Abstract
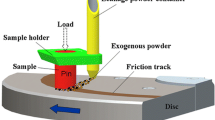
The antifriction ability of powder lubrication and the state of powder layer are strongly related to the service conditions. Therefore, the effects of sliding velocity and normal load under powder lubrication were studied using a face-to-face contact tribometer. In our work, some graphite, a widely used solid lubricant, was introduced into the frictional interface in the state of free powder. Varying friction coefficient and temperature rise were recorded online. The powder layer formed on the frictional surface of the bottom samples was observed by an optical microscope after tests. The comparative research demonstrated the tribological characteristics of powder lubrication are similar to that of polytetrafluoroethylene coating. Besides, the powder lubrication provides longer lubrication life, although the powder was difficult to seal and control during the tests. Within the proper range of sliding velocities and normal loads, the powder layer dynamically formed on the contact surface of the bottom samples, which resulted in the self-replenishing and oil-free lubrication. The powder layer inclined to deteriorate under lower velocity and higher load. The tests with higher velocity exhibited lower friction coefficient and higher temperature rise. The tests with lower load exhibited higher friction coefficient and lower temperature rise. The state of powder layer included typically four stages such as the full layer, the partial detachment, the serious detachment, and the complete destruction. The damage degree of powder layer is not in proportion to the friction coefficient or the temperature rise due to the particularity of powder lubrication.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wornyoh, E.Y.A., Jasti, V.K., Higgs, C.F.: A review of dry particulate lubrication: powder and granular materials. J. Tribol. 129, 438–449 (2007)
Iordanoff, I., Khonsari, M.M.: Granular lubrication: toward an understanding of the transition between kinetic and quasi-fluid regime. J. Tribol. 126, 137–145 (2004)
Khonsari, M.M.: On the modeling of multi-body interaction problems in tribology. Wear 207, 55–62 (1997)
Greenberg, R., Halperin, G., Etsion, I., Tenne, R.: The effect of WS2 nanoparticles on friction reduction in various lubrication regimes. Tribol. Lett. 17, 179–186 (2004)
Jeng, Y.R., Tsai, H.J.: Grain-flow lubrication of finite-width slider bearings with rough surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 13, 219–232 (2002)
Kaur, R.G., Heshmat, H.: 100 mm diameter self-contained solid/powder lubricated auxiliary bearing operated at 30,000 rpm. Tribol. Trans. 45, 76–84 (2002)
Heshmat, H., Brewe, D.: Performance of powder-lubricated journal bearings with MoS2 powder—experimental-study of thermal phenomena. J. Tribol. 117, 506–512 (1995)
Higgs, C.F., Heshmat, C.A., Heshmat, H.S.: Comparative evaluation of MoS2 and WS2 as powder lubricants in high speed, multi-pad journal bearings. J. Tribol. 121, 625–630 (1999)
Heshmat, H.: Wear reduction systems for coal-fueled diesel-engines. 1. The basics of powder lubrication. Wear 162, 508–517 (1993)
Reddy, N.S.K., Kwang-Sup, S., Yang, M.Y.: Experimental study of surface integrity during end milling of Al/SiC particulate metal-matrix composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 201, 574–579 (2008)
Reddy, N.S.K., Rao, P.V.: Experimental investigation to study the effect of solid lubricants on cutting forces and surface quality in end milling. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 46, 189–198 (2006)
Kimura, R., Yoshida, M., Sasaki, G., Pan, J., Fukunaga, H.: Characterization of heat insulating and lubricating ability of powder lubricants for clean and high quality die casting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 130, 289–293 (2002)
Elkholy, K.N., Khonsari, M.M.: Experimental investigation on the stick-slip phenomenon in granular collision lubrication. J. Tribol. 130, 7 (2008)
Elkholy, K.N., Khonsari, M.M.: Granular collision lubrication: experimental investigation and comparison to theory. J. Tribol. 129, 923–932 (2007)
Jang, J.Y., Khonsari, M.M.: On the role of enduring contact in powder lubrication. J. Tribol. 128, 168–175 (2006)
Jang, J.Y., Khonsari, M.M.: On the granular lubrication theory. Proc. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 461, 3255–3278 (2005)
Yu, C.M., Craig, K., Tichy, J.: Granular collision lubrication. J. Rheol. 38, 921–936 (1994)
Yu, C.M., Tichy, J.: Granular collisional lubrication: effect of surface roughness, particle size and solids fraction. Tribol. Trans. 39, 537–546 (1996)
Higgs, C.F., Tichy, J.: Effect of particle and surface properties on granular lubrication flow. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. 222, 703–713 (2008)
Higgs, C.F., Tichy, J.: Granular flow lubrication: continuum modeling of shear behavior. J. Tribol. 126, 499–510 (2004)
Iordanoff, I., Elkholy, K., Khonsari, M.M.: Effect of particle size dispersion on granular lubrication regimes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. 222(6), 725–739 (2008)
Iordanoff, I., Fillot, N., Berthier, Y.: Numerical study of a thin layer of cohesive particles under plane shearing. Powder Technol. 159, 46–54 (2005)
Tichy, J., Berthier, Y., Iordanoff, I.: A continuum description of dense granular lubrication flow. J. Tribol. 130, 8 (2008)
Kabir, M.A., Lovell, M.R., Higgs, C.F.: Utilizing the explicit finite element method for studying granular flows. Tribol. Lett. 29, 85–94 (2008)
Higgs, C.F., Heshmat, H.: Characterization of pelletized MoS2 powder particle detachment process. J. Tribol. 123, 455–461 (2001)
Heshmat, H., Brewe, D.E.: Performance of a powder lubricated journal bearing with WS2 powder: experimental study. J. Tribol. 118, 484–491 (1996)
Heshmat, H.S., Dill, J.F.: Traction characteristics of high-temperature powder-lubricated ceramics (Si3N4/Alpha-SiC). Tribol. Trans. 35, 360–366 (1992)
Wang, W., Liu, X.J., Liu, K., Li, H.X.: Experimental study on the tribological properties of powder lubrication under plane contact. Tribol. Trans. 53, 274–279 (2010)
Gopal, A.V., Rao, P.V.: Performance improvement of grinding of SiC using graphite as a solid lubricant. Mater. Manuf. Process. 19, 177–186 (2004)
Kimura, R., Yoshida, M., Sasaki, G., Pan, J., Fukunaga, H.: Influence of abnormal structure on the reliability of squeeze castings. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 130, 299–303 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 50775060 and Grant No. 51005067.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Liu, X., Xie, T. et al. Effects of Sliding Velocity and Normal Load on Tribological Characteristics in Powder Lubrication. Tribol Lett 43, 213–219 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9802-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9802-x