Abstract
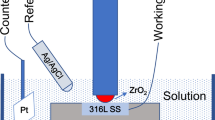
A new tribometer to investigate a conjoint effect of three-body abrasion and corrosion has been developed. In this design, a flat wear sample is loaded against a rotating cylindrical disc counterface and the abrasive slurry is delivered to the contact interface. Capabilities of the newly developed tribometer have been assessed through conducting abrasion–corrosion tests involving simultaneous electrochemical measurements. In this work, the stability of the passive layer on stainless steel under three-body abrasive wear in a near neutral electrolyte was investigated using potentiodynamic polarization tests. 316L Stainless Steel wear samples were abraded by coarse garnet particles in an aerated sodium sulphate electrolyte. The effects of load and speed on the polarization curves and passivity of 316L steel were determined. It was found that under abrasion–corrosion conditions 316L steel became more thermodynamically active and the passive corrosion rate has increased. Increasing the contact load resulted in a small increase in the passive corrosion current, while increasing the rotating speed had the opposite effect of decreasing the current. Linear polarization resistance method was used to analyse corrosion current changes with time during abrasion–corrosion testing. The existence of three distinct stages was explained by the third-body effect on the corrosion potential and current. First stage was revealed by continuous decrease of corrosion potential. Then, the potential reached a plateau for the second and third stages. In the first and second stages, particle constraint in the contact zone plays the major role and a linear rise in corrosion current with time has been recorded. After a certain amount of surface roughening, no further increase in particles entrapment is expected. Therefore, in the third stage steady-state corrosion current values are anticipated. The rig developed can also be used to simulate two-body abrasion–corrosion. The capabilities of the new rig have been compared against other experimental set-ups used in studies of combined abrasion–corrosion behaviour.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landolt, D.: Electrochemical and materials aspects of tribocorrosion systems. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 3121–3127 (2006)
Neville, A., Reyes, M., Xu, H.: Examining corrosion effects and corrosion/erosion interactions on metallic materials in aqueous slurries. Tribol. Int. 35, 643–650 (2002)
Stack, M.M., James, J.S., Lu, Q.: Erosion–corrosion of chromium steel in a rotating cylinder electrode system: some comments on particle size effects. Wear 256, 557–564 (2004)
Wood, R.J.K.: Tribo-corrosion of coatings: a review. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 5502–5521 (2007)
Ponthiaux, P., Wenger, F., Drees, D., Celis, J.P.: Electrochemical techniques for studying tribocorrosion processes. Wear 256, 459–468 (2004)
Assi, F., Bohni, H.: Study of wear–corrosion synergy with a new microelectrochemical technique. Wear 233–235, 505–514 (1999)
Watson, S.W., Friedersdorf, F.J., Madsen, B.W., Cramer, S.D.: Methods of measuring wear-corrosion synergism. Wear 181–183, 476–484 (1995)
Fang, C.K., Huang, C.C., Chuang, T.H.: Synergistic effects of wear and corrosion for Al2O3 particulate-reinforced 6061 aluminium matrix composites. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30A, 643–651 (1999)
Endo, K., Komai, K., Shiomi, H.: Effects of dissolved oxygen in saline corrosive wear of steel. Wear 30, 285–297 (1974)
Babaev, S.G., Amanov, Y.A.: Abrasive wear of 40kh steel in a crude oil medium. Chem. Petrol. Eng. 14, 849–852 (1978)
Allen, C., Ball, A., Protheroe, B.E.: The abrasive–corrosive wear of stainless steels. Wear 74, 287–305 (1981)
Noel, R.E.J., Ball, A.: On the synergistic effects of abrasion and corrosion during wear. Wear 87, 351–361 (1983)
Batchelor, A.W., Stachowiak, G.W.: Predicting synergism between corrosion and abrasive wear. Wear 123, 281–291 (1988)
Abdelkader, H., Elraghy, S.M.: Wear-corrosion mechanisms in stainless steel in chloride media. Corros. Sci. 26, 647–653 (1986)
Yahagi, Y., Mizutani, Y.: Corrosive wear of carbon and austenitic stainless steels in NaCl solution. Wear 110, 401–408 (1986)
