Abstract
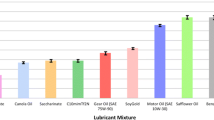
The lubricating properties of two ionic liquids (ILs) with the same anion but different cations, one ammonium IL [C8H17]3NH.Tf2N and one imidazolium IL C10mim.Tf2N, were evaluated both in neat form and as oil additives. Experiments were conducted using a standardized reciprocating sliding test with a segment of a Cr-plated diesel engine piston ring against a gray cast iron flat specimen. The cast iron surface was prepared with simulated honing marks as on a typical internal combustion engine cylinder liner. The selected ILs were benchmarked against conventional hydrocarbon oils. Substantial friction and wear reductions, up to 55% and 34%, respectively, were achieved for the neat ILs compared to a fully formulated 15W40 engine oil. Adding 5 vol% ILs into mineral oil has demonstrated significant improvement in the lubricity. One blend even outperformed the 15W40 engine oil with 9% lower friction and 34% less wear. Lubrication regime modeling, worn surface morphology examination, and surface chemical analysis were conducted to help understand the lubricating mechanisms for ILs. Results suggest great potential for using ionic liquids as base lubricants or lubricant additives for diesel engine applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tung, S.C., McMillan, M.L.: Automotive tribology overview of current advances and challenges for the future. Tribol. Int. 37, 517–536 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2004.01.013
Ye, C., Liu, W., Chen, Y., Yu, L.: Room-temperature ionic liquids: a novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2244–2245 (2001) doi:10.1039/b106935g
Ye, C., Liu, W., Chen, Y., Ou, Z.: Tribological behavior of Dy-sialon ceramics sliding against Si3N4 under lubrication of fluorine-containing oils. Wear 253, 579–584 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(02)00042-X
Liu, W., Ye, C., Chen, Y., Ou, Z., Sun, D.C.: Tribological behavior of sialon ceramics sliding against steel lubricated by fluorine-containing oils. Tribol. Int. 35, 503–509 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0301-679X(02)00044-0
Lu, Q., Wang, H., Ye, C., Liu, W., Xue, Q.: Room temperature ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-hexylimidazoliumbis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-imide as lubricant for steel–steel contact. Tribol. Int. 37, 547–552 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2003.12.003
Mu, Z., Zhou, F., Zhang, S., Liang, Y., Liu, W.: Effect of the functional groups in ionic liquid molecules on the friction and wear behavior of aluminum alloy in lubricated aluminum-on-steel contact. Tribol. Int. 38, 725–731 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2004.10.003
Jiménez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Iglesias, P., Carrión, F.J., Martínez-Nicolás, G.: 1-N-alkyl -3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids as neat lubricants and lubricant additives in steel–aluminium contacts. Wear 260, 766–782 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2005.04.016
Jiménez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Carrión, F.J., Martínez-Nicolás, G.: Room temperature ionic liquids as lubricant additives in steel–aluminium contacts: influence of sliding velocity, normal load and temperature. Wear 261, 347–359 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2005.11.004
Liu, X., Zhou, F., Liang, Y., Liu, W.: Tribological performance of phosphonium based ionic liquids for an aluminum-on-steel system and opinions on lubrication mechanism. Wear 261, 1174–1179 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2006.03.018
Liu, X., Zhou, F., Liang, Y., Liu, W.: Benzotriazole as the additive for ionic liquid lubricant: one pathway towards actual application of ionic liquids. Tribol. Lett. 23, 191–196 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11249-006-9050-7
Xia, Y., Wang, S., Zhou, F., Wang, H., Lin, Y., Xu, T.: Tribological properties of plasma nitrided stainless steel against SAE52100 steel under ionic liquid lubrication condition. Tribol. Int. 39, 635–640 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2005.04.030
Jiménez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D.: Ionic liquids as lubricants for steel–aluminum contacts at low and elevated temperatures. Tribol. Lett. 26, 53–60 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11249-006-9182-9
Mu, Z., Wang, X., Zhang, S., Liang, Y., Bao, M., Liu, W.: Investigation of tribological behavior of Al–Si alloy against steel lubricated with ionic liquids of 1-diethylphosphonyl-n-propyl-3-alkylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate. J. Tribol. 130, 034501 (2008). doi:10.1115/1.2913553
Yu, B., Zhou, F., Pang, C., Wang, B., Liang, Y., Liu, W.: Tribological evaluation of α,ω-diimidazoliumalkylene hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid and benzotriazole as additive. Tribol. Int. 41, 797–801 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2008.02.004
