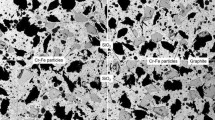
Abstract
Commercial high-speed train friction blocks with a hole in the middle of the surface and perforated blocks filled with additive materials are introduced in drag brake experiments conducted on a customized small-scaled braking dynamometer. These additive materials include Cu-based powder metallurgy material, composite material, and a Mn–Cu damping alloy. The results indicate that the filling materials significantly influence the wear behavior of a braking interface and the characteristics of friction-induced vibration. Under the same experimental conditions, the perforated blocks filled with different materials produce different types of wear debris and exhibit different wear evolutions, markedly changing the wear debris distribution and surface morphology. These changes lead to variations in thermal distribution on the surfaces of both the friction block and brake disc. The study also shows that as a filling material, the Mn–Cu damping alloy can suppress the friction-induced vibration of the brake system, resulting in the lowest level of brake noise among all brake systems. However, the original friction block (i.e., the block without any filling material) can trap wear debris because of its perforated structure. The structure produces less friction-induced vibration and noise, compared with the block filled with powder metallurgy material. The noise performance of the composite material block is superior to the noise performance of the block without any filling material (i.e., the original block) and the block with powder metallurgy material but inferior to that of the block filled with the Mn–Cu damping alloy. Finite element analysis indicates that the properties of the filling materials exert no effect on the unstable vibration intensity of the brake system. Therefore, the wear debris behavior of the filling materials and the interface wear characteristics influence the friction-induced vibration and noise of the brake system.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson, D.: Railway Noise and Vibration: Mechanisms, Modelling and Means of Control. Elsevier, Oxford (2008)
Verma, P.C., Menapace, L., Bonfanti, A., Ciudin, R., Gialanella, S., Straffelini, G.: Braking pad-disc system: wear mechanisms and formation of wear fragments. Wear 322–323, 251–258 (2015)
Shin, M.W., Kim, Y.H., Jang, H.: Effect of the abrasive size on the friction effectiveness and instability of brake friction materials: a case study with zircon. Tribol. Lett. 55(3), 371–379 (2014)
Zhou, H., Yao, P., Xiao, Y., Fan, K., Zhang, Z., Gong, T., Zhao, L., Deng, M., Liu, C., Ling, P.: Friction and wear maps of copper metal matrix composites with different iron volume content. Tribol. Int. 132, 199–210 (2019)
Kasem, H., Dufrenoy, P., Desplanques, Y.: Relationships between surface thermal gradients and disc distortion during stop-braking with high energy dissipation. Tribol. Lett. 48(2), 169–181 (2012)
Zhang, P., Zhang, L., Fu, K.X., Cao, J.W., Shijia, C.R., Qu, X.H.: Effects of different forms of Fe powder additives on the simulated braking performance of Cu-based friction materials for high-speed railway trains. Wear 414–415, 317–326 (2018)
Su, L., Gao, F., Han, X., Chen, J.: Effect of copper powder third body on tribological property of copper-based friction materials. Tribol. Int. 90, 420–425 (2015)
Liew, K.W., Nirmal, U.: Frictional performance evaluation of newly designed brake pad materials. Mater. Des. 48, 25–33 (2013)
Ma, J.J., Olofsson, U., Lyu, Y.Z., Wahlstrom, J., Astrom, A.H., Tu, M.H.: A comparison of airborne particles generated from disk brake contacts: induction versus frictional heating. Tribol. Lett. 68(1), 1–13 (2020)
Lyu, H.M., Walsh, S.J., Chen, G.X., Zhang, L.J., Qian, K.C., Wang, L.: Analysis of friction-induced vibration leading to brake squeal using a three degree-of-freedom model. Tribol. Lett. 65(3), 105 (2017)
Lorang, X., Foy-Margiocchi, F., Nguyen, Q.S., Gautier, P.E.: TGV disc brake squeal. J. Sound Vib. 293(3–5), 735–746 (2006)