Hong, M., Pyun, S.: Corrosive wear behaviour of 304-L stainless steel in 1 N H2S04 solution. Part 1: effect of applied potential. Wear 147, 59–67 (1991)
Garcia, I., Drees, D., Celis, J.P.: Corrosion-wear of passivating materials in sliding contacts based on a concept of active wear track area. Wear 249, 452–460 (2001)
Hedayat, A., Yannacopoulos, S., Postlethwaite, J., Sangal, S.: Aqueous corrosion of plain carbon steel during sliding wear. Wear 154, 167–176 (1992)
Mischler, S., Rosset, E., Stachowiak, G.W., Landolt, D.: Effect of sulphuric acid concentration on the rate of tribocorrosion of iron. Wear 167, 101–108 (1993)
Wu, P., Celis, J.P.: Electrochemical noise measurements on stainless steel during corrosion–wear in sliding contacts. Wear 256, 480–490 (2004)
Latona, N., Fetherston, P., Chen, A., Sridharan, K., Dodd, R.A.: Wear-corrosion comparisons of passivating vs nonpassivating alloys in aerated 3.5% aqueous solutions of sodium chloride. Corrosion 57, 884–888 (2001)
Yan, Y., Neville, A., Dowson, D.: Tribo-corrosion properties of cobalt-based medical implant alloys in simulated biological environments. Wear 263, 1105–1111 (2007)
Yu, S.Y., Ishii, H., Chuang, T.H.: Corrosive wear of SiC whisker- and 6061 aluminum alloy composites particulate-reinforced. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27A, 2653–2662 (1996)
Vieira, A.C., Ribeiro, A.R., Rocha, L.A., Celis, J.P.: Influence of pH and corrosion inhibitors on the tribocorrosion of titanium in artificial saliva. Wear 261, 994–1001 (2006)
Lambrechts, P., Goovaerts, K., Bharadwaj, D., Munck, J.D., Bergmans, L., Peumans, M., Meerbeek, B.V.: Degradation of tooth structure and restorative materials: a review. Wear 261, 980–986 (2006)
Sun, D., Wharton, J.A., Wood, R.J.K., Mab, L., Rainforth, W.M.: Microabrasion–corrosion of cast CoCrMo alloy in simulated body fluids. Tribol. Int. 42, 99–110 (2009)
Newman, R.C.: Understanding corrosion of stainless steel. Corrosion 57, 1030–1041 (2001)
Silverman, D.C.: Rotating cylinder electrode for velocity sensitivity testing. Corrosion 40, 220–1041 (1984)
Tian, B.R., Cheng, Y.F.: Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of X-65 steel in the simulated oil sand slurry I: effects of hydrodynamic condition. Corros. Sci. 50(3), 773–779 (2008)
Neville, A., Hodgkiess, T., Dallas, J.T.: A study of the erosion–corrosion behaviour of engineering steels for marine pumping applications. Wear 187, 497–507 (1995)
Clark, H.M.: Particle velocity and size effects in laboratory slurry erosion measurements. Tribol. Int. 35, 617–624 (2002)
Harvey, T.J., Wharton, J.A., Wood, R.J.K.: Development of synergy model for erosion–corrosion of carbon steel in a slurry pot. Tribology 1, 33–47 (2007)
Meuter, P.: Protecting pumps against abrasive wear. World Pumps 2006(482), 18–20 (2006)
Landolt, D., Mischler, S., Stemp, M., Barril, S.: Third body effects and material fluxes in tribocorrosion systems involving a sliding contact. Wear 256, 517–524 (2004)
Gant, A.J., Gee, M.G., May, A.T.: Microabrasion of WC–Co hardmetals in corrosive media. Wear 256, 954–962 (2004)
Stack, M.M., Jawan, H., Mathew, M.T.: On the construction of micro-abrasion maps for a steel/polymer couple in corrosive environments. Tribol. Int. 38, 848–856 (2005)
Bello, J.O., Wood, R.J.K., Wharton, J.A.: Synergistic effects of micro-abrasion–corrosion of UNS S30403, S31603 and S32760 stainless steels. Wear 263, 149–159 (2007)
Barton, N. A.: Erosion in elbows in hydrocarbon production systems: review document. Health and Safety Executive, UK (2003)
Janikowski, D.S.: Selecting tubing materials for power generation heat exchangers. Mater. Perform. 47, 58–63 (2008)
Lepisto, T.T., Mantyla, T.A.: Degradation of TZP ceramics in humid atmosphere. In: Clark, D.E., Zoitos, B.K. (eds.) Corrosion of Glass, Ceramics and Ceramic Superconductors, pp. 492–513. Noyes Publications, NJ (1992)
Stachowiak, G.B., Stachowiak, G.W.: The effects of particle characteristics on three-body abrasive wear. Wear 249, 201–207 (2001)
Tylczak, J.H.: Friction, lubrication and wear technology. In: Henry, S.D. (ed.), ASM Handbook, Vol. 18, pp. 184–190. ASM International (1992)
Beverskog, B., Puigdomenech, I.: Pourbaix diagram. Corrosion 55, 1077–1088 (1999)
Stephen, T.W.: An Introduction to Electrochemical Corrosion Testing for Practicing Engineers and Scientists. PairODocs Publications, WI (1994)
