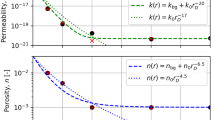
Abstract
An integrated reservoir-geomechanics-fracture model is implemented in a deep shale gas reservoir in the Sichuan Basin, Western China, to optimize the parent–child well spacing under various complex natural fracture settings. The integrated multiphysics model employs an embedded discrete fracture model to characterize fluid flow through complex natural and hydraulic fractures, a finite element method geomechanics model to predict the 3D spatiotemporal stress changes, and a displacement discontinuity method hydraulic fracture model to simulate the multicluster fracture propagation under the depletion-induced heterogeneous stress field. Field case studies on two complex natural fracture patterns (i.e., orthogonal and clustered natural fractures) show that (a) the orientation change of maximum horizontal stress (SHmax) is negligible since the target shale gas reservoir is highly stressed and under large horizontal stress contrast; (b) the decrease in minimum horizontal stress (Shmin) over the stimulated reservoir volume is about 30–50% of pore pressure drop due to the rapid pressure depletion; (c) decreasing the parent–child horizontal/vertical spacing or elongating the production time aggravates the asymmetry growth of child-well fractures in either natural fracture pattern; (d) the parent and child wells are suggested to space farther under the clustered natural fracture pattern to avoid undesirable interwell fracture interference caused by the irregular localized stress sink. This work delivers a comprehensive understanding of the geomechanics consequences under different natural fracture settings and provides practical guidance on infill operations in layered formations of the Sichuan Basin.
Article Highlights
-
An integrated reservoir-geomechanics-fracture model is employed to optimize the parent–child well spacing in a multilayer deep shale gas reservoir with complex natural fractures
-
The complex fracture network, in situ stress change, and multicluster fracture propagation are simulated by EDFM, FEM geomechanics model, and DDM hydraulic fracture model, respectively
-
The impacts of orthogonal and clustered natural fractures on spatiotemporal stress evolution and parent–child well layout are investigated based on actual field datasets
-
The parent–child well spacing is optimized by incorporating geomechanics responses in addition to fluid-flow simulation to provide hands-on guidance for the Sichuan Basin























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(a\) :
-
One-half element length (m)
- \(a_{\max }\) :
-
Langmuir volume (m3 kg−1)
- \(A\) :
-
Area (m2)
- \({\mathbf{b}}\) :
-
Body force (m s−2)
- \(d\) :
-
Average distance (m)
- \(D\) :
-
Displacement of elements (m)
- \({\mathbf{D}}\) :
-
Stiffness tensor (MPa)
- \(E\) :
-
Young’s modulus (GPa)
- \(K\) :
-
Stress intensity factor (MPa m0.5)
- \({\mathbf{K}}\) :
-
Permeability tensor (mD)
- \(L\) :
-
Length of fracture-intersection line (m)
- \({\mathbf{n}}_{{\text{f}}}\) :
-
Normal vector of the fracture plane, dimensionless
- \(p\) :
-
Pore pressure (MPa)
- \(P_{c}\) :
-
Langmuir pressure (MPa)
- \(q\) :
-
Sink or source rate (kg m−3 s−1)
- \(q_{{{\text{ads}}}}\) :
-
Adsorption term, dimensionless
- \(S\) :
-
Saturation (%)
- \(S_{0}\) :
-
Cohesion (MPa)
- \(T\) :
-
Transmissibility factor (mD-m)
- \({\mathbf{u}}\) :
-
Displacement vector (m)
- \({\mathbf{v}}\) :
-
Darcy’s velocity (m s−1)
- \(w\) :
-
Fracture aperture (m)
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Biot–Willis coefficient, dimensionless
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Permeability decay coefficient (MPa−1)
- \({{\varvec{\updelta}}}\) :
-
Kronecker delta, dimensionless
- \({{\varvec{\upvarepsilon}}}\) :
-
Strain tensor, dimensionless
- \(\mu\) :
-
Friction coefficient, dimensionless
- \(\nu\) :
-
Poisson’s ratio, dimensionless
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- \({{\varvec{\upsigma}}}\) :
-
Total stress tensor (MPa)
- \(\sigma_{n\beta }\) :
-
Normal stress on the interface (MPa)
- \(\tau_{\beta }\) :
-
Shear stress on the interface (MPa)
- \(\phi\) :
-
Porosity (%)
References
Ajisafe, F.O., Solovyeva, I., Morales, A., Ejofodomi, E., Marongiu-Porcu, M.: Impact of well spacing and interference on production performance in unconventional reservoirs, Permian Basin. Presented at the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Austin, Texas, USA, 24–26 July. URTEC-2690466-MS (2017). https://doi.org/10.15530/URTEC-2017-2690466
Bachman, R.C., Sen, V., Khalmanova, D., M’Angha, V.O., Settari, A.: Examining the effects of stress dependent reservoir permeability on stimulated horizontal montney gas wells. Presented at the Canadian Unconventional Resources Conference, Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 15–17 November. SPE-149331-MS (2011). https://doi.org/10.2118/149331-MS
