Abstract
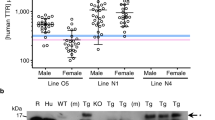
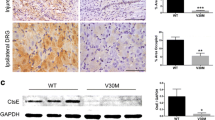
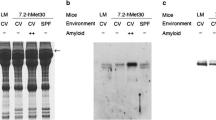
Transthyretin (TTR) associated amyloidosis is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by peripheral and autonomic neuropathy. Both genetic and environmental factors are thought to be involved in development of TTR associated amyloidosis. Previously, we demonstrated that amyloid deposition was observed in various tissues of transgenic mouse lines carrying a human mutant TTR (Met30) gene. To analyze the influence of environmental factors on TTR amyloidosis, these amyloidogenic transgenic mouse models were kept under conventional (CV) or specific pathogen free (SPF) conditions. Although the serum levels of Met30 for mice housed in the CV and SPF conditions were similar, amyloid deposition was observed in CV conditions, but not in SPF conditions. In addition, the extent of amyloid deposition in transgenic mice was dependent on duration kept under CV conditions. There were significant differences in proportion of amyloid deposition in several tissues between CV and SPF conditions. Maintenance of these mice at 30°C did not induce amyloid deposition in SPF conditions. These results suggest that the SPF conditions can completely prevent amyloid deposition, and that environmental factors can affect the onset and progression even in a single gene disorder.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida MR, Macedo B, Cardoso I, Alves I, Valencia G, Arsequell G, Planas A, Saraiva MJ (2004) Selective binding to transthyretin and tetramer stabilization in serum from patients with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy by an iodinated diflunisal derivative. Biochem J 381:351–356
Ando Y (2005) Liver transplantation and new therapeutic approaches for familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP). Med Mol Morphol 38:142–154
Ando Y, Nyhlin N, Suhr O, Holmgren G, Uchida K, el Sahly M, Yamashita T, Terasaki H, Nakamura M, Uchino M, Ando M (1997) Oxidative stress is found in amyloid deposits in systemic amyloidosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 232:497–502
Andrade C (1952) A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy; familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain 75:408–427
Benson MD, Dwulet FE (1985) Identification of carriers of a variant plasma prealbumin (transthyretin) associated with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy type I. J Clin Invest 75:71–75
Conrad CC, Marshall PL, Talent JM, Malakowsky CA, Choi J, Gracy RW (2000) Oxidized proteins in Alzheimer’s plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:678–681
Ferrao-Gonzales AD, Palmieri L, Valory M, Silva JL, Lashuel H, Kelly JW, Foguel D (2003) Hydration and packing are crucial to amyloidogenesis as revealed by pressure studies on transthyretin variants that either protect or worsen amyloid disease. J Mol Biol 328:963–974
Glenner GG (1980a) Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 302:1283–1292
Glenner GG (1980b) Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis: the beta-fibrilloses (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 302:1333–1343
Hosono M, Hanada K, Toichi E, Naiki H, Higuchi K, Hosokawa T (1997) Immune abnormality in relation to nonimmune diseases in SAM mice. Exp Gerontol 32:181–195
Jirtle RL, Skinner MK (2007) Environmental epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Nat Rev Genet 8:253–262
Johnson SM, Petrassi HM, Palaninathan SK, Mohamedmohaideen NN, Purkey HE, Nichols C, Chiang KP, Walkup T, Sacchettini JC, Sharpless KB, Kelly JW (2005a) Bisaryloxime ethers as potent inhibitors of transthyretin amyloid fibril formation. J Med Chem 48:1576–1587
Johnson SM, Wiseman RL, Sekijima Y, Green NS, Adamski-Werner SL, Kelly JW (2005b) Native state kinetic stabilization as a strategy to ameliorate protein misfolding diseases: a focus on the transthyretin amyloidoses. Acc Chem Res 38:911–921