Scully, J.R.: The polarization resistance method for determination of instantaneous corrosion rates. In: Schweitzer, P.A. (ed.) Electrochemical Techniques in Corrosion Science and Engineering, pp. 125–150. CRC Press (2003)
Walter, G.W.: A review of impedance plot methods used for corrosion performance analysis of painted metals. Corros. Sci. 26, 681–703 (1986)
Rammelt, U., Reinhard, G.: On the applicability of a constant phase element (CPE) to the estimation of roughness of solid metal electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 35, 1045–1049 (2001)
Bardwell, J.A., Sproule, G.I., MacDougall, B., Graham, M.J., Davenport, A.J., Isaacs, H.S.: In situ XANES detection of Cr(VI) in the passive film on Fe-26Cr. J. Electrochem. Soc. 139, 371–373 (1992)
Bojinov, M., Fabricius, G., Kinnunen, P., Laitinen, T., Makela, K., Saario, T., Sundholm, G.: The mechanism of transpassive dissolution of Ni–Cr alloys in sulphate solutions. Electrochim. Acta 45, 2791–2802 (2000)
Bojinov, M., Fabricius, G., Laitinen, T., Saario, T.: Transpassivity mechanism of iron-chromium–molybdenum alloys studied by AC impedance, DC resistance and RRDE measurements. Electrochim. Acta 44, 4331–4343 (1999)
Betova, I., Bojinov, M., Laitinen, T., Makela, K., Pohjanne, P., Saario, T.: The transpassive dissolution mechanism of highly alloyed stainless steels I. Experimental results and modelling procedure. Corros. Sci. 44, 2675–2697 (2002)
Schmuki, P., Virtanen, S., Isaacs, H.S., Ryan, M.R., Davenport, A.J., Bohni, H., Stenberge, T.: Electrochemical behaviour of Cr2O3/Fe2O3 artificial passive films studied by in situ XANES. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145, 791–801 (1998)
Ali, S.I., Abbaschian, G.J.: The chloride corrosion of austenitic stainless steels and of an inconel alloy in hot acidic media. Corros. Sci. 18, 15–19 (1978)
El-Egamy, S.S., Badaway, W.A.: Passivity and passivity breakdown of 304 stainless steel in alkaline sodium sulphate solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 34, 1153–1158 (2004)
Savitzky, A., Golay, M.J.E.: Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least square procedures. Anal. Chem. 36, 1627–1639 (1964)
Stern, M., Geary, A.L.: Electrochemical polarization. J. Electrochem. Soc. 104, 56–59 (1957)
Iwabuchi, A., Tsukamoto, T., Shimizu, T., Yashiro, H.: The mechanism of corrosive wear of an austenitic stainless steel in an aqueous electrolyte solution. Tribol. Trans. 41, 96–102 (1998)
Mischler, S.: Triboelectrochemical techniques and interpretation methods in tribocorrosion: a comparative evaluation. Tribol. Int. 41, 573–583 (2008)
Landolt, D., Mischler, S., Stemp, M.: Electrochemical methods in tribocorrosion: a critical appraisal. Electrochim. Acta 46, 3913–3929 (2001)
Gant, A.J., Gee, M.G., May, A.T.: The evaluation of tribocorrosion synergy for WC-Co hardmetals in low stress abrasion. Wear 256, 500–516 (2004)
Stachowiak, G.B., Stachowiak, G.W.: Wear mechanisms in ball-cratering tests with large abrasive particles. Wear 256, 600–607 (2004)
Stachowiak, G.B., Stachowiak, G.W., Celliers, O.: Ball-cratering abrasion tests of high-Cr white cast irons. Tribol. Int. 38, 1076–1087 (2005)
Rabinowicz, E., Dunn, L.A., Russel, P.G.: A study of abrasive wear under three-body abrasive conditions. Wear 4, 345–355 (1961)
Misra, A., Finnie, I.: Correlations between two-body and three-body abrasion and erosion of metals. Wear 68, 33–39 (1981)
Kelly, D.A., Hutchings, I.M.: A new method for measurement of particle abrasivity. Wear 250, 76–80 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Western Australia, for its support during the preparation of this manuscript. The postgraduate scholarship provided by the CRC Centre for Integrated Engineering Asset Management (CIEAM) is greatly acknowledged. Special thanks to Mr Dennis Brown of the School of Mechanical Engineering Workshop for the manufacturing of the test rig.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salasi, M., Stachowiak, G.B. & Stachowiak, G.W. New Experimental Rig to Investigate Abrasive–Corrosive Characteristics of Metals in Aqueous Media. Tribol Lett 40, 71–84 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9640-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9640-2