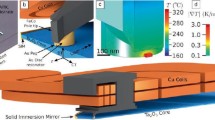
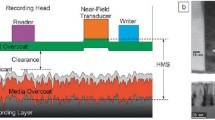
Abstract
In heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR), a tiny area of magnetic recording media has to be heated up to a high temperature with laser to lower the coercivity temporarily for information to be written on the area. In a humid environment, some of the water vapor molecules adsorb on the disk surface to form a water film. In HAMR writing, the adsorbed water film on the disk surface will desorb instantly from the high-temperature laser heating area to become high-temperature high-pressure water vapor. The water vapor molecules will transfer extra heat from the high-temperature laser heating area on the disk surface to the slider, which makes the temperature of the slider surface higher in a humid environment than that in dry air. The heat transfer increases dramatically with relative humidity and with the decrease in slider–disk spacing.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shukla, N., Svedberg, E., van de Veerdonk, R.J.M., Ma, X.D., Gui, J., Gellman, A.J.: Water adsorption on lubricated a-CHx in humid environments. Tribol. Lett. 15, 9–14 (2003)
Shukla, N., Gellman, A.J., Ma, X.D., Gui, J.: Effect of humidity on lubricated carbon overcoats. Tribol. Lett. 12, 105–109 (2002)
Karis, T.E., Tawakkul, M.A.: Water adsorption and friction on thin film magnetic recording disks. Tribol. Trans. 46, 469–478 (2003)
Smallen, M., Lee, J.K., Chao, A., Enguero, J.: The role of disk carbon and slider in water adsorption. IEEE Trans. Magn. 30, 4137–4139 (1994)
Karis, T.E.: Water adsorption on thin film media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 225, 196–203 (2000)
Li, Y.F., Trauner, D., Talke, F.E.: Effect of humidity on stiction and friction of the head/disk interface. IEEE Trans. Magn. 26, 2487–2489 (1990)
Lei, R.Z., Gellman, A.J.: Humidity effects on PFPE lubricant bonding to a-CHx overcoats. Langmuir 16, 6628–6635 (2000)
Tyndall, G.W., Waltman, R.J., Pacansky, J.: Effect of adsorbed water on perfluoropoyether-lubricated magnetic recording disks. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 6287–6296 (2001)
Tian, H., Matsudaira, T.: The role of relative humidity, surface roughness and liquid build-up on static friction behavior of the head/disk interface. J. Tribol. 115, 28–35 (1993)
Bhushan, B., Kotwal, C.A., Chilamakuri, S.K.: Kinetic meniscus model for prediction of rest stiction. J. Tribol. 120, 42–53 (1998)
Kasaia, P.H., Raman, V.: Z-dol versus Z-tetraol: bonding and durability in magnetic hard disk application. Tribol. Lett. 16, 29–36 (2004)
Kasaia, P.H., Raman, V.: Perfluoropolyethers with dialkylamine end groups: ultrastable lubricant for magnetic disk application. Tribol. Lett. 12, 117–122 (2002)
Novotny, V., Staud, N.: Correlation between environmental and electrochemical corrosion of thin film magnetic recording media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 135, 2931–2938 (1988)
Dubin, P.R., Winn, K.D., Davis, L.P., Cutler, R.A.: Degradation of co-based thin-film recording materials in selected corrosive environments. J. Appl. Phys. 53, 2579–2581 (1982)
Ma, Y.S., Liu, B.: Lubricant transfer from disk to slider in hard disk drives. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 143516 (2007)
Ma, Y.S., Liu, B.: Dominant factors in lubricant transfer and accumulation in slider–disk interface. Tribol. Lett. 29, 119–127 (2008)
Kim, S.H., Dai, Q., Marchon, B., Flechsig, K.: Humidity effects on lubricant transfer in the head–disk interface of a hard disk drive. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 07B704 (2009)
Ma, Y.S., Liu, B.: Contribution of water vapor to slider air-bearing pressure in hard disk drives. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 223502 (2007)
Strom, B.D., Zhang, S.Y., Lee, S.C., Khurshudov, A., Tyndall, G.W.: Effects of humid air on air-bearing flying height. IEEE Trans. Magn. 43, 3301–3304 (2007)
