Abstract
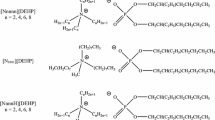
A new series of tricresyl phosphate (TCP)-based ionic liquids (ILs) were synthesized by mixing TCP with lithium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide (LiTFSI). Their tribological properties in pentaerythritol ester were investigated using an Optimol SRV oscillating friction and wear tester. LiTFSI/TCP (0.75/1 molar ratio, TCPL3) exhibits the best friction-reducing and antiwear properties under given experimental conditions. Compared with conventional lubricant additive TCP, TCPL3 could significantly improve the tribological properties of polyol ester, especially under high-temperature condition. Worn surfaces were analyzed using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectrometer (XPS). Surface analysis demonstrates that the outstanding lubricating properties are attributed to the formation of boundary film which is composed of iron fluoride, lithium phosphate, and lithium polyphosphates. Unexpectedly, a remarkable synergistic effect between TCPL3 and typical high-temperature antioxidant N-phenyl-α-naphthylamine in terms of antioxidation property was also observed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snyder, C.E., Dolle, R.E.: Development of polyperfluoroalkylethers as high temperature lubricants and hydraulic fluids. ASLE Trans. 19(3), 171–180 (1976)
Wu, J., Lu, X., Feng, X., Shi, Y.: Halogen-free ionic liquids as excellent lubricants for PEEK-stainless steel contacts at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 104, 1–9 (2016)
Yokoyama, F.: Application: estimation of service lives and operating temperature ranges of high-temperature lubricating oils using thermal analysis. J. Phys. Sci. Appl. 4(8), 516–523 (2014)
Bartl, P., Völkl, C.: Thermo-oxidative stability of high-temperature stability polyol ester jet engine oils—a comparison of test methods. Lubr. Sci. 17(3), 179–189 (2000)
Gohardani, A.S., Doulgeris, G., Singh, R.: Challenges of future aircraft propulsion: a review of distributed propulsion technology and its potential application for the all electric commercial aircraft. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 47(5), 369–391 (2011)
Ohnabe, H., Masaki, S., Onozuka, M., Miyahara, K., Sasa, T.: Manufacturing: potential application of ceramic matrix composites to aero-engine components. Compos. Part A 30(4), 489–496 (1999)
El-Magly, I.A., Nagib, H.K., Mokhtar, W.M.: Aspects of the behavior of some pentaerythritol ester base synlubes for turbo-engines. Egypt. J. Pet. 22(1), 169–177 (2013)
Sianesi, D., Zamboni, V., Fontanelli, R., Binaghi, M.J.W.: Perfluoropolyethers: their physical properties and behaviour at high and low temperatures. Wear 18(2), 85–100 (1971)
Nader, B.S., Kar, K.K., Morgan, T.A., Pawloski, C.E., Dilling, W.L.: Development and tribological properties of new cyclotriphosphazene high temperature lubricants for aircraft gas turbine engines. Tribol. Trans. 35(1), 37–44 (1992)
Smith, R., Walowit, J., McGrew, J.M.: Elastohydrodynamic traction characteristics of 5P4E polyphenyl ether. J. Lubr. Technol. 95(3), 353–360 (1973)
Zeng, Z., Phillips, B.S., Xiao, J.-C., Shreeve, J.N.M.: Polyfluoroalkyl, polyethylene glycol, 1, 4-bismethylenebenzene, or 1, 4-bismethylene-2, 3, 5, 6-tetrafluorobenzene bridged functionalized dicationic ionic liquids: synthesis and properties as high temperature lubricants. Chem. Mater. 20(8), 2719–2726 (2008)
Wu, X., Wang, X., Liu, W.J.R.A.: Tribological properties of naphthyl phenyl diphosphates as antiwear additive in polyalkylene glycol and polyurea grease for steel/steel contacts at elevated temperature. RSC Adv. 4(12), 6074–6082 (2014)
Chen, Z., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Gunsel, S., Luo, J.: Ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets with superior extreme pressure property as boundary lubricants. Sci. Rep. 5, 12869 (2015)
Bermudez, M.D., Jimenez, A.E., Sanes, J., Carrion, F.J.: Ionic liquids as advanced lubricant fluids. Molecules 14(8), 2888–2908 (2009)
Minami, I.: Ionic liquids in tribology. Molecules 14(6), 2286–2305 (2009)
Zhang, S., Hu, L., Qiao, D., Feng, D., Wang, H.: Vacuum tribological performance of phosphonium-based ionic liquids as lubricants and lubricant additives of multialkylated cyclopentanes. Tribol. Int. 66, 289–295 (2013)
