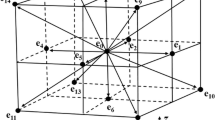
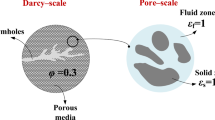
Abstract
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is of great potential in stimulating reservoirs. Thanks to the low viscosity and ultralow temperature, which makes it easy to penetrate rock pores and intensified rock failure. However, the flow and heat transfer characteristics of LN2 in rock pores are still not well understood, which limits the development of LN2 fracturing technology. To address this issue, a flow and heat transfer model was established based on Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM). A connectivity sandstone pore model was presented, combining CT scanning and the improved connectivity algorithm proposed in this paper. A series of simulations were conducted to investigate how the existence of pores and the fluid flow affect heat transfer. Moreover, a pore-scale Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) simulation optimization method was proposed to improve the calculation efficiency. The results indicate that the existence of pores and fluid flow will inhibit and assist the heat transfer, respectively. Besides, the effect of pore itself on heat transfer is greater than that of pore flow. Meanwhile, the flow and heat transfer of LN2 and two other common fracturing fluids were compared. Under the same condition, the velocity of LN2 and its rate of cooling rock are the greatest, followed by supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) and water. As a kind of fracturing fluid, LN2 is better than the other two fluids in terms of flow and heat transfer characteristics. This study provides an in-depth understanding of the mechanism of heat transfer between rocks and LN2.
































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahrami, H., Rezaee, M. R., Nazhat, D., Ostojic, J., Clennell, B. and Jamili, A.: Effect of water blocking damage on flow efficiency and productivity in tight gas reservoirs. Conference Name. OnePetro. (2011).
Benzi, R., Succi, S., Vergassola, M.: The lattice boltzmann equation: Theory and applications. Phys. Rep. 222, 145–197 (1992)
Blum, H.: A transformation for extracting new descriptors of shape. Models Perception Speech Visual Forms 1967, 362–380 (1967)
Cai, J., Huai, X.: Study on fluid-solid coupling heat transfer in fractal porous medium by lattice boltzmann method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 30, 715–723 (2010)
Cai, C., Li, G., Huang, Z., Shen, Z., Tian, S.: Rock pore structure damage due to freeze during liquid nitrogen fracturing. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39, 9249–9257 (2014)
Cengel, Y.A.: Introduction to thermodynamics and heat transfer. McGraw-Hill, New York (1997)
Chen, S., Doolen, G.D.: Lattice boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 329–364 (1998)
Contrino, D., Lallemand, P., Asinari, P., Luo, L.-S.: Lattice-boltzmann simulations of the thermally driven 2d square cavity at high rayleigh numbers. J. Comput. Phys. 275, 257–272 (2014)
Duval, F., Fichot, F., Quintard, M.: A local thermal non-equilibrium model for two-phase flows with phase-change in porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 47, 613–639 (2004)
El Abrach, H., Dhahri, H., Mhimid, A.: Numerical simulation of drying of a saturated deformable porous media by the lattice boltzmann method. Transp. Porous Media 99, 427–452 (2013)
Grundmann, S. R., Rodvelt, G. D., Dials, G. A. and Allen, R. E.: Cryogenic nitrogen as a hydraulic fracturing fluid in the devonian shale. Conference Name. OnePetro. (1998).
Guo, Z., Shi, B., Zheng, C.: A coupled lattice bgk model for the boussinesq equations. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 39, 325–342 (2002)
Hao, L., Cheng, P.: Lattice boltzmann simulations of anisotropic permeabilities in carbon paper gas diffusion layers. J. Power Sources 186, 104–114 (2009)
Hao, L., Cheng, P.: Pore-scale simulations on relative permeabilities of porous media by lattice boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53, 1908–1913 (2010)
Hongjun, W., Feng, M., Xiaoguang, T., Zuodong, L., Zhang, X., Zhenzhen, W., Denghua, L., Bo, W., Yinfu, X., Liuyan, Y.: Assessment of global unconventional oil and gas resources. Pet. Explor. Dev. 43, 925–940 (2016)
Huang, C., Shi, B., He, N., Chai, Z.: Implementation of multi-gpu based lattice boltzmann method for flow through porous media. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 7, 1–12 (2015)
Jeong, N., Choi, D.H., Lin, C.-L.: Estimation of thermal and mass diffusivity in a porous medium of complex structure using a lattice boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51, 3913–3923 (2008)
Kang, Q., Tsimpanogiannis, I.N., Zhang, D., Lichtner, P.C.: Numerical modeling of pore-scale phenomena during co2 sequestration in oceanic sediments. Fuel Process. Technol. 86, 1647–1665 (2005)
Keehm, Y., Mukerji, T., Nur, A.: Permeability prediction from thin sections: 3d reconstruction and lattice-boltzmann flow simulation. Geophys. Res. Letters. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GL018761
Kopanidis, A., Theodorakakos, A., Gavaises, E., Bouris, D.: 3d numerical simulation of flow and conjugate heat transfer through a pore scale model of high porosity open cell metal foam. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53, 2539–2550 (2010)
Lallemand, P., Luo, L.-S.: Theory of the lattice boltzmann method: Dispersion, dissipation, isotropy, galilean invariance, and stability. Phys. Rev. E 61, 6546 (2000)
Lallemand, P., Luo, L.-S.: Theory of the lattice boltzmann method: Acoustic and thermal properties in two and three dimensions. Phys. Rev. E 68, 036706 (2003)
Li, X., Ma, T., Liu, J., Zhang, H., Wang, Q.: Pore-scale investigation of gravity effects on phase change heat transfer characteristics using lattice boltzmann method. Appl. Energy 222, 92–103 (2018)
Li, J., Hong, F., Xie, R., Cheng, P.: Pore scale simulation of evaporation in a porous wick of a loop heat pipe flat evaporator using lattice boltzmann method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 102, 22–33 (2019)
Li, W. and Huang, Z.: Effects of pore structure parameters on the permeability of porous media as simulated by lbm. Conference Name. OnePetro. (2020).