Behm, E., Al Asimi, M., Al Maskari, S., Juna, W., Klie, H., Le, D., Lutidze, G., Rastegar, R., Reynolds, A., Tathed, V., Younis, R., Zhang, Y.: Middle east steamflood field optimization demonstration project. Presented at the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 11–14 November. SPE-197751-MS (2019). https://doi.org/10.2118/197751-MS
Biot, M.A.: General theory of three-dimensional consolidation. J. Appl. Phys. 12(2), 155–164 (1941). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1712886
Biot, M.A.: Theory of elasticity and consolidation for a porous anisotropic solid. J. Appl. Phys. 26(2), 182–185 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1721956
Chen, J., Wei, Y., Wang, J., Yu, W., Qi, Y., Wu, J., Luo, W.: Inter-well interference and well spacing optimization for shale gas reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 6(5), 301–312 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnggs.2021.09.001
Defeu, C., Williams, R., Shan, D., Martin, J., Cannon, D., Clifton, K., Lollar, C.: Case study of a landing location optimization within a depleted stacked reservoir in the Midland Basin. Presented at the SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, 5–7 February. SPE-194353-MS (2019). https://doi.org/10.2118/194353-MS
Guo, X., Wu, K., Killough, J.: Investigation of production-induced stress changes for infill-well stimulation in Eagle Ford Shale. SPE J. 23(04), 1372–1388 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2118/189974-PA
Jun, Q., Xian, C., Liang, X., Zhao, C., Wang, G., Wang, L.: Characterizing and modeling multi-scale natural fractures in the Ordovician-Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi Shale Formation in South Sichuan Basin. Presented at the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Austin, Texas, USA, 24–26 July. URTEC-2691208-MS (2017). https://doi.org/10.15530/URTEC-2017-2691208
Langmuir, I.: The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40(9), 1361–1403 (1918). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Li, L., Lee, S.H.: Efficient field-scale simulation of black oil in a naturally fractured reservoir through discrete fracture networks and homogenized media. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 11(04), 750–758 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2118/103901-PA
Li, T., Razavi, O., Olson, J.E.: Modeling fracture in layered formations using a simplified 3D displacement discontinuity method. Paper presented at the 52nd U.S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, Seattle, Washington, USA, 17–20 June. ARMA-2018-1079 (2018)
Liang, X., Liu, X., Shu, H., Xian, C., Zhang, Z., Zhao, C., Li, Q., Zhang, L.: Characterization of complex multiscale natural fracture systems of the Silurian LongMaXi Gas Shale in the Sichuan Basin, China. Presented at the SPE Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition, Brisbane, Australia, 9–11 November. SPE-176938-MS (2015). https://doi.org/10.2118/176938-MS
Lindsay, G., Miller, G., Xu, T., Shan, D., Baihly, J.: Production performance of infill horizontal wells vs. pre-existing wells in the major US unconventional basins. Presented at SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, 23–25 January. SPE-189875-MS (2018). https://doi.org/10.2118/189875-MS
Liu, H.: Fluid Flow in the Subsurface: History, Generalization and Applications of Physical Laws. Springer, Cham (2017)
Liu, L., Liu, Y., Yao, J., Huang, Z.: Efficient coupled multiphase-flow and geomechanics modeling of well performance and stress evolution in shale-gas reservoirs considering dynamic fracture properties. SPE J. 25(03), 1523–1542 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2118/200496-PA
Liu, Y., Kalinin, D., Li, D., Jiao, Y., Li, R.: Understanding the complexity of fracturing in the Sichuan Shale Gas Reservoir in China. Presented at the SPE/AAPG/SEG Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 18–19 November. URTEC-198248-MS (2019). https://doi.org/10.15530/AP-URTEC-2019-198248
Marongiu-Porcu, M., Lee, D., Shan, D., Morales, A.: Advanced modeling of interwell-fracturing interference: an Eagle Ford shale-oil study. SPE J. 21(05), 1567–1582 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2118/174902-PA
Mi, L., Jiang, H., Mou, S., Li, J., Pei, Y., Liu, C.: Numerical simulation study of shale gas reservoir with stress-dependent fracture conductivity using multiscale discrete fracture network model. Part. Sci. Technol. 36(2), 202–211 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/02726351.2016.1241844
Moinfar, A., Varavei, A., Sepehrnoori, K., et al.: Development of an efficient embedded discrete fracture model for 3D compositional reservoir simulation in fractured reservoirs. SPE J. 19(02), 289–303 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2118/154246-PA