Ma, Y.S., Liu, B.: Further study of the effect of water vapor on slider air bearing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 45, 5006–5009 (2009)
Kryder, M.H., Gage, E.C., McDaniel, T.W., Challener, W.A., Rottmayer, R.E., Ju, G., Hsia, Y.-T., Erden, M.F.: Heat assisted magnetic recording. Proc. IEEE 96, 1810–1835 (2008)
Ma, Y.S., Man, Y.J., Shakerzadeh, M., Seet, H.L., Ji, R., Zheng, R.Y., Chung, H.J., Chen, X.Y., Hu, J.F., Yamamoto, T., Hempstead, R.: Laser-heating-induced damage to ultrathin carbon overcoat in heat-assisted magnetic recording. Tribol. Lett. 53, 303–310 (2014)
Ma, Y.S., Chen, X.Y., Liu, B.: Experimental study of lubricant depletion in heat assisted magnetic recording: effects of laser heating duration and temperature. Microsyst. Technol. 19, 291–297 (2013)
Ma, Y.S., Chen, X.Y., Liu, B.: Experimental study of lubricant depletion in heat assisted magnetic recording over the lifetime of the drive. Tribol. Lett. 47, 175–182 (2012)
Wang, N., Komvopoulos, K.: Thermal stability of ultrathin amorphous carbon films for energy-assisted magnetic recording. IEEE Trans. Magn. 47, 2277–2282 (2011)
Challener, W.A., Peng, C.B., Itagi, A.V., Karns, D., Peng, W., Peng, Y.G., Yang, X.M., Zhu, X.B., Gokemeijer, N.J., Hsia, Y.-T., Ju, G., Rottmayer, R.E., Seigler, M.A., Gage, E.C.: Heat-assisted magnetic recording by a nearfield transducer with efficient optical energy transfer. Nat. Photon. 3, 220–224 (2009)
Buck, A.L.: New equations for computing vapor pressure and enhancement factor. J. Appl. Meteorol. 20, 1527–1532 (1981)
Badmann, R., Stockhausen, N., Setzer, M.J.: The Statistical thickness and the chemical potential of adsorbed water films. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 82, 534–542 (1981)
Shiramatsu, T., Kurita, M., Miyake, K., Suk, M., Ohki, S., Tanaka, H., Saegusa, S.: Drive integration of active flying-height control slider with micro thermal actuator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 42, 2513–2515 (2006)
Xiong, S.M., Bogy, D.B.: Flying height modulation for a dual thermal protrusion slider in heat assisted magnetic recording (HAMR). IEEE Trans. Magn. 49, 5222–5226 (2013)
Liu, N., Zheng, J.L., Bogy, D.B.: Thermal flying-height control sliders in air–helium gas mixtures. IEEE Trans. Magn. 47, 100–104 (2011)
Liu, N., Zheng, J.L., Bogy, D.B.: Predicting the flying performance of thermal flying-height control sliders in hard disk drives. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 016102 (2010)
Chen, D., Liu, N., Bogy, D.B.: A phenomenological heat transfer model for the molecular gas lubrication system in hard disk drives. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 084303 (2009)
Bird, G.A.: Molecular Gas Dynamics and the Direct Simulation of Gas Flows. Oxford University Press, New York (1994)
Poling, B.E., Prausnitz, J.M., O’Connell, J.: The Properties of Gases and Liquids, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (2001)
Lide, D.R.: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 89th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2009)
Lemmon, E.W., Jacobsen, R.T., Penoncello, S.G., Friend, D.G.: Thermodynamic properties of air and mixtures of nitrogen, argon, and oxygen from 60 to 2000 K at pressures to 2000 MPa. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 29, 331–385 (2000)
Wagner, W., Kretzschmar, H.-J.: International Steam Tables: Properties of Water and Steam Based on the Industrial Formulation IAPWS-IF97, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Beirão, S.G.S., Ribeiro, A.P.C., Lourenço, M.J.V., Santos, F.J.V., Nieto de Castro, C.A.: Thermal conductivity of humid air. Int. J. Thermophys. 33, 1686–1703 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y.S., Zhou, W.D., Yu, S.K. et al. Adsorbed Water Film and Heat Conduction from Disk to Slider in Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording. Tribol Lett 56, 93–99 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0388-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0388-y