Abstract
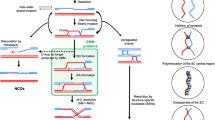
Meiosis is a specialized set of two nuclear divisions, meiosis I and II, by which a diploid cell produces four haploid daughters. After premeiotic DNA replication, homologous chromosomes pair and recombine, and then disjoin at meiosis I. Subsequently, at meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome segregate. In nearly all eukaryotes, meiotic chromosome pairing culminates in the formation of a ladderlike supramolecular protein structure, the synaptonemal complex (SC) (Page and Hawley, 2004). The rungs of the ladder are known as transverse filaments (TFs). Genes encoding TF proteins have been identified in a limited number of organisms, and their function has been studied by mutational analysis. Although TF proteins show little amino acid sequence conservation, their structure and function are largely conserved. In all analyzed species, TF proteins are required for meiotic reciprocal recombination (crossing over).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MP Colaiácovo AJ MacQueen E Martinez-Perez K McDonald A Adamo A La Volpe AM Villeneuve (2003) ArticleTitleSynaptonemal complex assembly in C. elegans is dispensable for loading strand-exchange proteins but critical for proper completion of recombination Dev Cell 5 463–474 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00232-6 Occurrence Handle12967565
T los Santos Particlede N Hunter C Lee B Larkin J Loidl NM Hollingsworth (2003) ArticleTitleThe Mus81/Mms4 endonuclease acts independently of double-Holliday junction resolution to promote a distinct subset of crossovers during meiosis in budding yeast Genetics 164 81–94 Occurrence Handle12750322
FAT Vries Particlede E Boer Particlede M Bosch Particlevan den WM Baarends M Ooms L Yuan J-G Liu C Heyting A Pastink (2005) ArticleTitleMouse Sycp1 functions in synaptonemal complex assembly, meiotic recombination and XY body formation Genes Dev 19 1376–1389 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.329705 Occurrence Handle15937223
H Dong GS Roeder (2000) ArticleTitleOrganization of the yeast Zip1 protein within the central region of the synaptonemal complex J Cell Biol 148 417–426 Occurrence Handle10662769
JC Fung B Rockmill M Odell GS Roeder (2004) ArticleTitleImposition of crossover interference through the nonrandom distribution of synapsis initiation complexes Cell 116 795–802 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00249-1 Occurrence Handle15035982
KJ Hillers (2004) ArticleTitleCrossover interference Curr Biol 14 R1036–R1037 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.cub.2004.11.038 Occurrence Handle15620632
KJ Hillers AM Villeneuve (2003) ArticleTitleChromosome-wide control of meiotic crossing over in C. elegans Curr Biol 13 1641–1647 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.cub.2003.08.026 Occurrence Handle13678597
JK Jang DE Sherizen R Bhagat EA Manheim KS McKim (2003) ArticleTitleRelationship between DNA double-strand breaks to synapsis in Drosophila J Cell Sci 116 3069–3077 Occurrence Handle10.1242/jcs.00614 Occurrence Handle12799415
JG Liu L Yuan E Brundell B Bjorkroth B Daneholt C Höög (1996) ArticleTitleLocalization of the N-terminus of SCP1 to the central element of the synaptonemal complex and evidence for direct interactions between the N-termini of SCP1 molecules organized head-to-head Exp Cell Res 226 11–19 Occurrence Handle10.1006/excr.1996.0197 Occurrence Handle8660934
AJ MacQueen MP Colaiácovo K McDonald AM Villeneuve (2002) ArticleTitleSynapsis-dependent and -independent mechanisms stabilize homolog pairing during meiotic prophase in C. elegans Genes Dev 16 2428–2442 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.1011602 Occurrence Handle12231631
RL Meuwissen HH Offenberg AJ Dietrich A Riesewijk M Iersel Particlevan C Heyting (1992) ArticleTitleA coiled-coil related protein specific for synapsed regions of meiotic prophase chromosomes EMBO J 11 5091–5100 Occurrence Handle1464329
SL Page RS Hawley (2004) ArticleTitleThe genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20 525–558 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.cellbio.19.111301.155141 Occurrence Handle15473851
SL Page RS Hawley (2001) ArticleTitlec(3)G encodes a Drosophila synaptonemal complex protein Genes Dev 15 3130–3143 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.935001 Occurrence Handle11731477
SL Page RS Hawley (2003) ArticleTitleChromosome choreography: The meiotic ballet Science 301 785–789 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1086605 Occurrence Handle12907787
K Schmekel RL Meuwissen AJ Dietrich AC Vink J Marle Particlevan H Veen Particlevan C Heyting (1996) ArticleTitleOrganization of SCP1 protein molecules within synaptonemal complexes of the rat Exp Cell Res 226 20–30 Occurrence Handle10.1006/excr.1996.0198 Occurrence Handle8660935
A Storlazzi L Xu A Schwacha N Kleckner (1996) ArticleTitleSynaptonemal complex (SC) component Zip1 plays a role in meiotic recombination independent of SC polymerization along the chromosomes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93 9043–9048 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.93.17.9043 Occurrence Handle8799151
M Sym JA Engebrecht GS Roeder (1993) ArticleTitleZip1 is a synaptonemal complex protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis Cell 72 365–378 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0092-8674(93)90114-6 Occurrence Handle7916652
M Sym GS Roeder (1995) ArticleTitleZip1-induced changes in synaptonemal complex structure and polycomplex assembly J Cell Biol 128 455–466 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.128.4.455 Occurrence Handle7860625
L Yuan E Brundell C Höög (1996) ArticleTitleExpression of the meiosis-specific synaptonemal complex protein 1 in a heterologous system results in the formation of large protein structures Exp Cell Res 229 272–275 Occurrence Handle10.1006/excr.1996.0371 Occurrence Handle8986609
D Zickler N Kleckner (1999) ArticleTitleMeiotic chromosomes: integrating structure and function Annu Rev Genet 33 603–754 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.genet.33.1.603 Occurrence Handle10690419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heyting, C. Meiotic Transverse Filament Proteins: Essential for Crossing Over. Transgenic Res 14, 547–550 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-005-8925-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-005-8925-y