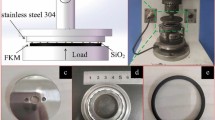
Abstract
Due to thermal degradation, the tribological performance of fluororubber (FKM) at high temperature is not satisfactory, despite its excellent temperature resistance. In this paper, the friction and wear process of FKM O-rings were traced by the tribo-test, which compares the wear behaviors at different stages of the wear process. Results showed that under the influence of thermal degradation of FKM, the wear rate and friction coefficient decrease, while the friction instability increases. This phenomenon is caused by the deterioration of the mechanical properties affects the development of the typical wear pattern of FKM in unsteady state (running-in stage). The wear debris is more likely to adhere to the surface of the wear scar, which causes the friction form to change from two-body abrasion to three-body abrasion. Findings from this study can enhance understanding of tribology behaviors of FKM O-ring seals under the high temperature condition and can help develop higher-performance alternatives.
Graphic Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Sui, P.C., Anderle, S.: Optimization of contact pressure profile for performance improvement of a rotary elastomeric seal operating in abrasive drilling environment. Wear 271, 2466–2470 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2011.02.021
Orazzini, S., Kasirin, R., Ferrari, G., Bertini, A., Bizzocchi, I., Ford, R., Li, Q., Zhang, M.: New HT/HP technology for geothermal application significantly increases on-bottom drilling hours. SPE/IADC Drill. Conf. Proc. 1, 70–89 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2118/150030-ms
Qin, K., Zhou, Q., Zhang, K., Feng, Y., Zhang, T., Zheng, G.: Tribology international non-uniform abrasive particle size e ff ects on friction characteristics of FKM O-ring seals under three-body abrasion. Tribiol. Int. 136, 216–223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2019.03.051
Dong, C.L., Yuan, C.Q., Bai, X.Q., Yan, X.P., Peng, Z.: Tribological properties of aged nitrile butadiene rubber under dry sliding conditions $. Wear 322–323, 226–237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2014.11.010
Wang, Q., Pei, J., Li, G., He, X., Niu, Y., Li, G.: Accelerated aging behaviors and mechanism of fluoroelastomer in lubricating oil medium. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 38, 853–866 (2020)
Sugama, T.: Surface analyses of fluoroelastomer bearings exposed to geothermal environments. Mater. Lett. 50, 66–72 (2001)
Akhlaghi, S., Pourrahimi, A.M., Sjöstedt, C., Bellander, M., Hedenqvist, M.S., Gedde, U.W.: Degradation of fluoroelastomers in rapeseed biodiesel at different oxygen concentrations. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 136, 10–19 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.12.006
Balasooriya, W., Schrittesser, B., Pinter, G., Schwarz, T.: Induced material degradation of elastomers in harsh environments. Polym. Test. 69, 107–115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.05.016
Wang, Y., Bai, Y.: The functionalization of fluoroelastomers: approaches, properties, and applications. RSC Adv 6, 53730–53748 (2016)
Persson, B.: Role of frictional heating in rubber friction. Tribol. Lett. 56, 77–92 (2014)
Hakami, F., Pramanik, A., Basak, A.K., Ridgway, N.: Elastomers’ wear: comparison of theory with experiment. Tribol. Int. 135, 46–54 (2019)
Harsha, A.P., Tewari, U.S., Venkatraman, B.: Three-body abrasive wear behaviour of polyaryletherketone composites. Wear 254, 680–692 (2003)
Budinski, K.G.: Resistance to particle abrasion of selected plastics. Wear 203, 302–309 (1997)
Yoshihide, F., Hirotaka, Y.: Mechanism of rubber abrasion part 3: how is friction linked to fracture in rubber abrasion? Wear 188, 19–26 (1995)
Lancaster, J.K.: Relationships between the wear of polymers and their mechanical properties. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Conference Proceedings. SAGE Publications Sage, London, 98–106 1968
Hu, X.Y., Shuai, C.H., Yang, X.: Effects of polytetrafluoroethylene micro powder on friction and wear properties of fluororubber. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 35, 69–73 (2019)
Liang, H., Fukahori, Y., Thomas, A.G., Busfield, J.J.C.: The steady state abrasion of rubber: why are the weakest rubber compounds so good in abrasion? Wear 268, 756–762 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.11.015
Schapery, R.A.: A model for the prediction of rubber friction with Schallamach waves. Tribol. Int. 143, 106018 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2019.106018
Denardin, E.L.G., Janissek, P.R., Samios, D.: Time-temperature dependence of the thermo-oxidative aging of polychloroprene rubber—the time-temperature-transformation (TTT) superposition method and the lifetime prediction. Thermochim. Acta. 395, 159–167 (2003)
Zhang, S.W.: Studies on rubber wear. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 212, 227–234 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1243/1350650981542047
Zhang, S.W.: Investigation of abrasion of nitrile rubber, (1984)
Schallamach, A.: How does rubber slide? Wear 17, 301–312 (1971)
Fukahori, Y., Gabriel, P., Busfield, J.J.C.: How does rubber truly slide between Schallamach waves and stick-slip motion? Wear 269, 854–866 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.08.016
Molnar, W., Nevosad, A., Rojacz, H., Adam, K., Henze, H.J., Ripoll, M.R., Badisch, E.: Two and three-body abrasion resistance of rubbers at elevated temperatures. Wear 414–415, 174–181 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2018.08.015
Ageing, A.H., Results, T.: Ageing of rubber. Technology. 44, (1939)
Miyahara, K., Bae, D.S., Kimura, T., et al.: Phase instability and toughness change during high temperature exposure of various steels for the first wall structural materials of a fusion reactor[J]. J. Nucl. Mater. 226(1–2), 92–103 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3115(95)00118-2
