Abstract
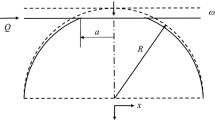
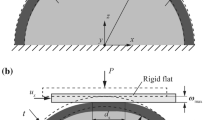
A theoretical model is developed to study the effect of dwell time on the junction growth and static friction of a creeping polymer sphere in contact with a rigid flat under full stick contact condition. A rapid normal loading into the elastic–plastic contact regime is followed by a rest period during which creep takes place causing contact area growth, and stress relaxation that can completely eliminate the plastic zone in the sphere. At the end of this rest time, an increasing tangential loading is applied to the flat till sliding inception occurs. During this loading step, further increase of the contact area and reappearing of a plastic zone in the sphere take place. An increase in static friction resulting from the dwell time during the creep stage is clearly demonstrated and explained.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Contact area
- C1, C2, C3, C4:
-
Modified time hardening parameters
- d :
-
Diameter of contact area
- E :
-
Young’s modulus of the sphere
- K T :
-
Tangential stiffness
- \( K_{\text{T}}^{*} \) :
-
Dimensionless tangential stiffness \( K_{\text{T}} \omega_{0} /P \)
- L c :
-
Critical normal load for full stick contact condition
- P :
-
Normal load
- P*:
-
Dimensionless normal load P/L c
- Q :
-
Tangential load
- Q*:
-
Dimensionless tangential load Q/L c
- R :
-
Radius of the sphere
- t :
-
Dwell time
- u x :
-
Tangential displacement of the flat
- \( u_{x}^{*} \) :
-
Dimensionless tangential displacement u x /ω 0
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- δ c :
-
Critical interference for full stick contact condition
- ɛ :
-
Equivalent von Misses strain
- μ :
-
Static friction coefficient
- ν :
-
Poisson’s ratio of the sphere
- σ :
-
Equivalent von Misses stress
- σ Y :
-
Yield stress
- ω :
-
Normal interference
- 0:
-
At t = 0
- c:
-
Critical value for first plastic yield under normal load
- cr:
-
Creep component
- max:
-
At sliding inception
References
Rymuza, Z., Kusznierewicz, Z., Solarski, T., Kwacz, M., Chizhik, S.A., Goldade, A.V.: Static friction and adhesion in polymer–polymer microbearings. Wear 238, 56–69 (2000)
Feyzullahoglu, E., Saffak, Z.: The tribological behaviour of different engineering plastics under dry friction conditions. Mater. Des. 29, 205–211 (2008)
Deladi, E.L., de Rooij, M.B., Schipper, D.J.: Modeling of static friction in rubber–metal contact. Tribol. Int. 40, 588–594 (2007)
McKellop, H.A.: The lexicon of polyethylene wear in artificial joints. Biomaterials 28, 5049–5057 (2007)
Li, Y.F., Trauner, D., Talke, F.E.: Effect of humidity on stiction and friction of the head/disk interface. IEEE Trans. Magn. 26, 2487–2489 (1990)
Coulomb, C.A.: Theorie des machines simples. Mem. Math. Phys. Acad. Sci. 10, 161–331 (1785)
Merkher, Y., Sivan, S., Etsion, I., Maroudas, A., Halperin, G., Yosef, A.: A rational human joint friction test using a human cartilage-on-cartilage arrangement. Tribol. Lett. 22, 29–36 (2006)
Gitis, N.V., Volpe, L.: Nature of static friction time dependence. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 25, 605–612 (1992)
Ishlinskii, A., Kragelskii, I.: On stick-slip in sliding. J. Tech. Phys. 14, 276–282 (1944). (in Russian)
Kato, S., Sato, N., Matsubayashi, T.: Some considerations on characteristics of static friction of machine tool slideways. J. Lub. Technol. Trans. ASME 94, 234–247 (1972)
Rabinowicz, E.: The intrinsic variables affecting the stick-slip process. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lon. 71, 668–675 (1958)
Ferrero, J.F., Barrau, J.J.: Study of dry friction under small displacement and near-zero sliding velocity. Wear 209, 322–327 (1997)
Al-Bender, F., Lampaert, V., Swevers, J.: A novel generic model at asperity level for dry friction force dynamics. Tribol. Lett. 16, 81–93 (2004)
Tabor, D.: Junction growth in metallic friction: the role of combined stresses and surface contamination. Proc. R. Soc. A 251, 378–393 (1959)
Mindlin, R.D.: Compliance of elastic bodies in contact. J. Appl. Mech. 71, 259–268 (1949)
Chang, W.R., Etsion, I., Bogy, D.B.: A static friction coefficient model for metallic rough surfaces. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 110, 57–63 (1988)
Kogut, L., Etsion, I.: A semi-analytical solution for the sliding inception of a spherical contact. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 125, 499–506 (2003)
Brizmer, V., Kligerman, Y., Etsion, I.: Elastic–plastic spherical contact under combined normal and tangential loading in full stick. Tribol. Lett. 25, 61–70 (2007)
Brizmer, V., Kligerman, Y., Etsion, I.: A model for junction growth of a spherical contact. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 129, 783–790 (2007)
Ovcharenko, A., Halperin, G., Etsion, I.: In situ and real-time optical investigation of junction growth in spherical elastic–plastic contact. Wear 264, 1043–1050 (2008)
Johnson, K.L.: Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1985)
Brot, C.C., Etsion, I., Kligerman, Y.: A contact model for a creeping sphere and a rigid flat. Wear 265, 598–605 (2008)
Ovcharenko, A., Halperin, G., Etsion, I.: Experimental study of a creeping polymer sphere in contact with a rigid flat. J. Tribol. Trans. ASME 131, 011404 (2009)
Findley, W.N., Lai, J.S., Onaran, K.: Creep and Relaxation of Nonlinear Viscoelastic Materials. Dover Publications, Inc., New York (1989)
Cheng, L., Xia, X., Yu, W., Scriven, L.E., Gerberich, W.W.: Flat-punch indentation of viscoelastic material. J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys. 38, 10–22 (2000)
Giri, M., Bousfield, D., Unertl, W.N.: Stress intensity in viscoelastic contacts. Tribol. Lett. 9, 33–39 (2000)
O’Toole, J.L.: Creep Properties of Plastics. McGraw-Hill, New York (1969)
Brizmer, V., Kligerman, Y., Etsion, I.: The effect of contact conditions and material properties on the elasticity terminus of a spherical contact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 5736–5749 (2006)
Greenwood, J.A., Williamson, J.B.P.: Contact of nominally flat surfaces. Proc. Roy. Soc. A 295, 300–319 (1966)
Bartenev, G.M., Lavrentev, V.V.: Friction and Wear of Polymers. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1981)
Benabdallah, H.S.: Static friction coefficient of some plastics against steel and aluminum under different contact conditions. Tribol. Int. 40, 64–73 (2007)
Baumberger, T.: Contact dynamics and friction at solid–solid interface: material versus statistical aspects. Solid State Commun. 102, 175–185 (1997)
Dokos, S.J.: Sliding friction under extreme pressures. J. Appl. Mech. 13, A148–A156 (1946)
Pascoe, M.W., Tabor, D.: The friction and deformation of polymers. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lon. A 235, 210–224 (1956)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malamut, S., Kligerman, Y. & Etsion, I. The Effect of Dwell Time on the Static Friction in Creeping Elastic–Plastic Polymer Spherical Contact. Tribol Lett 35, 159–170 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9445-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9445-3