Abstract
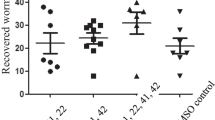
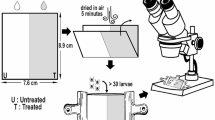
Nematode resistance to anthelmintic drugs affects small ruminant production globally. This study evaluated in vivo effects of five plant extracts as alternative nematode treatments. Animals were divided into six groups. Each group was randomly assigned a treatment: Abamectin and Praziquantel (CAP) (positive Control), ethanol extracts of Ananas comosus (AC), Aloe ferox (AF), Allium sativum (AS), Lespedeza cuneata (LC) and Warburgia salutaris (WS). These were applied as an oral dose (100 mg kg−1 BW), one dose per week per sheep for 42 days (Phase 1). From day 42 sheep were orally dosed for 3 consecutive days with the same treatments in the same groups (Phase 2). Rectal faecal samples were taken every 7 days up to day 63. Eggs per gram of faeces were counted in individual rectal samples, L3 larval stage was counted in faecal cultures, with four replicates per group. For plant extracts, EPG decreased (P < 0.001) with time and efficacy of plant increased (P < 0.001) with time. Ananas comosus and L. cuneata treatments had the highest efficacies of 58 % and 61 %, respectively, in Phase 1; and 77 % and 81 %, respectively, in Phase 2. Continuous treatment with these plants could further reduce nematode parasites and improve host health.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ademola, I.O., Fagbemi, B.O. and Idowu, S.O., 2004. Evaluation of the anthelmintic activity of Khaya senegalensis extract against gastrointestinal nematodes of sheep: in vitro and in vivo studies. Veterinary Parasitology, 122, 151–164
Ahmed, M., 2010. Gastrointestinal (nematode) Infections in small ruminants: epidemiology, anthelmintic efficacy and the effect of wattle tannins. MSc thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa
Akhtar, M., 1999. Biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes in pigeonpea field crops using neem-based products and manurial treatments. Applied Soil Ecology, 12, 191–195
Akhtar, M. and Malik, A. 2000. Roles of organic soil amendments and soil organisms in the biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes: a review. Bioresource Technology, 74, 35–47
Ameh, S.J., Obodozie, O.O., Abubakar, M.S. and Garba, M., 2010. Current phytotherapy–an inter-regional perspective on policy, research and development of herbal medicine. Medicinal Plants Research, 4, 1508–1516
Amin, M.R., Mostofa, M., Awal, M.A. and Sultana, M.A., 2008. Effects of garlic, turmeric and betel leaf against gastrointestinal nematodes in cattle. Bangladesh Veterinary Medicine, 6, 115–119
Aremu, A.O., 2009. Pharmacology and phytochemistry of South African plants used as anthelmintics. MSc thesis, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa
Baloyi, M.A., Laing, M.D. and Yobo, K.S., 2012. Use of mixed cultures of biocontrol agents to control sheep nematodes. Veterinary Parasitology, 184, 367–370
Buttle, D.J., Behnke, J.M., Bartley, Y., Elsheikha, H.M., Bartley, D.J., Garnett, M.C., Donnan, A.A., Jackson, F., Lowe, A. and Duce, I.R., 2011. Oral dosing with papaya latex is an effective anthelmintic treatment for sheep infected with Haemonchus contortus. Parasites and Vectors, 4, 36 available on line: http://www.parasitesandvectors.com/content/4/1/36 accessed date: 01/04/2011
Cringoli, G., Veneziano, V., Rinaldi, L., Sauve, C., Rubino, R., Fedele, V. and Cabaret, J., 2007. Resistance of trichostrongyles to benzimidazoles in Italy: a first report in a goat farm with multiple and repeated introductions. Parasitology Research, 101, 577–581
Eguale, T., Tilahun, G., Debella, A., Feleke, A. and Makonnen, E., 2007. In vitro and in vivo anthelmintic activity of crude extracts of Coriandrum sativum against Haemonchus contortus. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 110, 428–433
Ferri, N., Yokoyama, K., Sadilek, M., Paoletti, R., Apitz-Castro, R., Gelb, M.H. and Corsini, A., 2003. Ajoene, a garlic compound, inhibits protein prenylation and arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation. Journal of Pharmacology, 138, 811–818.
Geary, T.G., Sangster, N.C. and Thompson, D.P., 1999. Frontiers in anthelmintic pharmacology. Veterinary Parasitology, 84, 275–295
Gillian, S., Behnke, J.M., Buttle, D.J. and Duce, L.R., 2004. Natural plant cysteine proteinases as anthelmintics. Trends in Parasitology, 20, 322–327
Hansen, J. and Perry, B. 1994. The epidemiology, diagnosis and control of helminth parasites of ruminants (Handbook). International Laboratory for Research on Animal Diseases Press, Nairobi, Kenya. Electronic version available in www.fao.org/wairdocs/ILRI/x5492E/x5492E00.HTM accessed on 11/4/2008
Hördegen, P., Cabaret, J., Hertzberh, H., Langhans, W. and Maurer, V., 2006. In vitro screening of six anthelmintic plant products against larval Haemonchus contortus with a modified methyl-thiazolyl-tetrazolium reduction assay. Ethnopharmacology, 108, 85–89
Iqbal, Z., Nadeem, Q.K., Khan, M.N., Akhtar, M.S. and Waraich, F.N., 2001. In vitro anthelmintic activity of Allium sativum, Zingiber officinale, Curcurbita mexicana and Ficus religiosa. International Agriculture and Biology, 3, 454–457
Leathwick, D.M., Pomroy, W.E. and Heath, A.C., 2001. Anthelmintic resistance in New Zealand. New Zealand Veterinary Journal, 49, 227–235.