Riffard, F., Buscail, H., Caudron, E., Cueff, R., Issartel, C., Perrier, S.: Yttrium implantation effect on 304L stainless steel high temperature oxidation at 1000 °C. J. Mater. Sci. 37, 3925–3933 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019667825476
Guo, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, D., Zhang, S.: Fretting wear behavior of rubber against concrete for submarine pipeline laying clamping. Wear 432, 102925 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.05.040
Lainé, E., Grandidier, J.C., Benoit, G., Omnès, B., Destaing, F.: Effects of sorption and desorption of CO2 on the thermomechanical experimental behavior of HNBR and FKM O-rings—influence of nanofiller- reinforced rubber. Polym. Test. 75, 298–311 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.02.010
Sugama, T., Pyatina, T., Redline, E., Mcelhanon, J., Blankenship, D.: Degradation of different elastomeric polymers in simulated geothermal environments at 300 °C. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 120, 328–339 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2015.07.010
Lv, X.R., Wang, H.M., Wang, S.J.: Effect of swelling nitrile rubber in cyclohexane on its ageing, friction and wear characteristics. Wear 329, 414–421 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.03.016
Kader, M.A., Bhowmick, A.K.: Thermal ageing, degradation and swelling of acrylate rubber, fluororubber and their blends containing polyfunctional acrylates. Polym. degrad. Stab. 79, 283–295 (2003)
Roche, N., Heuillet, P., Janin, C., Jacquot, P.: Surface & coatings technology mechanical and tribological behavior of HNBR modified by ion implantation, influence of aging. Surf. Coat. Technol. 209, 58–63 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.08.029
Xia, L., Wang, M., Wu, H., Guo, S.: Effects of cure system and filler on chemical aging behavior of fluoroelastomer in simulated proton exchange membrane fuel cell environment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 41, 2887–2895 (2016)
Mofidi, M., Kassfeldt, E., Prakash, B.: Tribological behaviour of an elastomer aged in different oils. Tribol. Int. 41, 860–866 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2007.11.013
Krick, B.A., Vail, J.R., Persson, B.N.J., Sawyer, W.G.: Optical in situ micro tribometer for analysis of real contact area for contact mechanics, adhesion, and sliding experiments. Tribol. Lett. 45, 185–194 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9870-y
Chen, G.X., Zhou, Z.R.: A self-excited vibration model based on special elastic vibration modes of friction systems and time delays between the normal and friction forces: a new mechanism for squealing noise. Wear 262, 1123–1139 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.11.014
Sun, D., Li, G., Wei, H., Liao, H.: tribology international experimental study on the chaotic attractor evolvement of the friction vibration in a running-in process. Tribiol. Int. 88, 290–297 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.03.033
Zakeri, M., Azimirad, V., Nia, A.S., Kharrati, H.: Proceedings of the institution of Mechanical Engineers. J. Syst. Control Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/0959651816634479
Zhang, T., Huang, H., Li, W., Chang, X., Cao, J., Hua, L.: Vulcanization modeling and mechanism for improved tribological performance of styrene-butadiene rubber at the atomic scale. Tribol. Lett. 68, 1–11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-01321-w
Mokhtari, M., Schipper, D.J., Tolpekina, T.V.: On the friction of carbon black- and silica-reinforced BR and S-SBR elastomers. Tribol. Lett. 54, 297–308 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0334-z
Zhu, Z., Cheng, Q., Jiang, C., Zhang, J., Jiang, H.: Scratch behavior of the aged hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber. Wear 352–353, 155–159 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.02.010
Roche, N., Heuillet, P., Janin, C., Jacquot, P.: Mechanical and tribological behavior of HNBR modified by ion implantation, influence of aging. Surf. Coatings Technol. 209, 58–63 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.08.029
Jiang, B., Jia, X., Wang, Z., Wang, T., Guo, F., Wang, Y.: Influence of thermal aging in oil on the friction and wear properties of nitrile butadiene rubber. Tribol. Lett. 67, 1–10 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-019-1201-8
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42072340 and No. 41672365), and the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC0603405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Consent for Publication
As corresponding author, I Qin Zhou, hereby confirm on behalf of all authors that: the authors have obtained the necessary authority for publication. The paper has not been published previously, that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere and that if accepted it will not be published elsewhere in the same form, in English or in any other language, without the written consent of the publisher. The paper does not contain material which has been published previously, by the current authors or by others, of which the source is not explicitly cited in the paper. Upon acceptance of an article by the journal, the author(s) will be asked to transfer the copyright of the article to the publisher. This transfer will ensure the widest possible dissemination of information.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, K., Zhou, Q., Zhang, K. et al. Differences in Wear Tongue Development: Thermal Degrade Effect on the Tribological Behavior of FKM O-Ring Seals. Tribol Lett 69, 125 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01489-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01489-9