.U., Eastridge, M.L., 2008. Milk yield, milk composition, eating behaviour, and lamb performance of ewes fed diets containing soybean hulls replacing coastcross (Cynodon species) hay. Journal of Animal Science, 86:3511–3521.
Association of Official Analytical Chemists—AOAC. 1990. Official methods of analysis. 15th Ed., Arlington, VA, USA.
Barber, P.J., 2004. Disordens of the parathyroid glands. Journal Feline Medicine Surgery, 6, 259–269.
Braithwaite, G.D., 1978. The effect of dietary protein intake on calcium metabolism of the pregnant ewe. British Journal of Nutrition, 40, 505–507.
Braithwaite, G.D., 1983a. Calcium and phosphorus requirements of the ewe during pregnancy and lactation. 1. Calcium. British Journal of Nutrition, 50, 711–722.
Braithwaite, G.D., 1983b. Calcium and phosphorus requirements of the ewe during pregnancy and lactation. 2. Phosphorus. British Journal of Nutrition, 50, 723–736.
Brasil, 1992. Secretaria Nacional de Irrigação. Departamento Nacional de Meteorologia. Normas climatológicas: 1961-1990. EMBRAPA-SPI, Brasília, p. 84.
Breves, G., Schroder, B., 1991. Comparative aspects of gastrointestinal phosphorus metabolism. Nutrition Research Reviews 4, 125–140.
Butler, W.R., Smith, R.D., 1989. Interrelationships between energy balance and postpartum reproductive function in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 72:767–783.
Cardoso, E.C., Oliveira, D.R., Balaro, M.F.A., Rodrigues, L.F.S.. Brandão, F.Z. 2011. Índices produtivos e perfil metabólico de ovelhas Santa Inês no pós-parto no nordeste do Pará. Revista Brasileira de Ciência Veterinária, 18, 114–120.
Casali, A.O., Detmann, E., Valadares Filho, S.C., Cunha, J.C.M., Detmann, K.S.C.D., Paulino, M.F., 2009. Estimação de teores de componentes fibrosos em alimentos para ruminantes em sacos de diferentes tecidos. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 38, 130–138.
Christenson, R.H., 1997. Biochemical markers of bone metabolism: an overview. Clinical Biochemistry, 30, 573–593.
Church, D. C. 1984. Alimentos y alimentacion del ganado. 7th ed. Hemisferio Sur, Montevideo
Datta, N.S., 2011. Osteoporotic fracture and parathyroid hormone. World Journal of Orthopdics, 18, 67–74.
Detmann, E., Valadares Filho, S.C., Paulino, M.F., 2001. Cromo e indicadores internos na determinação do consumo de novilhos mestiços, suplementados, a pasto. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 30, 1600–1609.
Doney, J.M., Peart, J.N., Smith, W.F., Louda, F., 1979. A consideration of the techniques for estimation of milk yield by suckled sheep and a comparison of estimates obtained by two methods in relation to the effect of breed, level of production and stage of lactation. Journal of Agricultural Science, 92:123–132.
González F.H.D., Barcellos J.O., Ospina H., Ribeiro L.A.O. (Eds.). Perfil metabólico em ruminantes: seu uso em nutrição e doenças nutricionais. Porto Alegre: Gráfica da Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul. 2000.
Greenwood, P.L., Hunt, A.S., Hermanson, J.W. 2000. Effects of birth weight and post natal nutrition on neonatal sheep. II. Skeletal muscle growth and development. Journal of Animal Science, 78, 50–61.
Hall, J.E., Guyton, C.A., 2011. Paratormônio, calcitonina, metabolismo de cálcio e fosfato, vitamina D, ossos e dentes. Tratado de Fisiologia Médica, p.1005–1018.
Herrick, J.B., 1993. Minerals in animal health. In: ASHMEAD, H.D. (Eds.) The roles of amino acid chelates in animal nutrition. New Jersey: Noyes Publication, p.3–20.
Horst, R.L., Goff, J.P., Reinhardt, A., 2005. Adapting to the transition between gestation and lactation: Differences between rat, human and dairy cow. Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia, 10, 141–156.
