Abstract
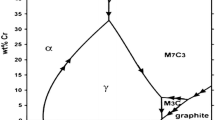
In this study, flux-cored arc welding was performed to deposit an Fe-based super-hard hardfacing whit 911 HV30 on an st37 substrate. The dry sand/rubber wheel abrasion test (ASTM G65) was performed to investigate the abrasive wear behavior of the hardfacing deposit and its average weight loss was measured to be 0.075 gr. The worn surface and cross sections of wear sample were studied by optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The results showed that the fracture behavior of the phases during abrasion testing is similar to their fracture behavior during macro-indentation fracture toughness testing investigated in the previous study (Bahoosh et al. in Eng Fail Anal 92:480–494, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.06.021, 2018). Consequently, the micro-mechanisms of abrasion resistance associated with the fracture behavior of the phases such as the fragmentation of the primary \({\text{M}}_{7} \left({\text{CB}} \right)_{3}\) in the preferred direction and higher abrasion resistance of the core–rim-structured phases were determined.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrasion resistant applications. Corodur welding wire Co. https://www.corodur.de/en/products/abrasion-resistant-applications (2019). Accessed 1 July 2019
ASTM-G65: Standard test method for measuring abrasion using the dry sand/rubber wheel apparatus. ASTM Int., West Conshohocken (2010)
Petrica, M., Katsich, C., Badisch, E., Kremsner, F.: Study of abrasive wear phenomena in dry and slurry 3-body conditions. Tribol. Int. 64, 196–203 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2013.03.028
Yüksel, N., Şahin, S.: Wear behavior–hardness–microstructure relation of Fe–Cr–C and Fe–Cr–C–B based hardfacing alloys. Mater. Des. 58, 491–498 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.02.032
Bedolla-Jacuinde, A., Guerra, F.V., Mejía, I., Zuno-Silva, J., Rainforth, M.: Abrasive wear of V-Nb–Ti alloyed high-chromium white irons. Wear 332, 1006–1011 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2015.01.049
Gualco, A., Svoboda, H.G., Surian, E.S.: Study of abrasive wear resistance of Fe-based nanostructured hardfacing. Wear 360, 14–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.04.011
Hutchings, I.M., Shipway, P.: Tribology. Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials. Presented at the (2017)
Hutchings, I.M.: Tribological properties of metal matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Technol. 10(6), 513–517 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1179/mst.1994.10.6.513
Correa, E.O., Alcântara, N.G., Tecco, D.G., Kumar, R.V.: The relationship between the microstructure and abrasive resistance of a hardfacing alloy in the Fe-Cr-C-Nb-V system. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38(8), 1671–1680 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9220-8
Doǧan, Ö.N., Hawk, J.A.: Effect of carbide orientation on abrasion of high Cr white cast iron. Wear 189(1–2), 136–142 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(95)06682-9
Coronado, J.J.: Effect of (Fe, Cr)7C3 carbide orientation on abrasion wear resistance and fracture toughness. Wear 270(3–4), 287–293 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.10.070
Meacham, B.E., Marshall, M.C., Branagan, D.J.: Palmqvist fracture toughness of a new wear-resistant weld alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37(12), 3617–3627 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-1056-0
Chotěborský, R.: Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure, hardness and abrasive wear resistance of high chromium hardfacing. Res. Agric. Eng. 59, 23–28 (2013)
Bahoosh, M., Shahverdi, H.R., Farnia, A.: Macro-indentation fracture mechanisms in a super-hard hardfacing Fe-based electrode. Eng. Fail. Anal. 92, 480–494 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.06.021
ISO 28079: Hardmetals—Palmqvist Toughness Test. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva (2009)
Sarin, V.K., Llanes, L., Mari, D.: Comprehensive Hard Materials, vol. 1, pp. 304–320. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2014)
basic welding filler metal technology, lesson viii: hardsurfacing electrodes. ESAB Co. http://www.esabna.com/euweb/awtc/lesson8_1.htm. Accessed 1 July 2019
Buchely, M.F., Gutierrez, J.C., León, L.M., Toro, A.: The effect of microstructure on abrasive wear of hardfacing alloys. Wear 259(1–6), 52–61 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2005.03.002
Kirchgaßner, M., Badisch, E., Franek, F.: Behaviour of iron-based hardfacing alloys under abrasion and impact. Wear 265(5–6), 772–779 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2008.01.004
Lin, C.-M., Chang, C.-M., Chen, J.-H., Wu, W.: Hardness, toughness and cracking systems of primary (Cr, Fe)23C6 and (Cr, Fe)7C3 carbides in high-carbon Cr-based alloys by indentation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527(18–19), 5038–5043 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.04.073
Lee, S., Choo, S.-H., Kim, N.J., Baek, E.-R., Ahn, S.: Correlation of microstructure and fracture toughness in high-chromium white iron hardfacing alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27(12), 3881–3891 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02595637
Zhou, Y.F., Qin, G.K., Jiang, P.J., Wang, S.F., Qi, X.W., Xing, X.L., Yang, Q.X.: Dry sliding wear behavior of (Cr, Fe)7C3-γ(Cr, Fe) metal matrix composite (MMC) coatings: the influence of high volume fraction (Cr, Fe)7C3 carbide. Tribol. Lett. 66(3), 108 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1053-7
Polak, R., Ilo, S., Badisch, E.: Relation between inter-particle distance (L IPD) and abrasion in multiphase matrix-carbide materials. Tribol. Lett. 33(1), 29–35 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9388-0
Adamiak, M., Górka, J., Kik, T.: Comparison of abrasion resistance of selected constructional materials. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 37(2), 375–380 (2009)
Dasgupta, R., Prasad, B.K., Modi, O.P., Jha, A.K.: A comparison of material removal mechanism under low stress abrasive condition of steel and hardfacing alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 8(4), 437–442 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994999770346738
Tang, X.H., Li, L., Hinckley, B., Dolman, K., Parent, L., Li, D.Y.: Beneficial effects of the core-shell structure of primary carbides in high-Cr (45 wt%) white cast irons on their mechanical behavior and wear resistance. Tribol. Lett. 58(3), 44 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0522-5
Berns, H.: Comparison of wear resistant MMC and white cast iron. Wear 254(1–2), 47–54 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(02)00300-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahoosh, M., Shahverdi, H.R. & Farnia, A. Abrasive Wear Behavior and Its Relation with the Macro-indentation Fracture Toughness of an Fe-Based Super-Hard Hardfacing Deposit. Tribol Lett 67, 100 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-019-1213-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-019-1213-4