Abstract
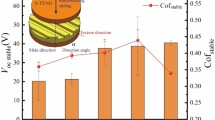
This article reports an investigation of the effect of melting and microstructure on the microscale friction of several silver–bismuth alloys using a high-temperature nanoindentation-tribotesting system. These studies showed that friction increases with temperature before melting. We modeled these results as due to the softening of the alloys with increasing temperature, which appears to adequately explain the experimental trend. The friction behavior upon melting depends on the alloy composition. For some alloy composition, friction was observed to exhibit a sharp decrease upon melting, while for another alloy composition, friction was observed to keep increasing with temperature. This unusual behavior can be explained by the difference in microstructure and phase composition as a function of temperature among different Ag–Bi alloys.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kogoh, S., Sakai, T., Asami, K.: Temperature dependence of tensile-strength and hardness for Nodular cast-Iron and their mutual correlation. J. Mater. Sci. 27(16), 4323–4328 (1992)
Xia, J., Dong, H.S., Bell, T.: Surface properties of a γ-based titanium aluminide at elevated temperatures. Intermetallics 10, 723–729 (2002)
Michel, M.D., Mikowski, A., Lepienski, C.M., Foerster, C.E., Serbena, F.C.: High temperature microhardness of soda-lime glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solid 348, 131–138 (2004)
Yonenaga, I.: Hardness, yield strength, and dislocation velocity in elemental and compound semiconductors. Mater. Trans. 46(9), 1979–1985 (2005)
Chwa, S.O., Klein, D., Liao, H.L., Dembinski, L., Coddet, C.: Temperature dependence of microstructure and hardness of vacuum plasma sprayed Cu-Mo composite coatings. Surf. Coatings Technol. 200(20–21), 5682–5686 (2006)
Hutchison, M.M., Louat, N.: Temperature dependence of yield strength in iron. Acta Metallurgica 10, 255–256 (1962)
Weidner, D.J., Wang, Y.B., Vaughan, M.T.: Yield strength at high-pressure and temperature. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21(9), 753–756 (1994)
Peng, J.X., Jing, F.Q., Li, D.H., Wang, L.L.: Pressure and temperature dependence of shear modulus and yield strength for aluminum, copper, and tungsten under shock compression. J. Appl. Phys. 98(1), Art No. 013508 (2005)
Drobyshevski, E.M., Kolesnikova, E.N., Yuferev, V.S.: Calculating the liquid film effect on solid armature rail-gun launching. IEEE Trans. Magn. 35(1), 53–58 (1999)
Crawford, R., Taylor, J., Keefer, D.: Solid ring armature experiments in a transaugmented railgun. IEEE Trans. Magn. 31(1), 138–143 (1995)
Liu, S.B., Wang, Q.: A three-dimensional thermomechanical model of contact between non-conforming rough surfaces. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 123(1), 17–26 (2001)
Liu, G., Wang, Q., Liu, S.B.: A three-dimensional thermal-mechanical asperity contact model for two nominally flat surfaces in contact. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 123(3), 595–602 (2001)
Wu, J., Pecht, M.G.: Contact resistance and fretting corrosion of lead-free alloy coated electrical contacts. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 29(2), 402–410 (2006)
Wable, G.S., Chu, Q.Y., Damodaran, P., Srihari, K.: A systematic procedure for the selection of a lead-free solder paste in an electronics manufacturing environment. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 17(2), 32–39 (2005)
Suraski, D., Seelig, K.: The current status of lead-free solder alloys. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manufact. 24(4), 244–248 (2001)
Glavatskih, S.B.: Evaluating thermal performance of a PTFE-faced tilting pad thrust bearing. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 125(2), 319–324 (2003)
Lehmann, D., Hupfer, B., Lappan, U., Pompe, G., Haussler, L., Jehnichen, D., Janke, A., Geissler, U., Reinhardt, R., Lunkwitz, K., Franke, R., Kunze, K.: New PTFE-polyamide compounds. Des. Monomers Polym. 5(2–3), 317–324 (2002)
Samyn, P., De, B.P., Schouken, G., Van, P.A.: Large-scale tests on friction and wear of engineering polymers for material selection in highly loaded sliding systems. Mater. Des. 27(7), 535–555 (2006)
Kawachi, T., Takayanagi, S., Asakura, H., Ishikawa, H.: Development of lead free overlay for three layer bearings of highly loaded engines. SAE Technical Papers, Document number: 2005-01-1863
Smith, J.F., Zhang, S.: High temperature nanoscale mechanical property measurements. Surf. Eng. 16(2), 143–146 (2000)
Beake, B.D., Smith, J.F.: High-temperature nanoindentation testing of fused silica and other materials. Philos. Mag. A 82(10), 2179–2186 (2002)
Okamoto, H.: Desk Handbook: Phase Diagram for Binary Alloys. ASM International, Materials Park (2000)
Greenwood, N.N., Earnshaw, A.: Chemistry of the elements, 2nd edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1997)
Hall, E.O.: The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. B 64, 747–753 (1951)
Petch, N.J.: The cleavage strength of polycrystals. J. Iron Steel Inst. 174, 25 (1953)
Goddard, J., Wailman, H.: A theory of friction and wear during the abrasion of metals. Wear 5, 114–135 (1962)
Zou, M., Cai, L., Wang, H., Yang, D., Wyrobek, T.: Adhesion and friction studies of a selectively micro/nano-textured surface produced by UV assisted crystallization of amorphous silicon. Tribol. Lett. 20(1), 43–52 (2005)
Zou, M., Cai, L., Yang, D.: Nanotribology of a silica nanoparticle-textured surface. Tribol. Trans. 49(1), 66–71 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude for the financial support from US Office of Naval Research (MURI N00014-04-0599), and US Department of Energy (DE-FC26-04NT42263), as well as the gift support by the Taiho Kogyo Company to B. He and Q. Wang. However, any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsors. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Jim Smith from Micro Materials Ltd. for his helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, B., Ghosh, G., Chung, YW. et al. Effect of Melting and Microstructure on the Microscale Friction of Silver–Bismuth Alloys. Tribol Lett 38, 275–282 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9606-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9606-4