Yu, B., Bansal, D.G., Qu, J., Sun, X., Luo, H., Dai, S., Blau, P.J., Bunting, B.G., Mordukhovich, G., Smolenski, D.J.J.W.: Oil-miscible and non-corrosive phosphonium-based ionic liquids as candidate lubricant additives. Wear 289, 58–64 (2012)
Huang, G., Yu, Q., Cai, M., Zhou, F., Liu, W.: Investigation of the lubricity and antiwear behavior of guanidinium ionic liquids at high temperature. Tribol. Int. 114, 65–76 (2017)
Jimenez, A.-E., Bermúdez, M.D.: Ionic liquids as lubricants for steel–aluminum contacts at low and elevated temperatures. Tribol. Lett. 26(1), 53–60 (2007)
Fan, M., Liang, Y., Zhou, F., Liu, W.: Dramatically improved friction reduction and wear resistance by in situ formed ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2(17), 6824–6830 (2012)
Fan, M., Song, Z., Liang, Y., Zhou, F., Liu, W.: In situ formed ionic liquids in synthetic esters for significantly improved lubrication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4(12), 6683–6689 (2012)
Song, Z., Cai, M., Liang, Y., Fan, M., Zhou, F., Liu, W.: In situ preparation of anti-corrosion ionic liquids as the lubricant additives in multiply-alkylated cyclopentanes. RSC Adv. 3(44), 21715–21721 (2013)
Wu, X., Liu, J., Zhao, Q., Zhang, M., Zhao, G., Wang, X.: In Situ Formed Ionic Liquids in Polyol Esters as High Performance Lubricants for Steel/Steel Contacts at 300°C. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3(9), 2281–2290 (2015)
Wu, X., Zhao, G., Wang, X., Liu, W.: Preparation of High-Temperature Lubricants by Blending Castor Oil with Lithium Bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide. Tribol. Lett. 65(2), 51 (2017)
Zhang, C.-C., Zhang, F.-S.: Recovery of triphenyl phosphate from waste printed circuit boards by solvothermal process. Chem. Eng. J. 240, 10–15 (2014)
Cai, M., Liang, Y., Zhou, F., Liu, W.: Tribological properties of novel imidazolium ionic liquids bearing benzotriazole group as the antiwear/anticorrosion additive in poly(ethylene glycol) and polyurea grease for steel/steel contacts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 3(12), 4580–4592 (2011)
Naumkin, A.V., Kraut-Vass, A., Gaarenstroom, S.W., Powell, C.J.: NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database. https://srdata.nist.gov/xps/Default.aspx
Yao, M., Liang, Y., Xia, Y., Zhou, F.: Bisimidazolium ionic liquids as the high-performance antiwear additives in poly(ethylene glycol) for steel-steel contacts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 1(2), 467–471 (2009)
Gauthier, A., Montes, H., Georges, J.M.: Boundary lubrication with tricresylphosphate (TCP). Importance of corrosive wear. ASLE Trans. 25(4), 445–455 (2008)
Lu, R., Kobayashi, K., Nanao, H., Mori, S.: Deactivation effect of tricresyl phosphate (TCP) on tribochemical decomposition of hydrocarbon oil on a nascent steel surface. Tribol. Lett. 33(1), 1–8 (2008)
Johnson, D., Bachus, M., Hils, J.: Interaction between lubricants containing phosphate ester additives and stainless steels. Lubricants 1(2), 48–60 (2013)
Guan, B., Pochopien, B.A., Wright, D.S.: The chemistry, mechanism and function of tricresyl phosphate (TCP) as an anti-wear lubricant additive. Lubr. Sci. 28(5), 257–265 (2016)
Chao, T.S., Hutchison, D.A., Kjonaas, M.: Some synergistic antioxidants for synthetic lubricants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 23(1), 21–27 (1984)
Yao, J., Dong, J.: Antioxidation synergism between alkali metal salts and arylamine compounds in synthetic lubricants. Tribol. Trans. 39(2), 498–500 (1996)
Yao, J.: Evaluation of sodium acetylacetonate as a synergist for arylamine antioxidants in synthetic lubricants. Tribol. Trans. 30(11), 795–799 (1997)
Yao, J.: The role of sodium perfluorobutyrate in promoting the antioxidancy of dodpa in synthetic esters©. Tribol. Trans. 42(1), 84–89 (1999)
Yao, J.: Evaluation of alkali metal salts as deposit inhibitors for synthetic lubricants by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Thermochim. Acta. 296(1–2), 105–110 (1997)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial supports from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB0703802).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, R., Li, W., Zhao, Q. et al. In Situ Synthesized Phosphate-based Ionic Liquids as High-Performance Lubricant Additives. Tribol Lett 67, 60 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-019-1175-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-019-1175-6