Abdo, J., Nouby, M., Mathivanan, D., Srinivasan, K.: Reducing disc brake squeal through FEM approach and experimental design technique. Int. J. Veh. Noise Vib. 6(2/3/4), 230–246 (2010)
Kchaoua, M., Mat Lazimb, A.R., Abdul Hamid, M.K., Abu Bakar, A.R.: Experimental studies of friction-induced brake squeal: Influence of environmental sand particles in the interface brake pad-disc. Tribol. Int. 110, 307–317 (2017)
Peng, T., Yan, Q.Z., Li, G., Zhang, X.L., Wen, Z.F., Jin, X.S.: The braking behaviors of Cu-based metallic brake pad for high-speed train under different initial braking speed. Tribol. Lett. 65(4), 1–13 (2017)
Wei, L., Choy, Y.S., Cheung, C.S., Jin, D.: Tribology performance, airborne particle emissions and brake squeal noise of copper-free friction materials. Wear 448–449, 203215 (2020)
Lyu, Y., Bergseth, E., Tu, M., Olofsson, U.: Effect of humidity on the tribological behaviour and airborne particle emissions of railway brake block materials. Tribol. Int. 118, 360–367 (2018)
Ferrer, C., Pascual, M., Busquets, D., Rayón, E.: Tribological study of Fe-Cu-Cr-graphite alloy and cast iron railway brake shoes by pin-on-disc technique. Wear 268(5), 784–789 (2010)
Federici, M., Perricone, G., Gialanella, S., Straffelini, G.: Sliding behaviour of friction material against cermet coatings: pin-on-disc study of the running-in stage. Tribol. Lett. 66(2), 53 (2018)
Abbasi, S., Jansson, A., Olander, L., Olofsson, U., Sellgren, U.: A pin-on-disc study of the rate of airborne wear particle emissions from railway braking materials. Wear 284, 18–29 (2012)
Vakkalagadda, M.R.K., Srivastava, D.K., Mishra, A., Racherla, V.: Performance analyses of brake blocks used by Indian Railways. Wear 328–329, 64–76 (2015)
Mann, R., Magnier, V., Brunel, J.F., Brunel, F., Dufrenoy, P., Henrion, M.: Relation between mechanical behavior and microstructure of a sintered material for braking application. Wear 386, 1–16 (2017)
Xu, J.Y., Mo, J.L., Huang, B., Wang, X.C., Zhang, X., Zhou, Z.R.: Reducing friction-induced vibration and noise by clearing wear debris from contact surface by blowing air and adding magnetic field. Wear 408–409, 238–247 (2018)
Straffelini, G.: Friction and Wear, Methodologies for Design and Control. Springer, Switzerland (2015)
Quan, X., Mo, J.L., Huang, B., Tang, B., Ouyang, H.J., Zhou, Z.R.: Influence of the friction block shape and installation angle of high-speed train brakes on brake noise. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 142(3), 1–18 (2020)
Davin, E., Cristol, A.L., Brunel, J.F., Desplanques, Y.: Wear mechanisms alteration at braking interface through atmosphere modification. Wear 426–427, 1094–1101 (2019)
Österle, W., Dmitriev, A.: Functionality of conventional brake friction materials–perceptions from findings observed at different length scales. Wear 271(9–10), 2198–2207 (2011)
Rodrigues, A.C.P., Osterle, W., Gradt, T., Azevedo, C.R.F.: Impact of copper nanoparticles on tribofilm formation determined by pin-on-disc tests with powder supply: addition of artificial third body consisting of Fe3O4, Cu and graphite. Tribol. Int. 110, 103–112 (2017)
Abu Bakar, A.R., Ouyang, H., James, S., Li, L.: Finite element analysis of wear and its effect on squeal generation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D: J. Automob. Eng. 222(7), 1153–1165 (2008)
Wang, D.W., Mo, J.L., Ouyang, H., Zhou, Z.R.: Improving dynamic and tribological behaviours by means of a Mn-Cu damping alloy with grooved surface features. Tribol. Lett. 66(2), 1–16 (2018)
Tonazzi, D., Massi, F., Baillet, L., Brunetti, J., Berthier, Y.: Interaction between contact behaviour and vibrational response for dry contact system. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 110, 110–121 (2018)
Gultekin, D., Uysal, M., Aslan, S., Alaf, M., Guler, M.O., Akbulut, H.: The effects of applied load on the coefficient of friction in Cu-MMC brake pad/Al-SiCp MMC brake disc system. Wear 270(1), 73–82 (2010)
