Abstract
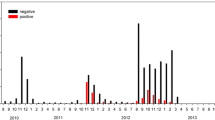
We surveyed a wild population of white-lipped peccaries (Tayassu pecari) in the Brazilian Pantanal for evidence of Leptospira interrogans. Serum samples from 71 free-ranging T. pecari were obtained between 2003 and 2005 in the southern Pantanal of Mato Grosso do Sul state. We used microscopic microagglutination to test for antibodies against 14 L. interrogans serovars (antibody titers ≥1:100 were considered seropositive). Seventy percent of captured animals tested positive for leptospirosis antibodies. Antibodies against icterohaemorrhagiae and autumnalis serovars were the most prevalent. We used log-linear analyses to test for associations among seropositivity, age class, and sex of captured animals. Seropositivity was strongly associated with animal age class, but independent of sex. Forty-six percent of animals less than 2 years old, 63% of adults during peak reproductive years, and 100% of the oldest age class were seropositive. A nonparametric multivariate procedure (MRPP) showed that the composition of serovar antibody types changed with age, and ANOVA models demonstrated that antibody titers increased with age, suggesting long-term exposure to a greater number and variety (i.e., serovar types) of L. interrogans infections. This study presents the first quantitative survey of antibodies against L. interrogans serovars in a T. pecari population of the Pantanal. The high prevalence of leptospirosis antibodies in free-ranging white-lipped peccaries and the potential impacts on reproduction and population dynamics emphasize the need for further studies investigating the roles of Pantanal wildlife and livestock in the transmission and maintenance of L. interrogans in the environment.
Resumo
Analisamos uma população silvestre de queixadas (Tayassu pecari) no Pantanal Brasileiro para a evidência de Leptospira interrogans. Amostras de soros de 71 queixadas de vida livre foram obtidas de animais capturados entre dezembro de 2003 e abril de 2005 no sul do Pantanal do Estado de Mato Grosso do Sul. Usamos o teste de microaglutinação microscópica para anticorpos contra 14 sorovares de L. interrogans (anticorpos ≥ 1:100 foram considerados como positivas). Setenta por cento dos animais capturados testados foram positivos para a presença de anticorpos de Leptospira. Anticorpos contra icterohaemorrhagiae e autumnalis foram os mais prevalentes. Utilizamos análises log-linear para testar as associações entre soropositividade, classe etária, e sexo. Soropositividade estava fortemente associada com a classe etária dos animais, mas independentes do sexo. Quarenta e seis por cento dos animais com menos de dois anos, 63% dos adultos, durante o pico da idade reprodutiva, e 100% na classe dos mais velhos foram soropositivos. Um procedimento multivariado não-paramétrico (MRPP) indicou que a composição de tipos de anticorpos contra um sorotipo variou com a idade, e os modelos ANOVA demonstraram que os títulos de anticorpos aumentaram com a idade, sugerindo que uma exposição de longo prazo aumentaria o número e a variedade (i.e. tipos de sorovar) de infecções por L. interrogans. Este estudo apresenta a primeira análise quantitativa de anticorpos contra L. interrogans sorovars na população de T. pecari do Pantanal. A alta prevalência de anticorpos de Leptospira em queixadas de vida silvestre e o potencial impacto sobre a reprodução e dinâmica populacional enfatiza a necessidade de mais estudos investigando o papel de outros animais silvestres do Pantanal e de animais de criação na transmissão e manutenção de L. Interrogans neste ambiente.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acoltzi, A., de la Peña-Moctezuma, A. and Valladares, J.C., 1990. Estudio serólogico de Leptospirosis en una colonia de pécaris de collar (Tayassu tajacu) albergada en el Zoológico de Chapultepec de la ciudad de México. Unpublished Medical Veterinarian thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México
