Abstract
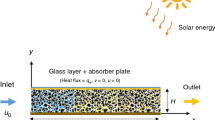
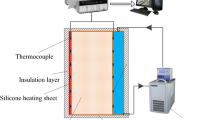
In recent years, photothermal conversion and enhanced heat transfer have received increasing attention. In order to enhance the heat transfer efficiency of photothermal conversion system, metal copper foam was partially filled in the hot surface of the photothermal conversion system. The natural convective characteristics of nanofluids in the photothermal conversion system partially filled with metal copper foam were experimentally investigated. The impact of different Fe3O4–H2O nanofluids mass fraction (ω = 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%), diverse pore densities (Φ = 15 PPI, 25 PPI, 35 PPI) and heating power (Q = 6 W, 12 W, 18 W) on natural convective heat transfer was discussed. It was found that the Nusselt number increases as the nanofluids mass fraction, but when the mass fraction is 0.3–0.5%, the enhancement ratio of Nusselt number does not increase significantly. For copper foams with the same porosity, as the pore density rises, the Nusselt number enhances more significantly. When pore density is 35 PPI, Nusselt number can be increased by 37.4%. The Nusselt number can be increased by increasing heating power, but the Nusselt number enhancement ratio is greater at smaller heating power.
Article Highlights
-
Finite-thickness metal copper foam is partially filled in the hot surface.
-
Effect of diverse pore densities of metal copper foam is studied.
-
Nusselt number can be increased by up to 37.4% when pore density is 35 PPI.
-
A smaller input power can result in a larger Nusselt number enhancement ratio.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Area of the copper, m2
- H :
-
Convection heat transfer coefficient, W⋅m−2⋅K−1
- I :
-
Electric current, A
- L :
-
Wetted perimeter, m
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Q:
-
Heating power, W
- Q net :
-
Effective heating power, W
- Q loss :
-
Heat loss, W
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- T H * :
-
Outer surface temperature of heating end, K
- T H :
-
Inner surface temperature of heating end, K
- T C * :
-
Outer surface temperature of cooling end, K
- T C :
-
Inner surface temperature of cooling end, K
- T m :
-
Qualitative temperature, K
- U :
-
Voltage, V
- W :
-
Cavity thickness, m
- ε :
-
Heat transfer enhancement ratio
- δ :
-
Copper plate thickness, m
- λ f :
-
Thermal conductivity of fluid, W⋅m−1⋅K−1
- λ w :
-
Thermal conductivity of copper plate, W⋅m−1⋅K−1
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity of nanofluids, Pa⋅s
- ρ :
-
Density of nanofluids, kg⋅m−3
- Φ :
-
Pore density, PPI
- φ :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction, %
- ω :
-
Nanoparticle mass fraction, %
References
Afrand, M.: Experimental study on thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol containing hybrid nano-additives and development of a new correlation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 110, 1111–1119 (2017a)
Afrand, M.: Using a magnetic field to reduce natural convection in a vertical cylindrical annulus. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 118, 12–23 (2017b)
Arbaban, M., Salimpour, M.R.: Enhancement of laminar natural convective heat transfer in concentric annuli with radial fins using nanofluids. Heat Mass Transf. 51(3), 353 (2014)
Attouchi, M.T., Larbi, S., Khelladi, S.: Effect of some parameters on natural convection heat transfer in finned enclosures-a case study. Int. J. Thermofluid Sci. Tech. 9(1), 090102 (2021)
Bahiraei, M., Heshmatian, S.: Efficacy of a novel liquid block working with a nanofluid containing graphene nanoplatelets decorated with silver nanoparticles compared with conventional CPU coolers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 127, 1233–1245 (2017a)
Bahiraei, M., Heshmatian, S.: Optimizing energy efficiency of a specific liquid block operated with nanofluids for utilization in electronics cooling: a decision-making based approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 154, 180–190 (2017b)
Bahiraei, M., Heshmatian, S.: Application of a novel biological nanofluid in a liquid block heat sink for cooling of an electronic processor: thermal performance and irreversibility considerations. Energy Convers. Manag. 149, 155–167 (2017c)
Bao, K., Hua, C., Wang, X., Han, X., Chen, G.: Experimental investigation on the heat transfer performance and evaporation temperature fluctuation of a new-type metal foam multichannel heat pipe. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 154, 119672 (2020)
Barnoon, P., Toghraie, D., Eslami, F., Mehmandoust, B.: Entropy generation analysis of different nanofluid flows in the space between two concentric horizontal pipes in the presence of magnetic field: single-phase and two-phase approaches. Comput. Math. Appl. 77(3), 662–692 (2019)
