Abstract
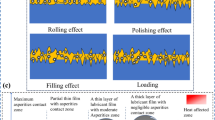
The mending effect and mechanism of metal nano-particles in an area undergoing wear are quite important for both the fundamental theory of nano-tribology and the development of lubricant additives. This paper presents research on the mending effect of copper nano-particles added to lubricant oil. Pin-on-disk experiments and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) observations show that copper nano-particles do display an excellent mending effect. The observation by Scanning Tunnelling Microscopy (STM) reveals that the mending effect results from the deposition of copper nano-particles onto the wear scar. It has also been disclosed by heating simulation that, due to nano-scale effects, which bring about decrease in the diffusion temperature of copper nano-particles, the heat generated by friction leads to the diffusion of copper nano-particles and their subsequent deposition, which finally results in the so-called mending effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Q. Xia and S. R. Kim, Lubr. Seal. 3 (1999) 33.
J. E. Mack and P. K. Mack, U. S. Patent, No. 4204968.
E. E. Strumban, U. S. Patent, No. 5523006.
Q. Xia, J. Y. Ding and X. G. Ma, Lubr. Oil 6 (1998) 137.
C. A. Melendre, A. Narayansamy and V. A. Maromi, J. Mater. Res. 5 (1989) 1246.
F. He, Z. Y. Zhang and Y. F. Xiao, Lubr. Seal. 5 (1997) 65.
T. Hisakado, T. Tsukizoe and H. Yoshikawa, Trans. ASME 2 (1983) 245.
B. X. Jiang, B. S. Chen and J. X. Dong, Lubr. Seal. 2 (1999) 50.
Z. W. Ou, B. S. Xu and et al., Mater. Res. Guid. 8 (2000) 28.
K. K. Fung, B. X. Qin and X. X. Zhang, Mater. Sci. and Eng. A286 (2000) 135.
L. D. Zhang and J. M. Mou, Nano-Material and Nano-Structure (Science Press, Beijing, 2001).
F. P. Bowdon and D. Tabor, The Friction and Lubrication of Solids (Oxford, Clarendon, 1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Li, X., Qin, B. et al. Investigation of the Mending Effect and Mechanism of Copper Nano-Particles on a Tribologically Stressed Surface. Tribology Letters 17, 961–966 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-8109-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-8109-6