Aguirre, A.A., Ostfeld, R.S., Tabor, G.M., House, C. and Pearl, M.C., 2002. Conservation Medicine: ecological health in practice, (Oxford University Press, New York)
Altrichter, M., Saenz, J.C. and Carillo, E., 1999. Chanchos cariblancos (Tayassu pecari) como depredadorees y dispersores de semillas en el Parque Nacional Corcovado, Costa Rica, Brenesia, 52, 53–59
Bharti, A.R., Nally, J.E., Ricaldi, J.N., Mathias, M.A., Diaz, M.M., Lovett, M.A., Levett, P.N., Gilman, R.H., Willig, M.R., Gotuzzo, E. and Vinetz, J.M., 2003. Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance, Lancet Infectious Diseases, 3, 757–771
Bodmer, R.E., Puertas, P., Aquino, R., Reyes, C., Fang, T. and Gottdenker, N., 1997. Manejo y uso sustentable de peccaries en la Amazonia Peruana. Occasional Paper of the IUCN Species Survival Commission No. 18, (UICN-Sur Quito, Ecuador y Secretaria CITES, Ginebra, Suiza)
Bolin, C.A., 1992. Leptospira interrogans Serovar hardjo Infection of Cattle, Proceedings American Association Bovine Practitioners, 24, 12–14
Boqvist, S., Thu, H.T., Vågsholm, I. and Magnusson, U., 2002. The impact of Leptospira seropositivity on reproductive performance in sows in southern Vietnam, Theriogenology, 58, 1327–1335
Carrol, A.G. and Campbell, R.S., 1987. Reproductive and leptospiral studies on beef cattle in central Queensland, Australian Veterinary Journal, 64, 1–5
Cole, J.R., Sulzer, C.R. and Pursell, A.R., 1973. Improved microtechnique for the leptospiral microscopic agglutination test, Applied Microbiology, 25, 976–980
Corn, J.L., Lee, R.M., Erickson, G.A. and Murphy, C., 1987. Serologic survey for evidence of exposure to vesicular stomatitis virus, pseudorabies virus, brucellosis and leptospirosis in collared peccaries from Arizona, Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 23, 551–557
Daszak, P., Epstein, J.H., Kilpatrick, A.M., Aguirre, A.A., Karesh, W. and Cunningham, A.A., 2007. Collaborative research approaches to the role of wildlife in zoonotic disease emergence. In: J.E. Childs, J.S. Mackenzie, J.A. Richt (eds), Current topics in microbiology and immunology, vol 315: wildlife and emerging zoonotic diseases: the biology, circumstances and consequences of cross-species transmission. Springer, Berlin, pp 463–475
Desmarchelier, P.M., 1987. Human leptospirosis in New South Wales, 1975-1985, The Medical Journal of Australia, 146, 353–357
Girio, R. J. S., Pereira, F.L.G., Marchiori Filho, M., Mathias, L.A., Herreira, R.C.P., Alessi A.C. and Girio, T.M.S. 2004. Pesquisa de anticorpos contra Leptospira spp. em animais silvestres e em estado feral da região de Nhecolândia, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brasil: utilização da técnica de imuno-histoquímica para detecção do agente. Ciência Rural 34:165–169
Gomes, S.L. and Villela, R., 1999. A descoberta do Paraiso. http://veja.abril.com.br/020699/p_086.html. Accessed 22 Sept 2008
Gottgens, J.F., Perry, J.E., Fortney, R.H., Meyer J., Benedict, M. and Wood, B.E., 2001. The Paraguay-Paraná Hidrovia: protecting the Pantanal with lessons from the past, Bioscience, 51, 301–308
Grooms, D.L., 2006. Reproductive losses caused by bovine viral diarrhea virus and leptospirosis, Theriogenology, 66, 624–628
Hathaway, S.C. and Little, T.W.A., 1981. Prevalence and clinical significance of leptospiral antibodies in pigs England, The Veterinary Record, 108, 224–227
Holmes, J.C., 1996. Parasites as threats to biodiversity in shrinking ecosystems, Biodiversity and Conservation, 5, 975–983
Jorge, R.S.P., 2008. Caracterização do estado sanitario dos carnivoros selvagens da RPPN SESC Pantanal e de animais domesticos da regiao. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Sao Paulo, USP, São Paulo