Liu, Z., Wu, H.: Pore-scale modeling of immiscible two-phase flow in complex porous media. Appl. Therm. Eng. 93, 1394–1402 (2016a)
Liu, Z., Wu, H.: Pore-scale study on flow and heat transfer in 3d reconstructed porous media using micro-tomography images. Appl. Therm. Eng. 100, 602–610 (2016b)
Liu, Z., Wu, H.: Numerical modeling of liquid–gas two-phase flow and heat transfer in reconstructed porous media at pore scale. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41, 12285–12292 (2016c)
Lyons, J., Nasrabadi, H., Nasr-El-Din, H.A.: A novel pore-scale thermal-fracture-acidizing model with heterogeneous rock properties. SPE J. 21, 280–292 (2016)
Mahmoudi, S., Hashemi, A., Kord, S.: Gas-liquid relative permeability estimation in 2d porous media by lattice boltzmann method: Low viscosity ratio 2d lbm relative permeability. Iran. J. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2, 34–49 (2013)
McDaniel, B., Grundmann, S. R., Kendrick, W. D., Wilson, D. R. and Jordan, S. W.: Field applications of cryogenic nitrogen as a hydraulic fracturing fluid. Conference Name. OnePetro. (1997).
Mei, R., Yu, D., Shyy, W., Luo, L.-S.: Force evaluation in the lattice boltzmann method involving curved geometry. Phys. Rev. E 65, 041203 (2002)
Mezrhab, A., Moussaoui, M.A., Jami, M., Naji, H., Bouzidi, M.H.: Double mrt thermal lattice boltzmann method for simulating convective flows. Phys. Letters A. 374, 3499–3507 (2010)
Neumann, R.F., Barsi-Andreeta, M., Lucas-Oliveira, E., Barbalho, H., Trevizan, W.A., Bonagamba, T.J., Steiner, M.B.: High accuracy capillary network representation in digital rock reveals permeability scaling functions. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–8 (2021)
Qian, J., Li, Q., Yu, K., Xuan, Y.: A novel method to determine effective thermal conductivity of porous materials. Sci. China Ser. E: Technol. Sci. 47, 716–724 (2004)
Ren, Q., He, Y.-L., Su, K.-Z., Chan, C.L.: Investigation of the effect of metal foam characteristics on the pcm melting performance in a latent heat thermal energy storage unit by pore-scale lattice boltzmann modeling. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part a: Appli. 72, 745–764 (2017)
Ren, Q., Meng, F., Guo, P.: A comparative study of pcm melting process in a heat pipe-assisted lhtes unit enhanced with nanoparticles and metal foams by immersed boundary-lattice boltzmann method at pore-scale. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 121, 1214–1228 (2018)
Scanlon, B.R., Reedy, R.C., Nicot, J.-P.: Comparison of water use for hydraulic fracturing for unconventional oil and gas versus conventional oil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 12386–12393 (2014)
Shahraeeni, M., Hoorfar, M.: Pore-network modeling of liquid water flow in gas diffusion layers of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 39, 10697–10709 (2014)
Shu, C., Liu, N., Chew, Y.-T.: A novel immersed boundary velocity correction–lattice boltzmann method and its application to simulate flow past a circular cylinder. J. Comput. Phys. 226, 1607–1622 (2007)
Siddiqi, K., Pizer, S.: Medial representations: Mathematics, algorithms and applications. Springer Science and Business Media, Dordrecht (2008)
Succi, S., Foti, E., Higuera, F.: Three-dimensional flows in complex geometries with the lattice boltzmann method. EPL Europhys. Letters. 10, 433 (1989)
Tritton, D.J.: Experiments on the flow past a circular cylinder at low reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 6, 547–567 (1959)
Wang, M., Pan, N.: Numerical analyses of effective dielectric constant of multiphase microporous media. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 114102 (2007)
Wang, M., Wang, J., Pan, N., Chen, S.: Mesoscopic predictions of the effective thermal conductivity for microscale random porous media. Phys. Rev. E 75, 036702 (2007)
Wang, J., Ju, Y., Huang, Y., Zheng, J., Zheng, Z.: Study of the influence of porous structure on the permeability of rock using lattice boltzmann method. Proc. Eng. 102, 1835–1841 (2015)
Yan, S., Zhuo, L., Jiang, Z., Qun, L., Dongdong, L., Zhiye, G.: Progress and development trend of unconventional oil and gas geological research. Pet. Explor. Dev. 44, 675–685 (2017)
Yang, P., Wen, Z., Dou, R., Liu, X.: Heat transfer characteristics in random porous media based on the 3d lattice boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 109, 647–656 (2017)
Zdravkovich, M. and Bearman, P.: Flow around circular cylinders—volume 1: Fundamentals, UK (1998).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52020105001), the ‘111’ project of China (Grant No. B17045), and the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 51725404).
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52020105001), the ‘111’ project of China (Grant No. B17045), and the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 51725404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Huang, Z. & Dai, X. Flow and Heat Transfer of Liquid Nitrogen in Rock Pores Based on Lattice Boltzmann Method. Transp Porous Med 149, 35–69 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01821-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01821-4