Abstract
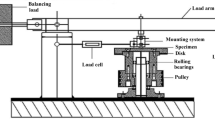
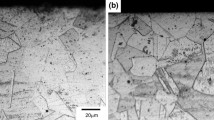
The friction and wear properties of Al–25Zn–3Cu alloy were investigated over a range of oil flow rate, pressure and sliding speed using a pin-on-disc machine, after examining its microstructure and mechanical properties. The results obtained were compared with those of a conventional-bearing material (SAE 65 bronze). It was observed that the microstructure of the Al–25Zn–3Cu alloy consisted of aluminium-rich α, eutectoid α + η and θ phases, while the microstructure of the SAE 65 bronze revealed copper-rich α, and eutectoid α + δ phases. It was found that the friction coefficient, temperature and wear volume of both the alloys decreased sharply with increasing oil flow rate and attained almost constant levels beyond a certain range of oil flow rate. It was also found that the friction coefficient and the wear volume of the alloys decreased with increasing pressure, but was observed to be almost independent of the sliding speed. The Al–25Zn–3Cu alloy exhibited higher wear resistance as compared to that of the bronze under all the test conditions. Smearing type of adhesion appeared to be the most effective wear mechanism for the Al–25Zn–3Cu alloy, while abrasion dominated one for the SAE 65 bronze.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemdağ, Y., Savaşkan, T.: Effects of silicon content on the mechanical properties and lubricated wear behaviour of Al–40Zn–3Cu–(0–5)Si alloys. Tribol. Lett. 29, 221–227 (2008)
Alemdağ, Y., Savaşkan, T.: Mechanical and tribological properties of Al–40Zn–Cu alloys. Tribol. Int. 42, 176–182 (2009)
Savaşkan, T., Alemdağ, Y.: Effects of pressure and sliding speed on the friction and wear properties of Al–40Zn–3Cu–2Si alloy: a comparative study with SAE 65 bronze. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 496, 517–523 (2008)
Murphy, S., Savaşkan, T.: Comparative wear behaviour of Zn–Al-based alloys in an automotive engine application. Wear 98, 151–161 (1984)
Murphy, S.: Solid-state reactions in the low-copper part of the Al–Cu–Zn system. Z. Metallkd. 71, 96–102 (1980)
Savaşkan, T., Murphy, S.: Mechanical properties and lubricated wear of Zn–25Al-based alloys. Wear 116, 211–224 (1987)
Lee, P., Savaşkan, T., Laufer, E.: Wear resistance and microstructure of Zn–Al–Si and Zn–Al–Cu alloys. Wear 117, 79–89 (1987)
Prasad, B.K.: Influence of heat treatment on the physical, mechanical and tribological properties of a zinc-based alloy. Z. Metallkd. 87, 226–232 (1996)
Azaklı, Z., Savaşkan, T.: An examination of frictional and sliding wear properties of Zn–40Al–2Cu–2Si alloy in case of oil cut off. Tribol. Int. 41, 9–16 (2008)
Savaşkan, T., Bican, O., Alemdağ, Y.: Developing aluminium-zinc-based a new alloy for tribological applications. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1969–1976 (2009)
Savaşkan, T., Hekimoğlu, A.P., Pürçek, G.: Effect of copper content on the mechanical and sliding wear properties of monotectoid-based zinc–aluminium–copper alloys. Tribol. Int. 37, 45–50 (2004)
Modi, O.P., Yadav, R.P., Prasad, B.K., Jha, A.K., Dasgupta, R., Dixit, G.: Effects of swaging and aluminum content on the microstructure and mechanical and sliding wear properties of zinc-based alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM 39(5), 582–586 (1998)
Prasad, B.K.: Sliding wear response of a zinc-based alloy and its composite and comparison with a gray cast iron: influence of external lubrication and microstructural features. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 392, 427–439 (2005)
Savaşkan, T., Bican, O.: Effects of silicon content on the microstructural features and mechanical and sliding wear properties of Zn–40Al–2Cu–(0–5)Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 404, 259–269 (2005)
Prasad, B.K.: Effect of silicon addition and test parameters on the sliding wear characteristics of zinc-based alloy containing 37.5% aluminium. Mater. Trans. JIM 38, 701–706 (1997)
Prasad, B.K.: Effects of partially substituting copper by silicon on the physical, mechanical and wear properties of a Zn–37.5%Al-based alloy. Mater. Charact. 44, 301–308 (2000)
Anantharaman, T.R., Ramaswamy, V., Butler, E.P.: Effect of matrix precipitation on cellular growth kinetics in an Al–28 at.%Zn alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 9, 240–244 (1974)
Rollason, E.C.: Metallurgy for Engineers. Edward Arnold, London (1973)
Ashby, M.F., Jones, D.R.H.: Engineering Materials. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1983)
Rabinowicz, E.: Friction and Wear of Materials. Willey, New York (1995)
Halling, J.: Principles of Tribology. Macmillan Education Ltd., London (1989)
Hutchings, I.M.: Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials. Edward Arnold, London (1992)
Bowden, F.W., Tabor, D.: The Friction and Lubrication of Solids. Clarendon Press, Oxford (2001)
Acknowledgement
The authors greatly appreciate the financial support provided by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) Grant No: 108M292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bican, O., Savaşkan, T. Influence of Test Conditions on the Lubricated Friction and Wear Behaviour of Al–25Zn–3Cu Alloy. Tribol Lett 37, 175–182 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9509-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9509-4