Abstract
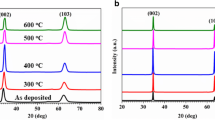
With the purpose of enhancing the photochemical water splitting performance, GZO film has been used to increase the charge transfer of the ZnO@GZO films. The characterization of ZnO film, GZO film and ZnO@GZO films was carried out by X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscope, DRUV-vis spectra (DRUV-vis), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), photoluminescence (PL) and photochemical water splitting. All samples show a related highly c-axis peak (002) from XRD patterns. DRUV-vis results show that the formed GZO film with wide band gap but low resistivity, would not affect the band gap of the ZnO@GZO films. PL results reveal that the decreased recombination of electron and hole, via the increased charge transfer by GZO film. XPS results hint that the obvious change of chemisorbed oxygen species on the surface of ZnO and GZO, and Ga atoms mainly substitute into Zn sites in the ZnO matrix. Compared with that of ZnO film, the ZnO@GZO films even with lower specific surface area, could efficiently enhance the photochemical water splitting performance via the charge-transfer effect of the GZO film.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Minami T (2005) Transparent conducting oxide semiconductors for transparent electrodes. Semicond Sci Technol 20:35–44
Hosono H (2007) Recent progress in transparent oxide semiconductors: materials and device application. Thin Solid Films 515:6000–6014
Schmidt-Mende L, MacManus-Driscoll JL (2007) ZnO-nanostructures, defects, and devices. Mater Today 10:40–48
Arya SK, Saha S, Ramirez-Vick JE et al (2012) Singh SP recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: review. Anal Chim Acta 737:1–21
Kozuka Y, Tsukazaki A, Kawasaki M (2014) Challenges and opportunities of ZnO-related single crystalline heterostructures. Appl Phys Rev 1:011303
Sebastian CD, David OS, Claire JC et al (2016) n-Type doped transparent conducting binary oxides: an overview. J Mater Chem C 4:6946–6961
Mizoguchi H, Woodward PM (2004) Electronic structure studies of main group oxides possessing edge-sharing octahedra: implications for the design of transparent conducting oxides. Chem Mater 16:5233–5248
Zou X, Fan H, Tian Y et al (2014) Synthesis of Cu2O/ZnO hetero-nanorod arrays with enhanced visible light-driven photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 15:1149–1156
Cai Y, Fan H, Xu M et al (2013) Rapid photocatalytic activity and honeycomb Ag/ZnO heterostructures via solution combustion synthesis. Colloid Surf A 436:787–795
Song N, Fan H, Tian H (2015) Reduced graphene oxide/ZnO nanohybrids: metallic Zn powder induced one-step synthesis for enhanced photocurrent andphotocatalytic response. Appl Surf Sci 353:580–587
Tian H, Fan H, Li M et al (2016) Zeolitic imidazolate framework coated ZnO nanorods as molecular sieving to improve selectivity of formaldehyde gas sensor. ACS Sens 1:243–250
Nulhakim L, Makino H (2016) Control of microstructure by using self-buffer layer and its effects on properties of Ga-doped ZnO thin films deposited by radio frequency magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 615:158–164
Zhu C, Li J, Yang Y et al (2017) Highly moisture and weak-acid resistant Ga-doped ZnO films with titanium dioxide co-doping fabricated by magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 634:155–159
Cuong HB, Lee CS, Jeong SH et al (2017) Realization of highly conductive Ga-doped ZnO film with abnormally wide band-gap using magnetron sputtering by simply lowering working pressure. Acta Mater 130:47–55
Gao W, Li Z (2004) ZnO thin films produced by magnetron sputtering. Ceram Int 30:1155–1159
Kim C, Kim S, Lee C (2005) Effects of RF power and substrate temperature during RF magnetron sputtering on grystal quality of ZnO thin films. Jpn J Appl Phys 44:8501–8503
Zou Y, Yang H, Wang H et al (2013) Microstructure, optical and photoluminescence properties of Ga-doped ZnO films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Physica B 414:7–11
Wu S, Chan C, Chien C (2016) Enhanced emission and photoconductivity due to photo-induced charge transfer from Au nanoislands to ZnO. Appl Phys Lett 108:041104
Barman MK, Mitra P, Bera R et al (2017) An efficient charge separation and photocurrent generation in the carbon dot-zinc oxide nanoparticle composite. Nanoscale 9:6791–6799
Saha M, Ghosh S, Ashok VD et al (2015) Carrier concentration dependent optical and electrical properties of Ga doped ZnO hexagonal nanocrystals. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:16067–16079
Zhu D, Wang Q, Han S et al (2014) Optimization of process parameters for the electrical properties in Ga-doped ZnO thin films prepared by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl Surf Sci 298:208–213
Ma L, Fan H, Li M et al (2015) A simple melamine-assisted exfoliation of polymeric graphitic carbon nitrides for highly efficient hydrogen production from water under visible light. J Mater Chem A 3:22404–22412
Chen S, Carraro G, Barreca D et al (2015) Aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition of Ga-doped ZnO films for energy efficient glazing: effects of doping concentration on the film growth behaviour and opto-electronic properties. J Mater Chem A 3:13039–13049
Bekermann D, Gasparotto A, Barreca D et al (2010) Highly oriented ZnO nanorod arrays by a novel plasma chemical vapor deposition process. Cryst Growth Des 10:2011–2018
Sahai A, Goswami N (2014) Probing the dominance of interstitial oxygen defects in ZnO nanoparticles through structural and optical characterizations. Ceram Int 40:14569–14578
Park GC, Hwang SM, Lim JH et al (2014) Growth behavior and electrical performance of Ga-doped ZnO nanorod/p-Si heterojunction diodes prepared using a hydrothermal method. Nanoscale 6:1840–1847
Cheon D, Soo M, Ham MH et al (2016) Resistive switching in an amorphous ZnO dielectric film prepared on a Ga-doped ZnO transparent electrode. RSC Adv 6:103864–103871
Jung H, Kim D, Kim H (2014) The electrical properties of low pressure chemical vapor deposition Ga doped ZnO thin films depending on chemical bonding configuration. Appl Surf Sci 297:125–129
Hinkle CL, Milojevic M, Brennan B et al (2009) Detection of Ga suboxides and their impact on III-V passivation and Fermi-level pinning. Appl Phys Lett 94:162101
Tian H, Fan H, Ma J et al (2017) Noble metal-free modified electrode of exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride/ZnO nanosheets for highly efficient hydrogen peroxide sensing. Electrochim Acta 247:787–794
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, S., Yamawaki, L., Zhang, P. et al. Charge-Transfer Effect of GZO Film on Photochemical Water Splitting of Transparent ZnO@GZO Films by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Top Catal 61, 1585–1590 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-018-0916-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-018-0916-3