Abstract
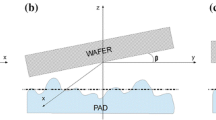
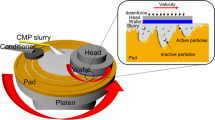
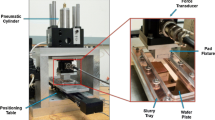
A three-dimensional contact mechanics formulation is presented for chemical mechanical polishing applications. The formulation is coupled with the Preston material removal equation in order to simulate the evolution of pressure and wafer height. The physics-based formulation allows the pressure and height to evolve such that dishing and erosion appear seamlessly. Results are compared against another feature-scale model and experiment. The methodology and model offer physics-based results that further the understanding of chemical mechanical polishing for a given layout.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, Y., Nassif, S.R., Pileggi, L.T., Strojwas, A.J.: Impact of interconnect variations on the clock skew of a gigahertz microprocessor. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 37th Annual Design Automation Conference, Los Angeles, California, USA (2000)
Comes, R., Terrell, E., Higgs, C.: Pad deflection-based model of chemical-mechanical polishing for use in CAD IC layout. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 23(1), 121–131 (2010)
Park, T., Tugbawa, T., Boning, D.S., Hymes, S., Brown, T., Smekalin, K., Schwartz, G.: Multi-level pattern effects in copper CMP. In: Proceedings of the CMP Symposium of the Electrochemical Society Meeting, pp. 94–100 (1999)
Shan, L., Levert, J., Meade, L., Tichy, J., Danyluk, S.: Interfacial fluid mechanics and pressure prediction in chemical mechanical polishing. J. Tribol. 122, 539 (2000)
He, L., Kahng, A.B., Tam, K.H., Xiong, J.: Design of integrated-circuit interconnects with accurate modeling of chemical-mechanical planarization. In: Proceedings SPIE 5756, Design and Process Integration for Microelectronic Manufacturing III, p. 109 (2005)
Mekkoth, J., Krishna, M., Qian, J., Hsu, W., Chen, C., Chen, Y., Tamarapalli, N., Cheng, W., Tofte, J., Keim, M.: Yield learning with layout-aware advanced scan diagnosis. In: International Symposium for Testing and Failure Analysis, vol. 32, p. 412. ASM International (1998)
Mehrotra, V., Sam, S.L., Boning, D., Chandrakasan, A., Vallishayee, R., Nassif, S.: A methodology for modeling the effects of systematic within-die interconnect and device variation on circuit performance. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 37th Annual Design Automation Conference, Los Angeles, California, USA (2000)
Terrell, E., Higgs III, C.: A particle-augmented mixed lubrication modeling approach to predicting chemical mechanical polishing. J. Tribol. 131, 012201 (2009)
Boning, D.S., Nassif, S.: Models of process variations in device and interconnect. In: Chandrakasan, A., Bowhill, W., Fox, F. (eds.) Design of High Performance Microprocessor Circuits, Chap. 6. IEEE Press, New York (2000)
Stine, B., Ouma, D., Divecha, R., Boning, D., Chung, J.: A closed-form analytic model for ILD thickness variation in CMP processes. A A 1, 2.0 (1997)
Stine, B.E., Boning, D.S., Chung, J.E., Camilletti, L., Kruppa, F., Equi, E.R., Loh, W., Prasad, S., Muthukrishnan, M., Towery, D.: The physical and electrical effects of metal-fill patterning practices for oxide chemical-mechanical polishing processes. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 45(3), 665–679 (1998)
Stine, B.E., Ouma, D.O., Divecha, R.R., Boning, D.S., Chung, J.E., Hetherington, D.L., Harwoo, C., Nakagawa, O.S., Oh, S.Y.: Rapid characterization and modeling of pattern-dependent variation in chemical-mechanical polishing. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 11(1), 129–140 (1998)
Tang, B.D., Xie, X., Boning, D.S.: Damascene chemical-mechanical polishing characterization and modeling for polysilicon microelectromechanical systems structures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, G582 (2005)
Boning, D.: Pattern dependent characterization of copper interconnect. In: Tutorial, international conference on microelectronic test structures (ICMTS) (2003)
Chekina, O., Keer, L., Liang, H.: Wear-contact problems and modeling of chemical mechanical polishing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145, 2100 (1998)
Vlassak, J.: A model for chemical-mechanical polishing of a material surface based on contact mechanics. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52(4), 847–873 (2004)
Yoshida, T.: Three-dimensional wafer process model for nanotopography. In: MRS Online Proceedings Library, vol. 767 (2003)
