Abstract
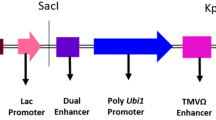
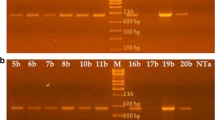
Tobacco plants (Nicotiana tabacum cv Samsun NN) have been transformed with the gene encoding the type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP) SNA-I′ from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) under the control of the Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S promoter. Previous research confirmed that these plants synthesize, correctly process and assemble a fully active RIP. Variability in protein expression was observed within the transgenic lines. The effects of the type-2 RIP SNA-I′ delivered through a leaf feeding assay were evaluated in the laboratory on two economically important pest insects belonging to the orders of Hemiptera, the tobacco aphid (Myzus nicotianae) and Lepidoptera, the beet armyworm (Spodoptera exigua). In the experiment with aphids, significant effects were observed on the life parameters, such as survival, intrinsic rate of increase, net reproductive rate, mean generation time and mean daily offspring, whereas with caterpillars significant reduction in fresh weight as well as retardation in development were observed. In addition, significant increases in mortality were noted for insects fed on the transgenic lines as compared to wild type plants. This information provides further support for RIPs having a role in plant resistance to insect pest species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbieri L, Battelli MG, Stirpe F (1993) Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants. Biochem Biophys Acta 1154:237–282
Barbieri L, Ciani M, Girbes T, Liu WY, Van Damme EJM, Peumans WJ, Stirpe F (2004) Enzymatic activity of toxic and non-toxic type 2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. FEBS Lett 563:219–222
Baykal U, Tumer NE (2007) The C-terminus of pokeweed antiviral protein has distinct roles in transport to the cytosol, ribosome depurination and cytotoxicity. Plant J 49:995–1007
Birch LC (1948) The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J Anim Ecol 17:15–26
Chen Y, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM (2002a) The Sambucus nigra type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein SNA-I′ exhibits in planta antiviral activity in transgenic tobacco. FEBS Lett 516:27–30
Chen Y, Vandenbussche F, Rougé P, Proost P, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM (2002b) A complex fruit-specific type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) is correctly processed and assembled in transgenic tobacco plants. Eur J Biochem 269:2897–2906
Deloach CJ (1974) Rate of increase of population of cabbage, green peach, and turnip aphids at constant temperatures. Ann Entomol Soc Am 67:332–340
Deraison C, Darboux I, Duportets L, Gorojankina T, Rahbé Y, Jouanin L (2004) Cloning and characterization of a gut-specific cathepsin L from the aphid Aphis gossypii. Insect Mol Biol 13:165–177
Dowd PF, Mehta AD, Boston RS (1998) Relative toxicity of the maize endosperm ribosome-inactivating protein to insects. J Agric Food Chem 46:3775–3779
Dowd PF, Zou WN, Gillikin JW, Johnson ET, Boston RS (2003) Enhanced resistance to Helicoverpa zea in tobacco expressing an activated form of maize ribosome-inactivating protein. J Agri Food Chem 51:3568–3574
Dowd PF, Rober AH, Pinkerton TS, Johnson ET, Lagrimini LM, Boston RS (2006) Relative activity of a tobacco hybrid expressing high levels of a tobacco anionic peroxidase and maize ribosome-inactivating protein against Helicoverpa zea and Lasioderma serricorne. J Agr Food Chem 54:2629–2634
Fitches E, Gatehouse JA (1998) A comparison of the short and long term effects of insecticidal lectins on the activities of soluble and brush border enzymes of tomato moth larvae (Lacanobia oleracea). J Insect Physiol 44:1213–1224
Frankel AE, Burbage C, Fu T, Tagge E, Chandler J, Willingham MC (1996) Ricin toxin contains at least three galactose-binding sites located in B chain subdominants 1α, 1β, and 2γ. Biochemistry 35:14749–14756
Gatehouse AMR, Barbieri L, Stirpe F, Croy RRD (1990) Effects of ribosome-inactivating proteins on insect development differences between Lepidoptera and Coleoptera. Entomol Exp Appl 54:43–51
Girbés T, Ferreras JM, Arias FJ, Stirpe F (2004) Description, distribution, activity and phylogenetic relationship of ribosome-inactivating proteins in plants, fungi and bacteria. Mini Rev Med Chem 4:461–476
Hakim RS, Blackburn M, Corti P, Gelman D, Goodman C, Elsen K, Loeb M, Lynn D, Smagghe G (2006) Growth and mitogenic effects of arylphorin in vivo and in vitro. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 64:63–73
Hulting FL, Orr DB, Obrycki JJ (1990) A computer program for calculation and statistical comparison of intrinsic rates of increase and associated life table parameters. Fla Entomol 73:601–612
