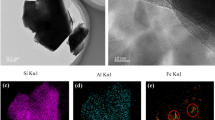
Abstract
In this work, the principles of environmentally friendly and efficient resource utilization have been implemented to move towards achieving carbon neutrality. Accordingly, the confined-space molecular-sieve properties of ZSM-5 zeolite were applied in cooperation with an external magnetic field with the aim to improve the catalytic LPG conversion and the selectivity of BTX (benzene, toluene, and xylenes) over Fe-Ga/ZSM-5 zeolites (0.5 wt.% Ga and 0.1 wt.% Fe). Effect of ZSM-5 particle sizes (0.6 μm, 1.1 μm, and 22.1 μm) on BTX yields and toluene to monoaromatic hydrocarbons were examined under magnetic field at a flux intensity of 28.7 mT in North-to-South direction and compared to those without magnetic field. The highest LPG conversion over Fe-Ga/ZSM-5 catalyst was found at the ZSM-5 particle size of 1.1 µm under external magnetic field, which is 1.2 times greater than that without magnetic field. The BTX yield was also increased by factors of 1.5 compared to those without magnetic field. The outstanding performance can be attributed to the synergistic effects between the external magnetic field and limited mass transfer within the confined-space zeolite. This combination facilitates and enhances the mass transfer ability and reaction performance of the reactant molecules. Consequently, this synergistic effect can lead to the development of green and sustainable innovations for chemical and separation processes in the future.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available in https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-023-01825-4. Any additional information is available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Jin X, Lee JH, Choi JW (2022) Catalytic co-pyrolysis of woody biomass with waste plastics: effects of HZSM-5 and pyrolysis temperature on producing high-value pyrolytic products and reducing wax formation. Energy 239:121739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121739
Pang XQ, Jia CZ, Chen ZX, Shi HS, Chen Z, Hu T, Wang T, Xu Z, Liu X, Zhang X, Wang E, Wu Z, Pang B (2022) Reduction of global natural gas hydrate (NGH) resource estimation and implications for the NGH development in the South China Sea. Pet Sci 19(1):3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petsci.2021.12.006
Song C, Gim MY, Lim YH, Kim DH (2019) Enhanced yield of benzene, toulene, and xylene from the co-aromatization of methane and propane over gallium supported on mesoporous ZSM-5 and ZSM-11. Fuel 251:404–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.079
Oseke GG, Atta AY, Mukhtar B, El-Yakubu BJ, Aderemi BO (2021) Increasing the catalytic stability of microporous Zn/ZSM-5 with copper for enhanced propane aromatization. J King Saud Univ—Eng Sci 33(8):531–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2020.07.014
Sun Y, Wei L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Li Y (2023) Coke formation over zeolite catalysts in light alkanes aromatization and anti-carbon-deposition strategies and perspectives: a review. Energy Fuels 37(3):1657–1677. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.2c03479
Liu D, Cao L, Zhang G, Zhao L, Gao J, Xu C (2021) Catalytic conversion of light alkanes to aromatics by metal-containing HZSM-5 zeolite catalysts—a review. Fuel Process Technol 216:106770. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.106770
Dehertog WJH, Fromen GF (1999) A catalytic route for aromatics production from LPG. Appl Catal A 189(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(99)00252-5
Lazaridis PA, Fotopoulos AP, Karakoulia SA, Triantafyllidis KS (2018) Catalytic fast pyrolysis of kraft lignin with conventional, mesoporous and nanosized ZSM-5 zeolite for the production of alkyl-phenols and aromatics. Front Chem 6:295–295. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00295
Zhang W, Fan S, Zhang J, Ma QX, Wang K, Zhao T (2019) Transformation of LPG on HZSM-5 catalyst: effects of tuned pores and acidity on product distribution. Fuel 254:115615
Hajimirzaee S, Soleimani Mehr A, Kianfar E (2020) Modified ZSM-5 zeolite for conversion of LPG to aromatics. Polycyclic Arom Comp. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406638.2020.1833048.