Kobayashi K, Suda T, Nan-Ya K, Sakaguchi N, Sakaguchi S, Miki I (2006) Cytokine production profile of splenocytes derived from zymosan A-treated SKG mice developing arthritis. Inflamm Res 55:335–341
Kohno K, Palha JA, Miyakawa K, Saraiva MJ, Ito S, Mabuchi T, Blaner WS, Iijima H, Tsukahara S, Episkopou V, Gottesman ME, Shimada K, Takahashi K, Yamamura K, Maeda S (1997) Analysis of amyloid deposition in a transgenic mouse model of homozygous familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Am J Pathol 150:1497–1508
Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W (1993) Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 75:263–274
Kullberg MC, Ward JM, Gorelick PL, Caspar P, Hieny S, Cheever A, Jankovic D, Sher A (1998) Helicobacter hepaticus triggers colitis in specific-pathogen-free interleukin-10 (IL-10)-deficient mice through an IL-12- and gamma interferon-dependent mechanism. Infect Immun 66:5157–5166
Matsuda H, Watanabe N, Geba GP, Sperl J, Tsudzuki M, Hiroi J, Matsumoto M, Ushio H, Saito S, Askenase PW, Ra C (1997) Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion with IgE hyperproduction in NC/Nga mice. Int Immunol 9:461–466
Murakami T, Yi S, Maeda S, Tashiro F, Yamamura K, Takahashi K, Shimada K, Araki S (1992) Effect of serum amyloid P component level on transthyretin-derived amyloid deposition in a transgenic mouse model of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Am J Pathol 141:451–456
Nagata Y, Tashiro F, Yi S, Murakami T, Maeda S, Takahashi K, Shimada K, Okamura H, Yamamura K (1995) A 6-kb upstream region of the human transthyretin gene can direct developmental, tissue-specific, and quantitatively normal expression in transgenic mouse. J Biochem 117:169–175
Nettleton EJ, Sunde M, Lai Z, Kelly JW, Dobson CM, Robinson CV (1998) Protein subunit interactions and structural integrity of amyloidogenic transthyretins: evidence from electrospray mass spectrometry. J Mol Biol 281:553–564
Niraula TN, Haraoka K, Ando Y, Li H, Yamada H, Akasaka K (2002) Decreased thermodynamic stability as a crucial factor for familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. J Mol Biol 320:333–342
Noguchi H, Ohta M, Wakasugi S, Noguchi K, Nakamura N, Nakamura O, Miyakawa K, Takeya M, Suzuki M, Nakagata N, Urano T, Ono T, Yamamura K (2002) Effect of the intestinal flora on amyloid deposition in a transgenic mouse model of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Exp Anim 51:309–316
Quintas A, Saraiva MJ, Brito RM (1997) The amyloidogenic potential of transthyretin variants correlates with their tendency to aggregate in solution. FEBS Lett 418:297–300
Sakashita N, Ando Y, Marklund SL, Nilsson P, Tashima K, Yamashita T, Takahashi K (1998) Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy type I with extracellular superoxide dismutase mutation: a case report. Hum Pathol 29:1169–1172
Saraiva MJ, Costa PP, Goodman DS (1983) Studies on plasma transthyretin (prealbumin) in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, Portuguese type. J Lab Clin Med 102:590–603
Sato T, Ando Y, Susuki S, Mikami F, Ikemizu S, Nakamura M, Suhr O, Anraku M, Kai T, Suico MA, Shuto T, Mizuguchi M, Yamagata Y, Kai H (2006) Chromium(III) ion and thyroxine cooperate to stabilize the transthyretin tetramer and suppress in vitro amyloid fibril formation. FEBS Lett 580:491–496
Shino A, Tsukuda R, Omori Y, Matsuo T (1987) Histopathologic observations on the senescence-accelerated mice (SAM) reared under specific pathogen free conditions. Acta Pathol Jpn 37:1465–1475
Stangou AJ, Hawkins PN (2004) Liver transplantation in transthyretin-related familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Curr Opin Neurol 17:615–620