Karesh, W.B., Uhart, M.M., Painter, R.L.E., Wallace, R.B., Braselton, W.E., Thomas, L.A., House, C., Macnamara, T.S. and Gottdenker, N.L., 1998. Health evaluation of white-lipped peccary populations in Bolivia. In: 1998 Proceedings of the Joint Conference of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians and the American Association of Wildlife Veterinarians, (Proceedings of the Joint Conference of the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians and the American Association of Wildlife Veterinarians, Omaha, Nebraska), 445–449
Keuroghlian, A. and Desbiez, A.L.J., 2010. Biometric and age estimation of live peccaries in the Southern Pantanal, Brazil, Suiform Soundings, 9, 24–35. http://data.iucn.org/themes/ssc/sgs/pphsg/Suiform%20soundings/Newsletter.htm
Keuroghlian, A. and Eaton, D.P., 2008a. Fruit availability and peccary frugivory in an isolated Atlantic forest fragment: effects on peccary ranging behavior and habitat use, Biotropica, 40, 62–70
Keuroghlian, A. and Eaton, D.P., 2008b. Importance of rare habitats and riparian zones in a tropical forest fragment - preferential use by Tayassu pecari, a wide-ranging frugivore, Journal of Zoology, 275, 283–293
Keuroghlian, A., Eaton, D.P. and Longland, W.S., 2004. Area use by white-lipped and collared peccaries (Tayassu pecari and Tayassu tajacu) in a tropical forest fragment, Biological Conservation, 120, 411–425
Keuroghlian, A., Eaton, D.P. and Desbiez A.L.J., 2009. Habitat use by Peccaries and Feral Pigs of the Southern Pantanal, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, Suiform Soundings, 8, 9–17, http://data.iucn.org/themes/ssc/sgs/pphsg/Suiform%20soundings/Newsletter%208(2).pdf
Kingscote, B.F., 1986. Leptospirosis in red foxes in Ontario, Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 22, 475–478
Levett, P.N., 2001. Leptospirosis, Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 14, 296–326
Loewenstein, L., McLachlan-Troup, T., Hartley, M. and English, A., 2008. Serological survey for evidence of Leptospira interrogans in free-living platypuses (Ornithorhynchus anatinus), Australian Veterinary Journal, 86, 242–245
Mathias, L.A., Girio, R.J. and Duarte, J.M., 1999. Serosurvey for antibodies against Brucella abortus and Leptospira interrogans in pampas deer from Brazil, Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 35, 112–114
Matthias, M.A. and Levett, P.N., 2002. Leptospiral carriage by mice and mongooses on the island of Barbados, West Indian Medical Journal, 51, 10–13
Mayor, P., Le Pendu, Y., Guimaraes, D.A., da Silva, J.V., Tavares, L., Tello, M., Pereira, W., Lopez-Bejar, M. and Jori, F., 2006. A health evaluation in a colony of captive collared peccaries (Tayassu tajacu) in the Eastern Amazon, Research in Veterinary Science, 81, 246–253
McCune, B. and Grace, J.B., 2002. Analysis of ecological communities. MjM Software Design, Gleneden Beach, Oregon, USA
McCune, B. and Mefford, M.J. 2006. PC-ORD. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data, Version 5.18. MjM Software Design, Gleneden Beach, OR, USA
Mendoza, P., Mayor, P., Le Pendu, Y., Guimaraes, D.A., Viana da Silva, J., Tavares, H.L., Tello, M., Pereira, W., Lopez-Béjar, M. and Jori, F., 2007. Antibodies against Leptospira spp. in captive collared peccaries, Peru. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 13, 793–794, http://www.cdc.gov/EID/content/13/5/793.htm
Mielke, P.W. and Berry, K.J., 2001. Permutation methods: a distance function approach. Springer, New York
Miranda, F.R., 2008. Pesquisa de anticorpos contra bacterias do genero Brucella spp, Leptospira spp, Chlamydophila spp em tamanduas-bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus, 1758), da RPPN SESC Pantanal, Parque Nacional da Serra da Canastra e Parque Nacional das Emas. Unpublished MS thesis, ESALQ/USP, Piracicaba, São Paulo