Liu RL, Zhu HQ, Wu ZW, Qin ZF, Fan WB, Wang JG (2015) Aromatization of propane over Ga-modified ZSM-5 catalysts. J Fuel Chem Technol 43(8):961–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(15)30027-X
Rodrigues VO (2010) Correlations between dispersion, acidity, reducibility, and propane aromatization activity of gallium species supported on HZSM5 zeolites. J Phys Chem C 114(10):4557–4567. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp910642p
Laredo GC, García-Gutiérrez JL, Pérez-Romo P, Olmos-Cerda EH (2021) Effect of the catalyst in the BTX production by hydrocracking of light cycle oil. Appl Petrochem Res 11(1):19–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13203-021-00266-y
Song Y, Lin W, Guo X, Dong L, Mu X, Tian H, Wang L (2019) Aromatization and isomerization of methylcyclohexane over Ni catalysts supported on different supports. Green Energy Environ 4(1):75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2018.05.003
Zhang Y, Wu S, Xu X, Jiang H (2020) Ethane aromatization and evolution of carbon deposits over nanosized and microsized Zn/ZSM-5 catalysts. Catal Sci Technol 10(3):835–843. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CY01903K
Sauer C, Schaefer A, Carlsson PA (2022) Isomorphous substitution of gallium into MFI-framework zeolite increases 2,5-dimethylfuran to aromatics selectivity and suppresses catalyst deactivation. Top Catal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-022-01776-2
Wan H, Chitta P (2016) Catalytic conversion of propane to BTX over Ga, Zn, Mo, and Re impregnated ZSM-5 catalysts. J Anal Appl Pyrol 121:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2016.08.018
Choudhary VR, Panjala D, Banerjee S (2002) Aromatization of propene and n-butene over H-galloaluminosilicate (ZSM-5 type) zeolite. Appl Catal A 231(1):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(02)00061-3
Sridhar A, Rahman M, Infantes-Molina A, Wylie BJ, Borcik CG, Khatib SJ (2020) Bimetallic Mo-Co/ZSM-5 and Mo-Ni/ZSM-5 catalysts for methane dehydroaromatization: a study of the effect of pretreatment and metal loadings on the catalytic behavior. Appl Catal A: General. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2019.117247
Uslamin EA, Saito H, Sekine Y, Hensen EJM, Kosinov N (2021) Different mechanisms of ethane aromatization over Mo/ZSM-5 and Ga/ZSM-5 Catalysts. Catal Today 369:184
Fadaeerayeni S, Chen G, Toghiani H, Xiang Y (2020) Mechanism and kinetics of ethane aromatization according to the chemical transient analysis. Top Catal 63(15):1463–1473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-020-01303-1
Xu B, Tan M, Wu X, Geng H, Song F, Ma Q, Luan C, Yang G, Tan Y (2021) Effects of silylation on Ga/HZSM-5 for improved propane dehydroaromatization. Fuel 283:118889
Lu J, Zhao Z, Xu C, Zhang P, Duan A (2006) Fe/HZSM-5 molecular sieves—highly active catalysts for catalytic cracking of isobutane to produce ethylene and propylene. Catal Commun 7(4):199–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2005.10.011
Oseke GG, Atta AY, Mukhtar B, Jibril BY, Aderemi BO (2020) Highly selective and stable Zn–Fe/ZSM-5 catalyst for aromatization of propane. Appl Petrochem Res 10(2):55–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13203-020-00245-9
Donphai W, Kunthakudee N, Munpollasri S, Sangteantong P, Tonlublao S, Limphirat W, Poo-arporn Y, Kiatphuengporn S, Chareonpanich M (2021) Application of magnetic field to CO hydrogenation using a confined-space catalyst: effect on reactant gas diffusivity and reactivity. RSC Adv 11(7):3990–3996. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra09870a
Kiatphuengporn S, Jantaratana P, Limtrakul J, Chareonpanich M (2016) Magnetic field-enhanced catalytic CO2 hydrogenation and selective conversion to light hydrocarbons over Fe/MCM-41 catalysts. Chem Eng J 306:866–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.029
Donphai W, Piriyawate N, Witoon T, Jantaratana P, Varabuntoonvit V, Chareonpanich M (2016) Effect of magnetic field on CO2 conversion over Cu-ZnO/ZrO2 catalyst in hydrogenation reaction. J CO2 Utiliz 16:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2016.07.007
Kiatphuengporn S, Chareonpanich M, Limtrakul J (2014) Effect of unimodal and bimodal MCM-41 mesoporous silica supports on activity of Fe–Cu catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation. Chem Eng J 240:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.090
Sriakkarin C, Umchoo W, Donphai W, Poo-arporn Y, Chareonpanich M (2018) Sustainable production of methanol from CO2 over 10Cu-10Fe/ZSM-5 catalyst in a magnetic field-assisted packed bed reactor. Catal Today 314:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.12.037
Umchoo W, Sriakkarin C, Donphai W, Warakulwit C, Poo-arporn Y, Jantaratana P, Witoon T, Chareonpanich M (2018) Green and sustainable methanol production from CO2 over magnetized FeCu/core–shell and infiltrate mesoporous silica-aluminosilicates. Energy Convers Manage 159:342–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.12.101
Munpollasri S, Poo-arporn Y, Donphai W, Sirijaraensre J, Sangthong W, Kiatphuengporn S, Jantaratana P, Witoon T, Chareonpanich M (2022) How magnetic field affects catalytic CO2 hydrogenation over Fe-Cu/MCM-41: In situ active metal phase—reactivity observation during activation and reaction. Chem Eng J 441:135952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135952
Yang Z, Zhang R, Liu R, Zhang S (2022) Elucidating the zeolite particle size effect on butene/isobutane alkylation. Ind Eng Chem Res 61(2):1032–1043. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.1c02038