Xiao, Y.L., Zhang, Z.Y., Yao, P.P., Fan, K.Y., Zhou, H.B., Gong, T.M., Zhao, L., Deng, M.W.: Mechanical and tribological behaviors of copper metal matrix composites for brake pads used in high-speed trains. Tribol. Int. 119, 585–592 (2018)
Zhao, S.Q., Yan, Q.Z., Peng, T., Zhang, X.L., Wen, Y.Y.: The braking behaviors of Cu-based powder metallurgy brake pads mated with C/C-SiC disk for high-speed train. Wear 448–449, 203237 (2020)
Sinou, J.J., Loyer, A., Chiello, O., Mogenier, G., Lorang, X., Cocheteux, F., Bellaje, S.: A global strategy based on experiments and simulations for squeal prediction on industrial railway brakes. J. Sound Vib. 332(20), 5068–5085 (2013)
Tang, B., Mo, J.L., Xu, J.W., Wu, Y.K., Zhu, M.H., Zhou, Z.R.: Effect of perforated structure of friction block on the wear, thermal distribution and noise characteristics of railway brake systems. Wear 426–427, 1176–1186 (2019)
Xiao, J.K., Xiao, S.X., Chen, J., Zhang, C.: Wear mechanism of Cu-based brake pad for high-speed train braking at speed of 380 km/h. Tribol. Int. 150, 106357 (2020)
Li, G., Yan, Q.Z., Xi, J.R., Qi, G.H., Yang, X.T.: The stability of the coefficient of friction and wear behavior of C/C-SiC. Tribol. Lett. 58(1), 1–7 (2015)
Su, L., Gao, F., Han, X., Fu, R., Zhang, E.: Tribological behavior of copper-graphite powder third body on copper-based friction materials. Tribol. Lett. 60(2), 30 (2015)
Lazzari, A., Tonazzi, D., Massi, F.: Squeal propensity characterization of brake lining materials through friction noise measurements. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 128, 216–228 (2019)
Singla, N., Brunel, J.F., Mege-Revil, A., Kasem, H., Desplanques, Y.: Experiment to investigate the relationship between the third-body layer and the occurrence of squeals in dry sliding contact. Tribol. Lett. 68, 4 (2020)
Bauzin, J.G., Laraqi, N.: Three-dimensional analytical calculation of the temperature in a brake disc of a high-speed train. Appl. Therm. Eng. 154, 668–675 (2019)
Osenin, Y.Y., Al-Makhdi, D.M., Osenin, Y.I., Sergienko, O.V., Sosnov, I.I., Chesnokov, A.V.: Providing the stability of the coefficient of friction of a vehicle disk brake under extreme operating conditions. J. Frict. Wear 37(3), 230–236 (2016)
Peng, T., Yan, Q.Z., Zhang, X.L.: Stability of metal matrix composite pads during high-speed braking. Tribol. Lett. 66(2), 63 (2018)
Chen, J.G., Gao, F.: Temperature field and thermal stress analyses of high-speed train brake disc under pad variations. Open Mech. Eng. J. 9(1), 371–378 (2015)
Renault, A., Massa, F., Lallemand, B., Tison, T.: Experimental investigations for uncertainty quantification in brake squeal analysis. J. Sound Vib. 367, 37–55 (2016)
Rodrigues, A.C.P., Yonamine, T., Albertin, E., Sinatora, A., Azevedo, C.R.F.: Effect of Cu particles as an interfacial media addition on the friction coefficient and interface microstructure during (steel/steel) pin on disc tribotest. Wear 330–331, 70–78 (2015)
Zhang, P., Zhang, L., Fu, K.X., Wu, P.F., Cao, J.W., Shijia, C.R., Qu, X.H.: Fade behaviour of copper-based brake pad during cyclic emergency braking at high speed and overload condition. Wear 428–429, 10–23 (2019)
Liaquat, H., Shi, X.L., Yang, K., Huang, Y.C., Liu, X.Y., Wang, Z.H.: Tribological behavior of TiAl metal matrix composite brake disk with TiC reinforcement under dry sliding conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26, 3457–3464 (2017)
Sun, W.T., Zhou, W.L., Liu, J.F., Fu, X.S., Chen, G.Q., Yao, S.: The size effect of SiO2 particles on friction mechanisms of a composite friction material. Tribol. Lett. 66, 35 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51822508) and Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program (No. 2020JDTD0012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Z.Y., Xiang, Z.Y., Tang, B. et al. Effect of Surface Modification on the Tribological Properties of Friction Blocks in High-Speed Train Brake Systems. Tribol Lett 69, 27 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01402-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01402-4