Mabusela, W.T., Stephen, A.M. and Botha, M.C., 1990. Carbohydrate polymers from Aloe ferox leaves. Phytochemistry, 29, 3555–3558
Maphosa, V., Masika, P.J., Bizimenyera, E.S. and Eloff, J.N., 2010. In vitro anthelmintic activity of crude aqueous extracts of Aloe ferox, Leonotis leonurus and Elephantorrhiza elephantina against Haemonchus contortus. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 42, 301–307
McCorkle, M., Mathias, E. and Schillhorn van Veen, T.W., 1996. Ethnoveterinary research and development, studies in indigenous knowledge and development. Intermediate Technology Publications, Southampton Row, London, 1–23
McGaw, L.J. and Eloff, J.N., 2008. Ethnoveterinary use of Southern African plants and scientific evaluation of their medicinal properties. Ethnopharmacology, 119, 686–699
Min, B.R., Barry, T.N., Attwood, G.T. and McNabb, W.C., 2003. The effect of condensed tannins on the nutrition and health of ruminants fed fresh temperate forages: a review. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 106, 3–19
Min, B.R., Pomroy, W.E., Hart, S.P. and Sahlu, T., 2004. The effect of short-term consumption of a forage containing condensed tannins on gastrointestinal nematode parasite infections in grazing goats. Small Ruminant Research, 51, 279–283
Minho, A.P., Bueno, I.C., Louvandini, H., Jackson, F., Gennari, S.M. and Abdalla, A.L., 2008. Effect of Acacia molissima tannin extract on the control of gastrointestinal parasites in sheep. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 147, 172–181
Mohanlall, V. and Odhav, B., 2009. Furans and furanones with antimycotoxigenic activity isolated from Warburgia salutaris (Canellaceae). Medicinal Plants Research, 3, 231–240
Molan, A.L., Waghorn, G.C., Min, B.R. and McNabb, W.C., 2000. The effect of condensed tannins from seven herbages on Trichostrongylus colubriformis larval migration in vitro. Folia Parasitological, 47, 39–44
Olayiwola, A., 1993. Nature’s medicinal bounty, don’t throw it away. World Health Forum, 14, 391–395
Overend, D.J., Phillips, M.L., Poultion, A.L. and Foster, C., 1994. Anthelmintic resistance in Australian sheep nematode populations. Australian Veterinary Journal, 71, 117–121
SAS., 2000. Statistical analysis system user’s guide (Version 8). SAS Institute Inc., SAS Campus Drive, Cary, N.C., USA
Schnyder, M., Torgerson, P.R., Schönmann, M., Kohler, L. and Hertzberg, H., 2005. Multiple anthelmintic resistance in Haemonchus contortus isolated from South African Boer goats in Switzerland. Veterinary Parasitology, 128, 285–290
Singh, T.U., Kumar, D., Tandan, S.K. and Mishra, S.K., 2009. Inhibitory effect of essential oils of Allium sativum and Piper longum on spontaneous muscular activity of liver fluke, Fasciola gigantica. Experimental Parasitology, 123, 302–308
Southcott, W.H., Major, G.W. and Barger, I.A., 1976. Seasonal pasture contamination and availability of nematodes for grazing sheep. Agriculture Research, 27, 277–286
Stepek, G., Lowe, A.E., Buttle, D.J., Duce, I.R. and Behnke, J.M., 2006. In vitro and in vivo anthelmintic efficacy of plant cysteine proteinases against the rodent gastrointestinal nematode, Thirchuris muris. Parasitology, 132, 681–689
Sujon, M.A., Mostofa, M., Jahan, M.S., Das, A.R. and Rob, S., 2008. Studies on medicinal plants against gastrointestinal nematodes of goats. Bangladesh Veterinary Medicine, 6, 179–183
Tembely, S., Lahlou-Kassi, A., Rege, J.E., Sovani, S., Diedhiou, M.L. and Bake, R.L., 1997. The epidemiology of nematode infections in sheep in a cool tropical environment. Veterinary Parasitology, 70, 129–141
Van Wyk, J.A., Cabaret, J. and Michael, L.M., 2004. Morphological identification of nematode larvae of small ruminants and cattle simplified. Veterinary Parasitology, 119, 277–306
Waller, P.J., Knox, M.R. and Faedo, M., 2001. The potential of nematophagous fungi to control the free-living stages of nematode parasites of sheep: Feeding and block studies with Duddingtonia flagrans. Veterinary Parasitology, 102, 321–330
Acknowledgements
The research fund was provided by the National Research Foundation, South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, M., Laing, M.D. & Nsahlai, I.V. In vivo effect of selected medicinal plants against gastrointestinal nematodes of sheep. Trop Anim Health Prod 46, 411–417 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-013-0506-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-013-0506-0