Olson, J.E.: Fracture aperture, length and pattern geometry development under biaxial loading: a numerical study with applications to natural, cross-jointed systems. Spec. Publ. 289(1), 123–142 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1144/SP289.8
Pei, Y., Yu, W., Sepehrnoori, K., Gong, Y., Xie, H., Wu, K.: The influence of development target depletion on stress evolution and infill drilling of upside target in the Permian Basin. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 24(03), 570–589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2118/205476-PA
Pei, Y., Yu, W., Sepehrnoori, K.: Investigation of vertical fracture complexity induced stress interference in multilayer shale gas reservoirs with complex natural fractures. Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Virtual, 26–29 October. SPE-201563-MS (2020). https://doi.org/10.2118/201563-MS
Pei, Y., Sepehrnoori, K.: Investigation of parent-well production induced stress interference in multilayer unconventional reservoirs. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 55, 2965–2986 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02719-1
Roussel, N.P., Florez, H.A., Rodriguez, A.A.: Hydraulic fracture propagation from infill horizontal wells. Presented at SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 30 September–2 October. SPE-166503-MS (2013). https://doi.org/10.2118/166503-MS
Safari, R., Lewis, R., Ma, X., Mutlu, U., Ghassemi, A.: Infill-well fracturing optimization in tightly spaced horizontal wells. SPE J. 22(02), 582–595 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2118/178513-PA
Sangnimnuan, A., Li, J., Wu, K.: Development of efficiently coupled fluid-flow/geomechanics model to predict stress evolution in unconventional reservoirs with complex-fracture geometry. SPE J. 23(03), 640–660 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2118/189452-PA
Sangnimnuan, A., Li, J., Wu, K., Holditch, S.: Impact of parent well depletion on stress changes and infill well completion in multiple layers in Permian Basin. Presented at SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Denver, Colorado, USA, 22–24 July. URTEC-2019-972-MS (2019). https://doi.org/10.15530/urtec-2019-972
Sepehrnoori, K., Xu, Y., Yu, W.: Embedded Discrete Fracture Modeling and Application in Reservoir Simulation. Elsevier: Developments in Petroleum Science, New York (2020)
Settari, A.T., Bachman, R.C., Walters, D.A.: How to approximate effects of geomechanics in conventional reservoir simulation. Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, USA, 9–12 October. SPE-97155-MS (2005). https://doi.org/10.2118/97155-MS
Wang, B., Fidelibus, C.: An open-source code for fluid flow simulations in unconventional fractured reservoirs. Geosciences 11(2), 106 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11020106
Wang, T., Tian, S., Liu, Q., Li, G., Sheng, M., Ren, W., Zhang, P.: Pore structure characterization and its effect on methane adsorption in shale kerogen. Pet. Sci. 18, 565–578 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12182-020-00528-9
Wang, J., Lee, H.P., Li, T., Olson, J.E.: Three-dimensional analysis of hydraulic fracture effective contact area in layered formations with natural fracture network. Presented at the 54th U.S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, Virtual, 28 June–1 July. ARMA-2020-1967 (2020)
Wu, K., Olson, J.E.: Simultaneous multifracture treatments: fully coupled fluid flow and fracture mechanics for horizontal wells. SPE J. 20(02), 337–346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2118/167626-PA
Wu, K., Olson, J.E.: Numerical investigation of complex hydraulic-fracture development in naturally fractured reservoirs. SPE Prod. Oper. 31(04), 300–309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2118/173326-PA
Xu, Y., Yu, W., Sepehrnoori, K.: Modeling dynamic behaviors of complex fractures in conventional reservoir simulators. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 22(03), 1110–1130 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2118/194498-PA
Yu, W., Sepehrnoori, K.: Simulation of gas desorption and geomechanics effects for unconventional gas reservoirs. Fuel 116, 455–464 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.032
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Reservoir Simulation Joint Industry Project at the Center for Subsurface Energy and the Environment at the University of Texas and SimTech LLC. We acknowledge Petrochina Southwest Oil & Gas Field Company for authorizing the publication of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, Y., Wu, J., Chang, C. et al. Parent–Child Well Spacing Optimization in Deep Shale Gas Reservoir with Two Complex Natural Fracture Patterns: A Sichuan Basin Case Study. Transp Porous Med 149, 147–174 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01824-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01824-1