Pensado, A.S., Comunas, M.J.P., Fernandez, J.: The pressure–viscosity coefficient of several ionic liquids. Tribol. Lett. 31, 107–118 (2008). doi:10.1007/s11249-008-9343-0
Nogi, T.: Some tribological properties of an ionic liquid. In: Proceedings of WTC2005 World Tribology Congress III, Washington, D.C., WTC2005-63326, September 12–16, 2005
Qu, J., Truhan, J.J., Dai, S., Luo, H., Blau, P.J.: Ionic liquids with ammonium cations as lubricants or additives. Tribol. Lett. 22, 207–214 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11249-006-9081-0
Qu, J., Truhan, J.J., Dai, S., Luo, H., Blau, P.J.: Lubricants or lubricant additives composed of ionic liquids containing ammonium cations. U.S. Patent Publication# US-2008-0070817-A1, 2008
Qu, J., Blau, P.J., Dai, S., Luo, H., Meyer, H.M., III, Truhan, J.J.: Tribological characteristics of aluminum alloys against steel lubricated by imidazolium and ammonium ionic liquids. Wear (2009, in press)
Kinzig, B.J., Sutor, P., Sawyer, G.W., Rennie, A., Dickrell, P., Gresham, J.: Novel ionic liquid lubricants for aerospace and MEMS. In: Proceedings of WTC2005 World Tribology Congress III, Washington, D.C., WTC2005-63744, September 12–16, 2005
Yu, G., Zhou, F., Liu, W., Liang, Y., Yan, S.: Preparation of functional ionic liquids and tribological investigation of their ultra-thin films. Wear 260, 1076–1080 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2005.07.021
Weng, L., Liu, X., Liang, Y., Xue, Q.: Effect of tetraalkylphosphonium based ionic liquids as lubricants on the tribological performance of a steel-on-steel system. Tribol. Lett. 26, 11–17 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11249-006-9175-8
Jiménez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Iglesias, P., Carrión, F.J., Martínez-Nicolás, G.: Neat ionic liquids and additives in lubrication of steel-aluminum. In: Proceedings of WTC2005 World Tribology Congress III, Washington, D.C., WTC2005-63120, September 12–16, 2005
Phillips, B.S., Zabinski, J.S.: Ionic liquid lubrication effects on ceramics in a water environment. Tribol. Lett. 17, 533–541 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:TRIL.0000044501.64351.68
Jiménez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D.: Imidazolium ionic liquids as additives of the synthetic ester propylene glycol dioleate in aluminium–steel lubrication. Wear 265, 787–798 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2008.01.009
Swatloski, R.P., Holbrey, J.D., Rogers, R.D.: Ionic liquids are not always green: hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate. Green Chem. 5, 361–363 (2003). doi:10.1039/b304400a
Baker, G.A., Baker, S.N.: A simple colorimetric assay of ionic liquid hydrolytic stability. Aust. J. Chem. 58, 174–177 (2005). doi:10.1071/CH05028
ASTM Test Standard G 181-04, ASTM International Annual Book of Standards, 03.02 (2004)
Truhan, J.J., Qu, J., Blau, P.J.: A rig test to measure friction and wear of heavy duty diesel engine piston rings and cylinder liners using realistic lubricants. Tribol. Int. 38, 211–218 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2004.08.003
Truhan, J.J., Qu, J., Blau, P.J.: The effect of lubricating oil condition on the friction and wear of piston ring and cylinder liner materials in a reciprocating bench test. Wear 259, 1048–1055 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2005.01.025
Blau, P.J.: Simulation of cylinder bore surface finish parameters to improve laboratory-scale friction tests in new and used diesel oil. In: Proceedings of ASME 2001 ICE Division Fall Technical Conference, Chicago, IL, September 23–26, 2001
Qu, J., Truhan, J.J.: An efficient method for accurately determining wear volumes of sliders with non-flat wear scars and compound curvatures. Wear 261, 848–855 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2006.01.009
Hamrock, B.J., Dowson, D.: Ball Bearing Lubrication—The Elastohydrodynamics of Elliptical Contacts. Wiley, New York (1981)
Nicholls, M.A., Do, T., Norton, P.R., Kasrai, M., Bancroft, G.M.: Review of the lubrication of metallic surfaces by zinc dialkyl-dithiophosphates. Tribol. Int. 38, 15–39 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2004.05.009
Acknowledgments
Research sponsored by the Vehicle Technologies Program, Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, and the SHaRE User Facility, which is sponsored by the Division of Scientific User Facilities, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725 with UT-Battelle LLC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Blau, P.J., Dai, S. et al. Ionic Liquids as Novel Lubricants and Additives for Diesel Engine Applications. Tribol Lett 35, 181–189 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9447-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9447-1