Huang X, Wang R, Pan X, Wang C, Fan M, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Peng J (2020) Catalyst design strategies towards highly shape-selective HZSM-5 for para-xylene through toluene alkylation. Green Energy & Environment 5(4):385–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2019.12.001
Harju H, Pipitone G, Lefferts L (2020) Influence of the catalyst particle size on the aqueous phase reforming of n-Butanol over Rh/ZrO2. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00017
Chareonpanich M, Namto T, Kongkachuichay P, Limtrakul J (2004) Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from lignite fly ash and rice husk ash. Fuel Process Technol 85(15):1623–1634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2003.10.026
Gil-Horán RH, Chavarría-Hernández JC, Quintana-Owen P, Gutiérrez-Alejandre A (2020) Ethanol conversion to short-chain olefins over ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts enhanced with P, Fe, and Ni. Top Catal 63(5):414–427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-020-01229-8
Li Q, Zhang F, Jarvis J, He P, Yung MM, Wang A, Zhao K, Song H (2018) Investigation on the light alkanes aromatization over Zn and Ga modified HZSM-5 catalysts in the presence of methane. Fuel 219:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.01.104
Van der Borght K, Galvita VV, Marin GB (2015) Ethanol to higher hydrocarbons over Ni, Ga, Fe-modified ZSM-5: effect of metal content. Appl Catal A 492:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.12.020
Denardin F, Perez-Lopez OW (2019) Tuning the acidity and reducibility of Fe/ZSM-5 catalysts for methane dehydroaromatization. Fuel 236:1293–1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.09.128
Xin M, Xing E, Gao X, Wang Y, Ouyang Y, Xu G, Luo Y, Shu X (2019) Ga substitution during modification of ZSM-5 and its influences on catalytic aromatization performance. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(17):6970–6981. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b00295
Chaudhary PK, Deo G (2022) Influence of particle size and metal-support interaction on the catalytic performance of Ni-Al2O3 catalysts for the dry and oxidative-dry reforming of methane. Coll Surf A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 646:128973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128973.
Xie JL, Jin QQ (2022) Effect of La/Ce modification over Cu based Y zeolite catalysts on high temperature selectivity for selective catalytic reduction with ammonia. J Cleaner Prod 362:132255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132255
Begum SH, Hung CT, Chen YT, Huang SJ, Wu PH, Han X, Liu SB (2016) Acidity-activity correlation over bimetallic iron-based ZSM-5 catalysts during selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J Mol Catal A: Chem 423:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.07.036
Caiola A, Robinson B, Bai X, Shekhawat D, Hu J (2021) Study of the hydrogen pretreatment of gallium and platinum promoted ZSM-5 for the ethane dehydroaromatization reaction. Ind Eng Chem Res 60(30):11421–11431. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.1c01555
Sharifi K, Halladj R, Royaee SJ (2020) An overview on the effects of metal promoters and acidity of ZSM-5 in performance of the aromatization of liquid hydrocarbons. Rev Adv Mater Sci 59(1):188–206. https://doi.org/10.1515/rams-2020-0037
Biz C, Gracia J, Fianchini M (2022) Review on magnetism in catalysis: from theory to PEMFC applications of 3d metal Pt-based alloys. Int J Mol Sci 23:14768
Xiao J, Wei J (1992) Diffusion mechanism of hydrocarbons in zeolites—I. Theory. Chem Eng Sci 47(5):1123–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(92)80236-6
Cao Q, Han X, Li L (2014) Configurations and control of magnetic fields for manipulating magnetic particles in microfluidic applications: magnet systems and manipulation mechanisms. Lab Chip 14(15):2762–2777. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4LC00367E
Vick WS (1991) Magnetic fluid conditioning. In: Conference on Environmental Engineering; American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, VA
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) through the Research Team Promotion Grant/Senior Research Scholar (Grant No. N42A640324); the Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC), the Ministry of Science and Technology, Thailand, through its program of Research Network of NANOTEC (RNN); the Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI); and Faculty of Engineering, Kasetsart University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD: investigation, writing—original draft. RC: investigation. PS: investigation. WD: methodology, data curation, validation. WL: investigation, data curation. YP: investigation, data curation. SN: investigation, data curation. SK: investigation, data curation. PJ: investigation, data curation (magnetic field). MC: conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision, writing—review & editing (Corresponding Author).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Z., Chotchaipitakkul, R., Sangteantong, P. et al. Catalytic LPG Conversion Over Fe-Ga Modified ZSM-5 Zeolite Catalysts with Different Particle Sizes: Effect of Confined-Space Zeolite and External Magnetic Field. Top Catal 66, 1594–1607 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-023-01825-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-023-01825-4