Abstract
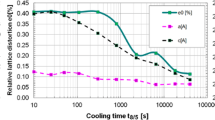
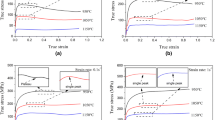
We developed a novel in situ observation method associated with synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction (XRD) that enables us to simultaneously monitor structural changes of materials, images at frictional interfaces, friction force and temperature with a time resolution on the order of tens of milliseconds. The in situ method was applied to study scuffing process of martensitic steel under a dry condition. The result shows that during scuffing, martensite to austenite phase transformation occurred with plastic flow. The generated austenite phase disappeared when the shear test was stopped. The austenite was present at a surface temperature lower than the nominal austenitisation temperature. After intermittent occurrences of the austenitisation with local plastic flow, the scuffing feature showed a larger amount of austenite, higher friction and greater plastic flow. The XRD spectra suggest that some metallurgical properties of the near-surface material of the steel may change at the scuffing-mode transition.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyson, A.: Scuffing—a review. Tribol. Int. 8, 77–87 (1975)
Blok, H.: The flash temperature concept. Wear 6, 483–494 (1963)
Johnson, R.R., Dow, T.A., Zhang, Y.Y.: Thermoelastic instability in elliptic contact between two sliding surfaces. Trans. ASME J. Tribol. 110, 80–86 (1988)
Ludema, K.C.: A review of scuffing and running-in of lubricated surface with asperities and oxides in perspective. Wear 100, 315–331 (1984)
Markov, D., Kelly, D.: Mechanisms of adhesion-initiated catastrophic wear: pure sliding. Wear 239, 189–210 (2000)
Sheiretov, T., Yoon, H., Cusano, C.: Scuffing under dry sliding conditions—part I: experimental studies. Tribol. Trans. 41, 435–446 (1998)
Sheiretov, T., Yoon, H., Cusano, C.: Scuffing under dry sliding conditions—part II: theoretical studies. Tribol. Trans. 41, 447–458 (1998)
Hershberger, J., Ajayi, O.O., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Formation of austenite during scuffing failure of SAE 4340 steel. Wear 256, 159–167 (2004)
Hershberger, J., Ajayi, O.O., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Evidence of scuffing initiation by adiabatic shear instability. Wear 258, 1471–1478 (2005)
Ajayi, O.O., Hersberger, J.G., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Microstructural evolution during scuffing of hardened 4340 steel—implication for scuffing mechanism. Tribol. Int. 38, 277–282 (2005)
Ajayi, O.O., Martin, C.L., Erck, R.A., Fenske, G.R.: Scuffing mechanism of near-surface material during lubricated severe sliding contact. Wear 271, 1750–1753 (2011)
Ajayi, O.O., Martin, C.L., Erck, R.A., Fenske, G.R.: Analytical predictive modeling of scuffing initiation in metallic materials in sliding contact. Wear 301, 57–61 (2013)
Enthoven, J., Spikes, H.A.: Infrared and visual study of the mechanisms of scuffing. Tribol. Trans. 39, 441–447 (1996)
Yagi, K., Ebisu, Y., Sugimura, J., Kajita, S., Ohmori, T., Suzuki, A.: In situ observation of wear process before and during scuffing in sliding contact. Tribol. Lett. 43, 361–368 (2011)
Li, H., Yagi, K., Sugimura, J., Kajita, S., Shinyoshi, T.: Role of wear particles in scuffing initiation. Tribol. Online 8, 285–294 (2013)
Chandrasekaran, M., Batchelor, A.W., Loh, N.L.: Direct observation of frictional seizure of mild steel sliding on aluminum by X-ray imaging Part I Methods. J. Mater. Sci. 35, 1589–1596 (2000)
Chandrasekaran, M., Batchelor, A.W., Loh, N.L.: Direct observation of frictional seizure of mild steel sliding on aluminum by X-ray imaging Part II Mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. 35, 1597–1602 (2000)
Chandrasekaran, M., Batchelor, A.W., Loh, N.L.: Frictional seizure of aluminium observed by X-ray imaging. Tribol. Int. 35, 297–308 (2002)
Jacobs, T.D.B., Carpick, R.W.: Nanoscale wear as a stress-assisted chemical reaction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 27, 108–112 (2013)