Kaneko, J.J., Harvey, J.W., Bruss, M.L., 2008. Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals. 6th ed. Academic Press, San Diego. 928p.
Karelakis, C., Abas, Z., Galanopoulos, K., 2013. Positive effects of the Greek economic crisis on livestock farmer behaviour. Agronomy for Sustainable Development. 33, 445–456.
Liesegang, A., Eicher, R., Sassi, M.L., Risteli, J., Kraenzlin, M., Riond, J.L., Wanner, M., 2000. Biochemical markers of bone formation and resorption around parturition and during lactation in dairy cows with high and low standard milk yields. Journal of Dairy Science, 83, 1773–1781.
McNamara, S., Murphy, J.J., Rath, M., O’Mara, F.P., 2003. Effects of different transition diets on energy balance, blood metabolites and reproductive performance in dairy cows. Livestock Production Science. 84, 195–206.
Menezes, L.F.O., Louvandini, H., Martha Júnior, G.B., Mcmanus, C., Barroso, G.G.J.E., Mendes, M.C.B., 2010. Desempenho de ovinos Santa Inês suplementados em três gramíneas pastejadas durante o período seco. Archivos de Zootecnia, 59, 299–302.
Mertens, D.R., 1994. Regulation of forage intake. In: G.C. Fahey Jr. (ed.) Forage quality, evaluation, and utilization. American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 450–493.
NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL – NRC. Nurient requirements of dairy cattle. Washington, DC: Agriculture Research Council, National Academy Press, 2001.
Nicodemo, M.L.F., Moraes, S.S., Thiago, L.R.L.S., CAxias, E.L., Macedo, M.C.M., Pires, P.P., Madruga, C.R., VAZ, E.C., Barrocas, G.E., 2005. Metabolismo de Vacas Jovens Nelore em Pastos de Brachiaria brizantha suplementadas ou não Durante a Seca com Fósforo/Cálcio e Concentrado. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 34, 316–326.
NRC, 2007. Nutrient Requirements of small Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, Cervids and New Words Camelids. National Academy Press. Washington, DC, 384p.
Payne, J.M., Dew, S.M., Manston, R., Faulks, M., 1970. The use of the metabolic profiles test in dairy herds. Veterinary Record, 87, 150–158,
Pulina, G., Nudda, A., Battacone, G., Dimauro, C., Mazzette, A., Bomboi, G., Floris, B., 2012. Effects of short-term feed restriction on milk yield and composition, and hormone and metabolite profiles in mid-lactation Sarda dairy sheep with different body condition score. Italian Journal of Animal Science,11:150–158.
Radostits, O.M., GAY, C.C., Blood D.C., Hinchcliff, K.W., 2002. Clínica Veterinária: um tratado de doenças dos bovinos, ovinos, suínos, caprinos e equinos. 9.ed. Guanabara Koogan, Rio de Janeiro. 1737p,
Ramin, A.G., Asri, S., Majdani, R., 2005. Correlations among serum glucose, betahidroxibutirate and urea concentrations in non-pregnant ewes. Small Ruminant Research 57, 265–269.
Rhoads, M.L., Kim, J.W., Collier, R.J., Crooker, B.A., Boisclair, Y.R., Baumgard, L.H., Rhoads, R.P., 2010. Effects of heat stress and nutrition on lactating holstein cows: II. Aspects of hepatic growth hormone responsiveness. Journal of Dairy Science 93, 170–179.
Ribeiro, L.A.O., Mattos, R.C., Gonzalez, F.H.D., Wald, V.B., Silva, M.A., Rosa, V.L., 2004. Perfil metabólico de ovelhas Border Leicester x Texel durante a gestação e a lactação. Revista Portuguesa de Ciências Veterinárias, 99, 155–159.
Ribeiro, L.F., Pérez, J.R.O., Carvalho, P.E.A., Silva, F.F., Muniz, J.A., Oliveira Júnior, G.M., Souza, N.V., 2007. Produção, composição e rendimento em queijo do leite de ovelhas Santa Inês tratadas com ocitocina. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 36:438–444.
Rocha, R.R., Santos, P.B., Nunes, A.G., Silva, T.P.D., Pereira, A.M., Torreão, J.N.C., (2014). Adaptive parameters and thermal comfort of postpartum ewes fed on concentrate supplementation in grazing system. Acta Scientiarum Animal Science 36, 317–321.