Yoshida, T.: Three-dimensional chemical mechanical polishing process model by BEM. In: Electrochemical Society Proceedings, vol. 99–37, pp. 593–604 (1999)
Rzehak, R., Vasilev, B.: Greenwood–Williamson model for pattern-dependent planarization. In: 2007 international conference on planarization/CMP technology (ICPT), pp. 1–6. VDE (2007)
Vasilev, B., Rzehak, R., Bott, S., Kücher, P., Bartha, J.W.: Greenwood–Williamson model combining pattern-density and pattern-size effects in CMP. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 24(2), 338–347 (2011)
Kaufman, A.: Volume visualization. Vis Comput 6(1), 1 (1990)
Dickrell, D.J., Dugger, M.T., Hamilton, M.A., Sawyer, W.G.: Direct contact-area computation for MEMS using real topographic surface data. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 16(5), 1263–1268 (2007)
Põdra, P., Andersson, S.: Wear simulation with the Winkler surface model. Wear 207(1–2), 79–85 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(96)07468-6
Sawyer, W.: Surface shape and contact pressure evolution in two component surfaces: application to copper chemical mechanical polishing. Tribol. Lett. 17(2), 139–145 (2004)
Noh, K., Saka, N., Chun, J.-H.: A multi-scale model for copper dishing in chemical-mechanical polishing. In: Molecular Engineering of Biological and Chemical Systems (MEBCS), vol. 1 (2005)
Higgs, C.F., Ng, S.H., Borucki, L., Yoon, I., Danyluk, S.: A mixed-lubrication approach to predicting CMP fluid pressure modeling and experiments. J. Electrochem. Soc. (2005). doi:10.1149/1.1855834
Shan, L., Levert, J., Meade, L., Tichy, J., Danyluk, S.: Interfacial fluid mechanics and pressure prediction in chemical mechanical polishing. J. Tribol. 122(3), 539–543 (2000)
Johnson, K.L.: Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1987)
Love, A.E.H.: The stress produced in a semi-infinite solid by pressure on part of the boundary. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 228(ArticleType: research-article/Full publication date: 1929/Copyright © 1929 The Royal Society), 377–420 (1929)
Xie, X.: Physical understanding and modeling of chemical mechanical planarization in dielectric materials. PhD Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge (2007)
Chekina, O., Keer, L., Liang, H.: Wear-contact problems and modeling of chemical mechanical polishing. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145(6), 2100–2106 (1998)
Cai, H.: Modeling of pattern dependencies in the fabrication of multilevel copper metallization. PhD Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge (2007)
Cai, H., Park, T., Boning, D., Kim, H., Kang, Y., Kim, S., Lee, J.-G: Coherent chip-scale modeling for copper CMP pattern dependence. In: MRS Proceedings, vol. 816 (2004)
Gbondo-Tugbawa, T.E.: Chip-scale modeling of pattern dependencies in copper chemical mechanical polishing processes. PHD Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge (2002)
Tugbawa, T., Park, T., Boning, D., Pan, T., Li, P., Hymes, S., Brown, T., Camilletti, L.: A mathematical model of pattern dependencies in Cu CMP processes. In: Electrochemical Society Meeting. Honolulu, HA, USA (1999)
Tugbawa, T., Park, T., Lee, B., Boning, D.: Modeling of pattern dependencies for multi-level copper chemical-mechanical polishing processes. In: MRS Online Proceedings Library, vol. 671 (2001)
Tugbawa, T., Park, T., Lee, B., Boning, D., Lefevre, P., Nguyen, J.: Modeling of pattern dependencies in abrasive-free copper chemical mechanical polishing processes. In: Proceedings of VLSI Multilevel Interconnect Conference, pp. 113–122 (2001)
Ng, S.H., Hight, R., Zhou, C., Yoon, I., Danyluk, S.: Pad soaking effect on interfacial fluid pressure measurements during cmp. J. Tribol. 125, 582 (2003)
Stein, D.J., Hetherington, D.L.: Review and experimental analysis of oxide CMP models. In: Electrochemical Society Proceedings, vol. 9937, pp. 217–233 (1999)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the NSF Division of Computing and Communication Foundations (CCF) within the CISE Directorate for supporting this Award 0811770 and the CSSI DFM working group led by Professor Shawn Blanton.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sierra Suarez, J.A., Higgs, C.F. A Contact Mechanics Formulation for Predicting Dishing and Erosion CMP Defects in Integrated Circuits. Tribol Lett 59, 36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0550-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0550-1