Chakraborty, S., Panigrahi, P.K.: Stability of nanofluid: a review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 174, 115259 (2020)
Chen, M., Wang, X., Hu, Y., He, Y.: Coupled plasmon resonances of Au thorn nanoparticles to enhance solar absorption performance. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 250, 107029 (2020)
Chen, X., Zhou, P., Yan, H., Chen, M.: Systematically investigating solar absorption performance of plasmonic nanoparticles. Energy. 216, 119254 (2021)
Chen, M., Chen, X., Yan, H., Zhou, P.: Theoretical design of nanoparticle-based spectrally emitter for thermophotovoltaic applications. Physica E. 126, 114471 (2021)
Chummar, A., Harish, R.: CFD simulation of laminar free convection flows of nanofluids in a cubical enclosure. Mater. Today Proc (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.10.105
Dehnavi, R., Rezvani, A.: Numerical investigation of natural convection heat transfer of nanofluids in a Γ shaped cavity. Superlattice. Microst. 52(2), 312–325 (2012)
Fan, F., Qi, C., Tang, J., Liu, Q., Wang, X., Yan, Y.: A novel thermal efficiency analysis on the thermo-hydraulic performance of nanofluids in an improved heat exchange system under adjustable magnetic field. Appl. Therm. Eng. 179, 115688 (2020)
Fan, Y., Zhao, Y., Torres, J.F., Xu, F., Lei, C., Li, Y., Carmeliet, J.: Natural convection over vertical and horizontal heated flat surfaces: a review of recent progress focusing on underpinnings and implications for heat transfer and environmental applications. Phys. Fluids. 33(10), 101301 (2021)
Giwa, S.O., Sharifpur, M., Ahmadi, M.H., Meyer, J.P.: A review of magnetic field influence on natural convection heat transfer performance of nanofluids in square cavities. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 145(5), 2581–2623 (2021)
Ho, C.J., Chen, M.W., Li, Z.W.: Numerical simulation of natural convection of nanofluid in a square enclosure: effects due to uncertainties of viscosity and thermal conductivity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51(17–18), 4506–4516 (2008)
Ho, C.J., Liu, W.K., Chang, Y.S., Lin, C.C.: Natural convection heat transfer of alumina-water nanofluid in vertical square enclosures: an experimental study. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49(8), 1345–1353 (2010)
Javadpour, A., Najafi, M., Lowrey, S.: Experimental study of natural convection heat transfer from horizontal cam tubes in a vertical array under constant heat flux. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-11119-0
Kargarsharifabad, H.: Experimental and numerical study of natural convection of Cu-water nanofluid in a cubic enclosure under constant and alternating magnetic fields. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 119, 104957 (2020)
Karimipour, A.: New correlation for Nusselt number of nanofluid with Ag/Al2O3/Cu nanoparticles in a microchannel considering slip velocity and temperature jump by using lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 91, 146–156 (2015)
Karimipour, A., Alipour, H., Akbari, O.A., Semiromi, D.T., Esfe, M.H.: Studying the effect of indentation on flow parameters and slow heat transfer of water-silver nano-fluid with varying volume fraction in a rectangular two-dimensional micro channel. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 8(15), 51707 (2015)
Karimipour, A., D’Orazio, A., Shadloo, M.S.: The effects of different nano particles of Al2O3 and Ag on the MHD nano fluid flow and heat transfer in a microchannel including slip velocity and temperature jump. Physica E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 86, 146–153 (2017)
Kavusi, H., Toghraie, D.: A comprehensive study of the performance of a heat pipe by using of various nanofluids. Adv. Powder Technol. 28(11), 3074–3084 (2017)
Kiwan, S., Alwan, H., Abdelal, N.: An experimental investigation of the natural convection heat transfer from a vertical cylinder using porous fins. Appl. Therm. Eng. 179, 115673 (2020)
Lenin, R., Joy, P.A., Bera, C.: A review of the recent progress on thermal conductivity of nanofluid. J. Mol. Liq. 338, 116929 (2021)
Li, J.Q., Mou, L.W., Zhang, J.Y., Zhang, Y.H., Fan, L.W.: Enhanced pool boiling heat transfer during quenching of water on superhydrophilic porous surfaces: effects of the surface wickability. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 125, 494–505 (2018)
Mahdy, A., Ahmed, S.E., Mansour, M.A.: Entropy generation for MHD natural convection in enclosure with a micropolar fluid saturated porous medium with Al2O3Cu water hybrid nanofluid. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control. 26(6), 1123–1143 (2021)
