Abstract
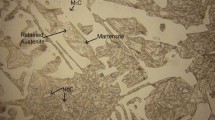
This investigation pertains to the analysis of the sliding wear response of a cast iron over a range of applied pressures in the presence of an oil lubricant. The effect of varying concentrations of lead particles suspended in the oil lubricant on the wear behaviour of the cast iron was also examined. The wear rate increased with pressure initially at a lower rate followed by a higher rate of increase beyond a specific pressure. Furthermore, the presence of suspended lead particles up to a specific concentration in the oil proved beneficial while the trend reversed at still higher concentrations. The extent of frictional heating increased with test duration at a high rate in the beginning of the tests. This was followed by a reduced rate of temperature increase at longer test durations. In some cases, the rate of temperature rise increased once again while it reduced in one case towards the end of the tests. The severity and extent of frictional heating also increased with pressure. Lead addition to the oil lubricant up to a specific concentration led to a reduced degree of heating while the trend reversed at still higher lead contents. Specimen seizure caused significantly high wear rate and frictional heating. The observed wear response of the samples has been explained in terms of specific characteristics like cracking tendency and lubricating and load bearing capacity of various microconstituents of the specimen material. Another important factor of concern affecting wear characteristics was observed to be lubricating film formation and its stability during sliding. The wear behaviour has also been substantiated through the characteristics of wear surfaces and subsurface regions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eyre, T.S.: Friction and wear of cast irons. In: Metals Handbook: Friction, Lubrication and Wear Technology, vol 18, 10th edn., pp. 695–701. ASM International, Materials Park (1992)
White, C.V.: Gray iron. In: Metals Handbook: Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels and High Performance Materials, vol 1, 10th edn., pp. 12–32. ASM International, Materials Park (1990)
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., He, R., Shen, B.: Investigation of tribological properties of brake shoe materials—phosphorous cast irons with different graphite morphologies. Wear 166, 179–186 (1993)
Boehringer, R.H.: Grease. In: Metals Handbook: Friction, Lubrication and Wear Technology, vol 18, 10th edn., pp. 123–131. ASM International, Materials Park (1992)
Bhushan, B., Gupta, B.K. (eds.): Solid lubricants and self-lubricating solids (Chap. 5). Handbook of Tribology, pp. 5.1–5.86. McGraw Hill, New York (1991)
Rizvi, S.Q.A.: Lubricant additives and their functions. In: Metals Handbook: Friction, Lubrication and Wear Technology, vol 18, 10th edn., pp. 98–112. ASM International, Materials Park (1992)
Yazun, M., Wancheng, Z., Shengna, L., Yuansheng, J., Yuscong, W., Simon, T.C.: Tribological performance of three advanced piston rings in the presence of MoDTC-modified GF-3 oils. Tribol. Lett. 18, 75–83 (2005)
Bailey, A.R., Samuels, L.E. (eds.): Foundry Metallography: An Elementary Analysis of Microstructure and Properties of Selected Foundry Alloys. Metallurgical Services, Betchworth, Surrey (1976)
Pratt, G.C.: Materials for plain bearings. Int. Metall. Rev. 18, 1–27 (1973)
Properties of cast copper alloys. In: Metals Handbook, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Pure Metals, vol 2, 9th edn., pp. 395–439. ASM International, Materials Park (1979)
Prasad, B.K., Patwardhan, A.K., Yegneswaran, A.H.: Microstructure and property characterization of a modified zinc-based alloy and comparison with bearing alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perfom. 7, 130–135 (1998)
Prasad, B.K., Patwardhan, A.K., Yegneswaran, A.H.: Dry sliding wear characteristics of some zinc-aluminium alloys: a comparative study with a bearing bronze at a slow speed. Wear 199, 142–151 (1996)
Prasad, B.K., Patwardhan, A.K., Yegneswaran, A.H.: Factors controlling the dry sliding wear behaviour of a leaded-tin bronze. Mater. Sci. Technol. 12, 427–435 (1996)
Prasad, B.K., Patwardhan, A.K., Yegneswaran, A.H.: Characterization of the wear response of a modified zinc-based alloy vis-a-vis a conventional zinc-based alloy and a bearing bronze at a high sliding speed. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27, 3513–3523 (1996)