Paes, R.C.S., Ribeiro, O.C., Carneiro Monteiro, L.A.R., Figueiredo, A.O., Neto, A.A.C., Oliveira, J.M., Da Rosa, G.O., Keuroghlian, A., Piovezan, U. and Herrera, H.M., 2008. Enfermidades de ocorrência no Porco Monteiro (Sus scrofa) no Pantanal Sul-Matogrossense, Brasil. In: 35°Congresso Brasileiro de Veterinária–CONBRAVET, 2008 (Anais do 35°CONBRAVET, 2008, Gramado, RS). http://www.sovergs.com.br/conbravet2008/anais/cd/resumos/R0865-1.pdf
Painter, L.R.E. 1998. Gardeners of the forest: plant-animal interactions in a Neotropical forest ungulate community. Unpublished PhD Dissertation, University of Liverpool, Liverpool
Pellegrin, A.O., Guimaraes, P.H.S., Sereno, J.R.B., Figueiredo, J.P., Lage, A.P., Moreira, E.C. and Leite, R.C., 1999. Prevalência da leptospirose em bovinos do Pantanal Mato-Grossense, Comunicado Técnico Embrapa Pantanal, 22, 1–9
Prescott, J.F. and Zuerner, R.L., 1993. Leptospira. In: C.L. Gyles and C.O. Thoen (eds), Pathogenesis of bacterial infections in animals, 2nd Edition, (Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa) 287–296
Santos, S.A., Pellegrin, A.O., Moraes, A.S., Barros, A.T.M., Comastri Filho, J.A., Serreno, J.R.B., Silva, R.A.M.S. and Abreu, U.G.P., 2002. Sistema de produção de gado de corte do Pantanal, (Embrapa, Corumbá, Sistema de Produção)
Silman, M.R., Terborgh, J.R. and Kiltie, R.A. 2003. Population regulation of a dominant rain forest tree by a major seed predator, Ecology, 84, 431–438
Sokal, R.R. and Rohlf, F.J., 1994. Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 3rd Edition, (W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, NY)
Sowls, L.K., 1997. Javelinas and other Peccaries, 2nd Edition, (Texas A&M University Press, Texas)
Tomich, R.G.P., Bomfim, M.R.Q., Koury, M., Pellegrin, A.O., Pellegrin, L.A., Ko, A.I. and Barbosa-Stanciol, E.F., 2007. Leptospirosis serosurvey in bovines from Brazilian Pantanal using IGG ELISA with recombinant protein LipL32 and microscopic agglutination test, Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 38, 674–680
Wilkinson, L., 1990. SYSTAT: The system for statistics, (SYSTAT, Inc., Evanston, IL)
Willink, P.W., Chernoff, B., Alonso, L.E., Montambault, J.R. and Lourival, R. (eds), 2001. A Biological Assessment of the Aquatic Ecosystems of the Pantanal, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brasil, RAP Bulletin of Biological Assessment, 18 (Center for Applied Biodiversity Science CABS, Conservation International, The Field Museum, Museu de Zoologia, Universidade de São Paulo, EMBRAPA, Universidade Federal de Mato Grosso do Sul)
Zar, J. H., 1996. Biostatistical analysis, 3rd Edition, (Prentice-Hall, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ)
Acknowledgements
This project was primarily funded by Earthwatch, IBC (Institute for Biological Conservation), CI-Brasil, Rio Tinto, HSBC, and Merrill Magowan also provided financial aid. The authors thank IAGRO–Campo Grande, Mato Grosso do Sul for their support. Special thanks to Ezidio Araujo (Baiano), Celso Vicente, Maria do Carmo Andrade, Earthwatch volunteers, and York High School from Maine, for all their field assistance and support. We would also like to thank Fazenda Rio Negro staff. We thank two anonymous reviewers and Leslie Harrison for making significant improvements to earlier drafts of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Freitas, T.P.T., Keuroghlian, A., Eaton, D.P. et al. Prevalence of Leptospira interrogans antibodies in free-ranging Tayassu pecari of the Southern Pantanal, Brazil, an ecosystem where wildlife and cattle interact. Trop Anim Health Prod 42, 1695–1703 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9622-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-010-9622-2