Rodrigues, C.A.F., Rodrigues, M.T., Branco, R.H., Carvalho, G.R., Torres, R.A., Torres Filho, R.A., 2007. Avaliação do consumo e de metabólitos plasmáticos de cabras gestantes com duas condições corporais alimentadas com dietas formuladas com diferentes níveis de energia. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 36, 945–952.
Rojas-Downing, M.M., Nejadhashemi, A.P., Harrigan, T., Woznicki, S.A., 2017. Climate change and livestock: Impacts, adaptation, and mitigation, Climate Risk Management, 16, 145–163.
Saliba, E.O.S., Ferreira, W.M., Pereira, R.A.N., 2003. Lignin from Eucalyptus grandis as indicator for rabbits in digestibility trials. Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, 3, 107–109.
Scarpino, F.B.O., Ezequiel, J.M.B., Silva, D.A.V., Van Cleef, E.H.C.B., 2014. Óleo de soja e óleo de soja residual em dietas para ovinos confinados: parâmetros sanguíneos. Archives of Zootecnia 63, 207–210.
Silva, T.P.D., Marques, C.A.T., Torreão, J.N.C., Araújo, M.J., Bezerra, L.R., 2015. Intake, digestibility, milk yield and indicators of the metabolic status of native ewes fed supplemented diet under grazing system. Italian Journal of Animal Science 14, 3738. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2015.3738.
Tamim, N.M., Angel, R. 2003. Phytate phosphorus hydrolysis as influenced by dietary calcium and micro-mineral source in broiler diets. Journal of Agricultural and food Chemistry, Easton, 51, 4687–4693.
Torreão, J.N.C., Marques, C.A.T., Bezerra, L.R., Araujo, M.J., Gottardi, F.P., Rocha, A.M., Oliveira, R.L., Souza Junior, E.L., 2014. Concentrate supplementation during pregnancy and lactation of ewes affects the growth rate of lambs from a variety of crosses. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia. 43, 544–550.
Van Mosel, M., Corlett, S.C., 1990. Assessment of bone turnover in the dry period of dairy cows by measurement of plasma bone GLA protein, total plasma alkaline phosphatase activity and urinary hydroxyproline. Experimental Physiology, 75, 827–837.
Van Saun R.J., Sniffen C.J., 2014. Transition cow nutrition and feeding management for disease prevention. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Food Animal Practice. 30, 689–719.
Van Soest, P.J, Robertson, J.B., Lewis, B.A., 1991. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polyssacharides in relation to animal nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science. 74, 3583–3597.
Van Soest, P.J., 1994. Nutritional ecology of the ruminant. Cornell University Press, Ithaca.
Walker, D.M.; Al-Ali, S.J, The endogenous phosphorus excretion of preruminant lambs. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 38, 1061–1069, 1987.
Wilson, S.J., McEwan, J.C., Sheard, P.W. et al. Early stages of myogenesis in a large mammal: formation of successive generations of myotubes in sheep tibialis cranialis muscle. Journal Muscle Research, v.13, n.5, p.535–550, 1992.
Wise, T., Roberts, A.J., Christenson, R.K., 1997. Relationships of light and heavy fetuses to uterine position, placental weight, gestational age, and fetal cholesterol concentrations. Journal of Animal Science, 75, 2197–2207.
Wu, Z., Satter, L.D., Blohowaiak, A.J., Stauffacher, R.H., Wilson, J.H., 2001. Milk production, estimated phosphorus excretion, and bone characteristics of dairy cows fed different amounts of phosphorus for two or three years. Journal of Dairy Science, 84, 1738–1748.
Young, M.F., 2003. Bone matrix proteins: their function, regulation and relationship to osteoporosis. Osteoporosis International, 14, 35–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Sousa, S.V., de Araújo, M.J., e Silva, T.P.D. et al. Dietary supplementation for Santa Inês hair ewes on pasture at pre- and postpartum periods: dry matter intake, digestibility, milk production, and mineral metabolism. Trop Anim Health Prod 50, 1903–1912 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-018-1643-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-018-1643-2