Michler, J., Rabe, R., Bucaille, J.L., Moser, B., Schwaller, P., Breguet, J.M.: Investigation of wear mechanisms through in situ observation during microscratching inside the scanning electron microscope. Wear 259, 18–26 (2005)
Ribeiro, R., Shan, Z., Minor, A.M., Liang, H.: In situ observation of nano-abrasive wear. Wear 263, 1556–1559 (2007)
Ishida, T., Sato, T., Fujita, H.: In-situ observation of shear deformation of gold single real contact point at the nanoscale. Tribol. Online 7, 127–131 (2012)
Hase, A., Mishina, H., Wada, M.: Acoustic emission in elementary processes of friction and wear: in-situ observation of friction surface and AE signals. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 3, 333–344 (2009)
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-Ray Diffraction. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA (1956)
Japan Institute of Metals and Materials: Metal Data Book. Maruzen, Tokyo (in Japanese) (1974)
Davis, J.R.: Metals Handbook: Desk, 2nd edn. ASM International, Ohio (1998)
Lee, Y.K., Shin, H.C., Leem, D.S., Choi, J.Y., Jin, W., Choi, C.S.: Reverse transformation mechanism of martensite to austenite and amount of retained austenite after reverse transformation in Fe-3Si-13Cr-7Ni (wt-%) martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 19, 393–398 (2003)
Danon, A., Servant, C., Alamo, A., Brachet, J.C.: Heterogeneous austenite grain growth in 9Cr martensitic steels: influence of the heating rate and the austenitization temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 348, 122–132 (2003)
Akimoto, S., Suzuki, T., Yagi, T., Shimomura, O.: Phase diagram of iron determined by high-pressure/temperature X-ray diffraction using synchrotron radiation. High Press. Res. Miner. Phys: A Volume in Honor of Syun-iti Akimoto, 149–154 (2013). doi:10.1029/GM039p0149/summary
Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.: Steels for bearings. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 268–435 (2012)
Kundrák, J., Gácsi, A., Gyáni, K., Bana, V., Tomolya, G.: X-ray diffraction investigation of white layer development in hard-turning surfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 62, 457–469 (2012)
Ramesh, A., Melkote, S.N., Allard, L.F., Riester, L., Watkins, T.R.: Analysis of white layers formed in hard turning of AISI 52100 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 390, 88–97 (2005)
Hosseini, S.B., Beno, T., Klement, U., Kaminski, J., Ryttberg, K.: Cutting temperatures during hard turning—measurements and effects on white layer formation in AISI 52100. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 214, 1293–1300 (2014)
Duffy, J., Chi, Y.C.: On the measurement of local strain and temperature during the formation of adiabatic shear band. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 157, 195–210 (1992)
Cho, K.M., Lee, S., Nutt, S.R., Duffy, J.: Adiabatic shear band formation during dynamic torsional deformation of an HY-100 steel. Acta. Metall. Mater. 41, 923–932 (1993)
Duan, C., Kong, W., Hao, Q., Zhou, F.: Modeling of white layer thickness in high speed machining of hardened steel based on phase transformation mechanism. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 69, 59–70 (2013)
Han, S., Melkote, S.N., Haluska, M.S., Watkins, T.R.: White layer formation due to phase transformation in orthogonal machining of AISI 1045 annealed steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 488, 195–204 (2008)
Popov, V.L.: Contact Mechanics and Friction Physical Principles and Application. Springer, Heidelberg (2010)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. Y. Hayashi at Toyota Central R&D Labs., Inc., who performed the XRD data acquisition. The synchrotron radiation experiments were performed at the BL33XU line of SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (Proposal No. 2013B7021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kajita, S., Yagi, K., Izumi, T. et al. In Situ X-Ray Diffraction Study of Phase Transformation of Steel in Scuffing Process. Tribol Lett 57, 6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0443-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0443-8