Mansour, R.B., Galanis, N., Nguyen, C.T.: Experimental study of mixed convection with water-Al2O3 nanofluid in inclined tube with uniform wall heat flux. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50(3), 403–410 (2011)
Mei, S., Qi, C., Liu, M., Fan, F., Liang, L.: Effects of paralleled magnetic field on thermo-hydraulic performances of Fe3O4-water nanofluids in a circular tube. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 134, 707–721 (2019)
Morimoto, T., Kumano, H.: Natural convection characteristics of phase-change material emulsions in a rectangular vessel with vertical heating/cooling walls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 183(Part C), 122234 (2022)
Muneeshwaran, M., Srinivasan, G., Muthukumar, P., Wang, C.C.: Role of hybrid-nanofluid in heat transfer enhancement-A review. Int. Commun. Heat Mass. Transf. 125, 105341 (2021)
Okonkwo, E.C., Wole-Osho, I., Almanassra, I.W., Abdullatif, Y.M., Al-Ansari, T.: An updated review of nanofluids in various heat transfer devices. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 145(6), 2817–2872 (2021)
Parveen, R., Mondal, P., Mahapatra, T.R.: Double diffusive magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) natural convection and entropy generation in a discretely heated inclined dome-shaped enclosure filled with cu-water nanofluid. J. Nanofluids. 10(4), 564–579 (2021)
Pordanjani, A.H., Aghakhani, S., Afrand, M., Sharifpur, M., Meyer, J.P., Xu, H., Ali, H.M., Karimi, N., Cheraghian, G.: Nanofluids: physical phenomena, applications in thermal systems and the environment effects-a critical review. J. Clean Prod. 320, 128573 (2021)
Qi, C., Wan, Y., Liang, L., Rao, Z., Li, Y.: Numerical and experimental investigation into the effects of nanoparticle mass fraction and bubble size on boiling heat transfer of TiO2-water nanofluid. J. Heat Transf. 138, 8 (2016)
Qi, C., Wang, G., Ma, Y., Guo, L.: Experimental research on stability and natural convection of TiO2-Water nanofluid in enclosures with different rotation angles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 396 (2017)
Rahmati, A.R., Akbari, O.A., Marzban, A., Toghraie, D., Karimi, R., Pourfattah, F.: Simultaneous investigations the effects of non-Newtonian nanofluid flow in different volume fractions of solid nanoparticles with slip and no-slip boundary conditions. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 5, 263–277 (2018)
Shahsavar, A., Sardari, P.T., Toghraie, D.: Free convection heat transfer and entropy generation analysis of water-Fe3O4/CNT hybrid nanofluid in a concentric annulus. Int. J. Numer. Method Heat Fluid Flow 29(3), 915–934 (2019)
Sharifpur, M., Giwa, S.O., Lee, K.Y., Ghodsinezhad, H., Meyer, J.P.: Experimental investigation into natural convection of zinc oxide/water nanofluids in a square cavity. Heat Transf. Eng. 42(19–20), 1675–1687 (2020)
Sheikholeslami, M., Seyednezhad, M.: Simulation of nanofluid flow and natural convection in a porous media under the influence of electric field using CVFEM. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 120, 772–781 (2018)
Sheikholeslami, M., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: On simulation of nanofluid radiation and natural convection in an enclosure with elliptical cylinders. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 115, 981–991 (2017)
Soltani, F., Toghraie, D., Karimipour, A.: Experimental measurements of thermal conductivity of engine oil-based hybrid and mono nanofluids with tungsten oxide (WO3) and MWCNTs inclusions. Powder Technol. 371, 37–44 (2020)
Toghraie, D., Sina, N., Jolfaei, N.A., Hajian, M., Afrand, M.: Designing an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) to predict the viscosity of Silver/Ethylene glycol nanofluid at different temperatures and volume fraction of nanoparticles. Phys. A 534, 122142 (2019)
Wang, X., Yan, X., Gao, N., Chen, G.: Prediction of thermal conductivity of various nanofluids with ethylene glycol using artificial neural network. J. Therm. Sci. 29(6), 1504–1512 (2020)
Yousif, A.A., Alomar, O.R., Hussein, A.T.: Impact of using triple adiabatic obstacles on natural convection inside porous cavity under non-darcy flow and local thermal non-equilibrium model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 130, 105760 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by "National Natural Science Foundation of China" (Grant No. 51606214).
Funding
This funding was provided by "National Natural Science Foundation of China" (Grant No. 51606214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Z., Qi, C., Zhang, L. et al. Effect of Metal Foam on Natural Convective Heat Transfer of Nanofluids in a Photothermal Conversion System. Transp Porous Med 142, 599–621 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01761-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-022-01761-z