Tagoe CE, Jacobson DR, Gallo G, Buxbaum JN (2003) Mice transgenic for human TTR have the same frequency of renal TTR deposition whether maintained in conventional or specific pathogen free environments. Amyloid 10:262–266
Takaoka Y, Tashiro F, Yi S, Maeda S, Shimada K, Takahashi K, Sakaki Y, Yamamura K (1997) Comparison of amyloid deposition in two lines of transgenic mouse that model familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, type I. Transgenic Res 6:261–269
Takaoka Y, Ohta M, Miyakawa K, Nakamura O, Suzuki M, Takahashi K, Yamamura K, Sakaki Y (2004) Cysteine 10 is a key residue in amyloidogenesis of human transthyretin Val30Met. Am J Pathol 164:337–345
Tawara S, Nakazato M, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Araki S (1983) Identification of amyloid prealbumin variant in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (Japanese type). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 116:880–888
Terazaki H, Ando Y, Fernandes R, Yamamura K, Maeda S, Saraiva MJ (2006) Immunization in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: counteracting deposition by immunization with a Y78F TTR mutant. Lab Invest 86:23–31
Wakasugi S, Inomoto T, Yi S, Naito M, Uehira M, wanaga T, Maeda S, Araki K, Miyazaki J, Takahashi K, Shimada K, Yamamura K (1987) A transgenic mouse model of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Proc Jpn Acad 63:344–347
Westermark P, Pitkanen P, Benson L, Vahlquist A, Olofsson BO, Cornwell GG 3rd (1985) Serum prealbumin and retinol-binding protein in the prealbumin-related senile and familial forms of systemic amyloidosis. Lab Invest 52:314–318
Wexler NS, Lorimer J, Porter J, Gomez F, Moskowitz C, Shackell E, Marder K, Penchaszadeh G, Roberts SA, Gayan J, Brocklebank D, Cherny SS, Cardon LR, Gray J, Dlouhy SR, Wiktorski S, Hodes ME, Conneally PM, Penney JB, Gusella J, Cha JH, Irizarry M, Rosas D, Hersch S, Hollingsworth Z, MacDonald M, Young AB, Andresen JM, Housman DE, De Young MM, Bonilla E, Stillings T, Negrette A, Snodgrass SR, Martinez-Jaurrieta MD, Ramos-Arroyo MA, Bickham J, Ramos JS, Marshall F, Shoulson I, Rey GJ, Feigin A, Arnheim N, Acevedo-Cruz A, Acosta L, Alvir J, Fischbeck K, Thompson LM, Young A, Dure L, O’Brien CJ, Paulsen J, Brickman A, Krch D, Peery S, Hogarth P, Higgins DS Jr, Landwehrmeyer B (2004) Venezuelan kindreds reveal that genetic and environmental factors modulate Huntington’s disease age of onset. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:3498–3503
Yamamura K, Wakasugi S, Maeda S, Inomoto T, Iwanaga T, Uehira M, Araki K, Miyazaki J, Shimada K (1987) Tissue-specific and developmental expression of human transthyretin gene in transgenic mice. Dev Genet 8:195–205
Yi S, Takahashi K, Naito M, Tashiro F, Wakasugi S, Maeda S, Shimada K, Yamamura K, Araki S (1991) Systemic amyloidosis in transgenic mice carrying the human mutant transthyretin (Met30) gene. Pathologic similarity to human familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, type I. Am J Pathol 138:403–412
Yoshitomi H, Sakaguchi N, Kobayashi K, Brown GD, Tagami T, Sakihama T, Hirota K, Tanaka S, Nomura T, Miki I, Gordon S, Akira S, Nakamura T, Sakaguchi S (2005) A role for fungal {beta}-glucans and their receptor dectin-1 in the induction of autoimmune arthritis in genetically susceptible mice. J Exp Med 201:949–960
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. O. Nakamura and Ms. Michiyo Nakata for their technical assistance. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and a grant from the Osaka Foundation of Promotion of Clinical Immunology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Seiya Inoue, Mika Ohta, and Zhenghua Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, S., Ohta, M., Li, Z. et al. Specific pathogen free conditions prevent transthyretin amyloidosis in mouse models. Transgenic Res 17, 817–826 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-008-9180-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-008-9180-9