Abstract
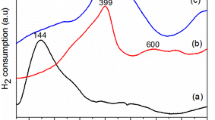
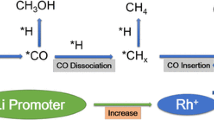
Low temperature ethanol steam reforming (ESR) was studied over a series of 1 wt% Rh–x % Fe catalysts with various Fe loading (x = 0–10 wt%) and on different supports (Ca–Al2O3, SiO2 and ZrO2). The results show that close interaction between Rh and Fe is required to reduce the CO selectivity to almost negligible values. In addition, Rh–Fe supported on Ca–Al2O3 exhibits the best performance in terms of CO selectivity and hydrogen yield as compared to other supports. Characterization by XPS and XANES indicates the presence of FexOy species upon reduction, resulting in the formation of coordinatively unsaturated ferrous (CUF) active sites along the Rh–FexOy interface. These CUF sites promote water–gas shift reaction during low temperature ESR. Temperature programmed oxidation and Raman spectroscopy of spent catalysts also indicate that the addition of iron oxide reduces coke deposition and forms more reactive coke. Hence, the catalyst lifespan is significantly extended.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Song C (2002) Catal Today 77:17
Hulteberg C (2012) Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:3978
Ni M, Leung DYC, Leung MKH (2007) Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:3238
Llorca J, de la Piscina PR, Dalmon J-A, Sales J, Homs N (2003) Appl Catal B 43:355
Zhang C, Zhang P, Li S, Wu G, Ma X, Gong J (2012) J Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:3295
Song H, Ozkan US (2009) J Catal 261:66
Lima da Silva A, Malfatti CldF, Müller IL (2009) Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:4321
Liguras DK, Kondarides DI, Verykios XE (2003) Appl Catal B 43:345
Chen L, Choong CKS, Zhong Z, Huang L, Ang TP, Hong L, Lin J (2010) J Catal 276:197
Lei Y, Cant NW, Trimm DL (2006) J Catal 239:227
Fornasiero P, Dimonte R, Rao GR, Kaspar J, Meriani S, Trovarelli A, Graziani M (1995) J Catal 151:168
Lin H-Y, Chen Y-W, Li C (2003) Thermochim Acta 400:61
Wielers AFH, Kock AJHM, Hop CECA, Geus JW, van Der Kraan AM (1989) J Catal 117:1
Chen W, Ding Y, Song X, Wang T, Luo H (2011) Appl Catal A 407:231
Kock AJHM, Fortuin HM, Geus JW (1985) J Catal 96:261
Wan H-J, Wu B-S, Zhang C-H, Xiang H-W, Li Y-W, Xu B-F, Yi F (2007) Catal Commun 8:1538
Yamashita T, Hayes P (2008) Appl Surf Sci 254:2441
Ratnasamy C, Wagner JP (2009) Catal Rev 51:325
Rodriguez JA, Liu P, Hrbek J, Evans J, Pérez M (2007) Angew Chem Int Ed 46:1329
Grenoble DC, Estadt MM, Ollis DF (1981) J Catal 67:90
Fu Q, Li W-X, Yao Y, Liu H, Su H-Y, Ma D, Gu X-K, Chen L, Wang Z, Zhang H, Wang B, Bao X (2010) Science 328:1141
Burch R, Hayes MJ (1997) J Catal 165:249
Chen L, Choong CKS, Zhong Z, Huang L, Wang Z, Lin J (2012) Int J Hydrogen Energy 37:16321
Roh H-S, Platon A, Wang Y, King D (2006) Catal Lett 110:1
Profeti LPR, Ticianelli EA, Assaf EM (2008) J Power Sour 175:482
Choong CKS, Huang L, Zhong Z, Lin J, Hong L, Chen L (2011) Appl Catal A 407:155
Solymosi F, Erdőhelyi A (1981) Surf Sci Lett 110:L630
Virginie M, Araque M, Roger A-C, Vargas JC, Kiennemann A (2008) Catal Today 138:21
Li Y, Bowker M (1993) Surf Sci 285:219
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Science and Engineering Research Council (SERC) of the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) of Singapore and Professor Lin Jianyi for his valuable and helpful comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choong, C.K.S., Chen, L., Du, Y. et al. Rh–Fe/Ca–Al2O3: A Unique Catalyst for CO-Free Hydrogen Production in Low Temperature Ethanol Steam Reforming. Top Catal 57, 627–636 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-013-0221-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-013-0221-0