Prasad, B.K., Patwardhan, A.K., Yegneswaran, A.H.: Wear characteristics of a zinc-based alloy compared with a conventional bearing bronze under mixed lubrication condition: effects of material and test parameters. Can. Metall. Q. 40, 193–210 (2001)
Prasad, B.K.: Sliding wear behaviour of bronzes under varying material composition, microstructure and test conditions. Wear 257, 110–123 (2004)
Prasad, B.K.: Dry sliding wear response of some bearing alloys as influenced by the nature of the microconstituents and sliding conditions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28, 809–815 (1997)
Mohan, S., Aggarwala, V., Ray, S.: Wear characteristics of stir cast aluminium-lead alloys. Z. Metallkd. 80, 904–908 (1989)
Tiwari, S.N., Malhotra, S.L., Pathak, J.P.: Seizure resistance of leaded aluminium bearing alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1, 1040–1045 (1985)
Tiwari, S.N., Malhotra, S.L., Pathak, J.P.: Microstructures and mechanical properties of leaded aluminum alloy. Met. Technol. 10, 413–423 (1983)
Aramov, Y.S., Filonenko, V.P., Gruzdov, A.P., Shlyapin, A.D.: Change of the structure and properties of alloys of aluminum with lead in the process of plastic strain. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 26, 543–546 (1984)
Prasad, B.K.: Effectiveness of an externally added solid lubricant on the sliding wear response of a zinc–aluminium alloy, its composite and cast iron. Tribol. Lett. 18, 135–143 (2005)
Prasad, B.K., Modi, O.P.: Sliding wear response of zinc-based alloy as affected by suspended solid lubricant particles in oil lubricant. Tribology 2, 84–91 (2008)
Prasad, B.K.: Sliding wear response of a cast iron under varying test environments and traversal speed and pressure conditions. Wear 260, 1333–1341 (2006)
Prasad, B.K.: Sliding wear response of cast iron as influenced by microstructural features and test condition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 456, 373–385 (2007)
Prasad, B.K.: Sliding wear response of spheroidal graphite cast iron as influenced by applied pressure, sliding speed and test environment. Can. Metall. Q. 47, 495–507 (2008)
Prasad, B.K.: Sliding wear characteristics of a gray cast iron as influenced by the sliding speed, load and environment. Tribology 2, 128–138 (2008)
Prasad, B.K.: Sliding wear behaviour of a cast iron as affected by test environment and applied load. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 161, 161–172 (2009)
Prasad, B.K.: Lubricated sliding wear behaviour of a cast iron: effect of graphite and/or talc fraction in oil. J. Mater. Eng. Perfom. doi:10.1007/s11665-009-9480-0 (in press)
Prasad, B.K.: Influence of suspended talc particles in oil and nature of material microconstituents on sliding wear characteristics of cast iron and zinc-based alloy. Can. Metall. Q. (in press)
Gulyaev, A.G. (ed.): Physical Metallurgy, vol. 1, pp. 198–216. Mir, Moscow (1980)
Prasad, B.K., Das, S.: The significance of matrix microstructure on the solid lubrication characteristics of graphite in aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 144, 229–235 (1991)
Rayiko, M.V., Dmytrychenko, N.F.: Some aspects of boundary lubrication in the local contact of friction surfaces. Wear 126, 69–78 (1988)
Modi, O.P., Prasad, B.K., Yegneswaran, A.H., Vaidya, M.L.: Dry sliding wear behaviour of squeeze cast aluminium alloy-silicon carbide composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 151, 235–245 (1992)
Mondal, D.P., Das, S., Rao, R.N., Singh, M.: Effect of SiC addition and running-in-wear on the sliding wear behaviour of Al–Zn–Mg aluminium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 402, 307–319 (2005)
Kennedy Jr., F.E.: Thermal and thermomechanical effects in dry sliding. Wear 100, 453–476 (1984)
Rigney, D.A., Chen, L.H., Naylor, M.G.S., Rosenfield, A.R.: Wear processes in sliding systems. Wear 100, 195–219 (1984)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, B.K., Rathod, S., Yadav, M.S. et al. The Influence of Lead Suspension in Oil Lubricant on the Sliding Wear Behaviour of Cast Iron. Tribol Lett 37, 289–299 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9526-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9526-3