Jouanin L, Bonade-Bottino M, Girard C, Morrot G, Giband M (1998) Transgenic plants for insect resistance. Plant Sci 131:1–11
Khan ZR, Saxena RC (1985) Behavioral and physiological responses of Sogatella furcifera (Homoptera: Delphacidae) to selected resistant and susceptible rice cultivars. J Econ Entomol 78:1280–1286
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Miller RG (1974) The jackknife-a review. Biometrika 61:1–15
Nielsen K, Boston RS (2001) Ribosome-inactivating proteins: a plant perspective. Annu Rev Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:785–816
Peumans WJ, Hao Q, Van Damme EJM (2001) Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: more than RNA N-glycosidases? FASEB J 15:1493–1506
Ranjekar PK, Patankar A, gupta V, Bhatnagar R, Bentur J, Kumar PA (2003) Genetic engineering of crop plants for insect resistance. Curr Sci 84:321–329
Sadeghi A, Broeders S, De Greve H, Hernalsteens JP, Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM, Smagghe G (2007) Expression of garlic leaf lectin under the control of the phloem-specific promoter Asus1 from Arabidopsis thaliana protects tobacco plants against the tobacco aphid (Myzus nicotianae). Pest Manag Sci 63:1215–1223
Sauvion N, Nardon C, Febvay G, Gatehouse AM, Rahbé Y (2004) Binding of the insecticidal lectin Concanavalin A in pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) and induced effects on the structure of midgut epithelial cells. J Insect Physiol 50:1137–1150
Silva CP, Silva JR, Vasconcelos FF, Petretski MDA, DaMatta RA, Ribeiro AF, Terra WR (2004) Occurrence of midgut perimicrovillar membranes in paraneopteran insect orders with comments on their function and evolutionary significance. Arthropod Structure Dev 33:139–148
Smagghe G, Pineda S, Carton B, Del Estal P, Budia F, Viñuela E (2003) Toxicity and kinetics for methoxyfenozide in greenhouse-selected Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag Sci 59:1203–1209
Steeves RM, Denton ME, Barnard FC, Henry A, Lambert JM (1999) Identification of three oligosaccharide binding sites in ricin. Biochemistry 38:11677–11685
Stirpe F (2004) Ribosome-inactivating proteins. Toxicon 44:371–383
Stirpe F, Battelli MG (2006) Ribosome-inactivating proteins: progress and problems. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1850–1866
Stirpe F, Barbieri L, Batelli MG, Isoria M, Lappi D (1992) Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: recent status and future prospects. BioTechnology 10:405–412
Van Damme EJM, Barre A, Rougé P, Van Leuven F, Peumans WJ (1996) The NeuAc (α–2, 6)-GalNAc-binding lectin from elderberry (Sambucus nigra) bark, a type-2 ribosome-inactivating protein with an unusual specificity and structure. Eur J Biochem 235:128–137
Van Damme EJM, Roy S, Barre A, Citores L, Mostafapous K, Rougé P, Van Leuven F, Girbes T, Goldstein IJ, Peumans WJ (1997) Elderberry (Sambucus nigra) bark contains two structurally different Neu5Ac(α2, 6)Gal/GalNAc-binding type-2 ribosome-inactivating proteins. Eur J Biochem 245:648–655
Van Damme EJM, Hao Q, Chen Y, Barre A, Vandenbussche F, Desmyter S, Rougé P, Peumans WJ (2001) Ribosome-inactivating proteins: a family of plant proteins that do more than inactivate ribosomes. Crit Rev Plant Sci 20:395–465
Van de Veire M, Smagghe G, Degheele D (1997) Laboratory test method to evaluate the effect of 31 pesticides on the predatory bug, Orius laevigatus (Het: Anthocoridae). Entomophaga 41:235–244
Vervecken W, Kleff S, Pfuller U, Bussing A (2000) Induction of apoptosis by mistletoe lectin I and its subunitsNo evidence for cytotoxic effects caused by isolated A- and B-chains. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 32:317–326
Wei GQ, Liu RS, Wang Q, Liu WY (2004) Toxicity of two type II ribosome-inactivating proteins (cinnamomin and ricin) to domestic silkworm larvae. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 57:160–165
Williams JM, Lea N, Lord JM, Roberts LM, Milford DV, Taylor CM (1997) Comparison of ribosome-inactivating proteins in the induction of apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 91:12–127
Acknowledgements
Sh. Shahidi-Noghabi is recipient of a doctoral grant from the Special Research Council of Ghent University. This research is also supported by project 3G016306 to G. Smagghe and E.J.M. Van Damme from the Fund of Scientific Research (FWO-Vlaanderen, Brussels, Belgium).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahidi-Noghabi, S., Van Damme, E.J.M. & Smagghe, G. Expression of Sambucus nigra agglutinin (SNA-I′) from elderberry bark in transgenic tobacco plants results in enhanced resistance to different insect species. Transgenic Res 18, 249–259 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-008-9215-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-008-9215-2