Abstract
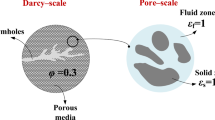
Digital rock analysis provides us a powerful tool for predicting geophysical properties and studying fluid and interfacial transport mechanisms in rocks. However, people have to struggle and find a balance between scanning resolution and sample size due to current limitations of imaging technologies. With satisfaction of resolution requirement, the sample size has to be larger than the critical size of representative element volume (REV), so that the consequent pore-scale models are able to provide meaningful geophysical predictions for upscaling to Darcy-scale analysis. Following our previous work [Energies, 11: 1798, 2018] on REV size for single-phase flow, this work considers the critical size of REV for multiphase flow in porous media. A multiphase lattice Boltzmann model has been developed for simulation of two-phase immiscible flow. The relative permeability, which can be influenced by the capillary number and wettability, and the saturation of phases are calculated for upscaling. The critical size of REV for multiphase flow in porous media is therefore found and compared with that for single-phase flow. It is found that the REV size for the relative permeability–saturation curve of multiphase flow, which is influenced by the phase interaction and wettability, is beyond twice of that for the absolute permeability of single-phase flow in the present study.
Article Highlights
-
The critical size of REV for multiphase flow in porous media is determined by pore-scale modeling.
-
The REV size of multiphase flow is beyond twice that of single-phase flow on the same porous structure.
-
The REV size for the relative permeability–saturation curve is influenced by the phase interaction and wettability.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The original data are not available publicly online but can be provided by the authors for interested researchers.
Code Availability
The source code is not available publicly online but can be provided by the authors for interested researchers.
References
Akai, T., Bijeljic, B., Blunt, M.J.: Wetting boundary condition for the color-gradient lattice boltzmann method: validation with analytical and experimental data. Adv Water Resour 116, 56–66 (2018)
Akbarabadi, M., Piri, M.: Relative permeability hysteresis and capillary trapping characteristics of supercritical CO2/brine systems: an experimental study at reservoir conditions. Adv Water Resour 52, 190–206 (2013)
Aliseda, A., Heindel, T.J.: X-ray flow visualization in multiphase flows. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 53(543), 567 (2021)
Alpak, F.O., Berg, S., Zacharoudiou, I.: Prediction of fluid topology and relative permeability in imbibition in sandstone rock by direct numerical simulation. Adv Water Resour 122, 49–59 (2018)
Avraam, D.G., Payatakes, A.C.: Flow mechanisms, relative permeabilities, and coupling effects in steady-state two-phase flow through porous media, the case of strong wettability. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 38(3), 778–786 (1999)
Ayub, M., Bentsen, R.G.: Interfacial viscous coupling: a myth or reality? J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 23(1), 13–26 (1999)
Ba, Y., Liu, H., Li, Q., Kang, Q., Sun, J.: Multiple-relaxation-time color-gradient lattice boltzmann model for simulating two-phase flows with high density ratio. Phys. Rev. E 94(2), 023310 (2016)
Bear, J.: Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Dover Publications, New York (1972)
Bentsen, R.G.: Effect of momentum transfer between fluid phases on effective mobility. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 21(1–2), 27–42 (1998)
Blunt, M.J., Bijeljic, B., Dong, H., Gharbi, O., Iglauer, S., Mostaghimi, P., Paluszny, A., Pentland, C.: Pore-scale imaging and modelling. Adv. Water Resour. 51, 197–216 (2013)
Brackbill, J.U., Kothe, D.B., Zemach, C.: A continuum method for modeling surface-tension. J. Comput. Phys. 100(2), 335–354 (1992)
Chen, S., Doolen, G.D.: Lattice boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 30, 329–364 (1998)
Chen, Y., Li, Y., Valocchi, A.J., Christensen, K.T.: Lattice Boltzmann simulations of liquid CO2 displacing water in a 2D heterogeneous micromodel at reservoir pressure conditions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 212, 14–27 (2018)
Dai, Z., Middleton, R., Viswanathan, H., Fessenden-Rahn, J., Bauman, J., Pawar, R., Lee, S.-Y., McPherson, B.: An integrated framework for optimizing CO2 sequestration and enhanced oil recovery. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 1(1), 49–54 (2014)
d’Humieres, D., Ginzburg, I., Krafczyk, M., Lallemand, P., Luo, L.S.: Multiple-relaxation-time lattice boltzmann models in three dimensions. Philos Trans Royal Soc London Serv: Maths Phys Eng Sci 360(1792), 437–451 (2002)
Dou, Z., Zhou, Z.-F.: Numerical study of non-uniqueness of the factors influencing relative permeability in heterogeneous porous media by lattice boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 42, 23–32 (2013)
Dullien, F.A.L., Dong, M.: Experimental determination of the flow transport coefficients in the coupled equations of two-phase flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 25(1), 97–120 (1996)
Gharbi, O., Blunt, M.J.: The impact of wettability and connectivity on relative permeability in carbonates: a pore network modeling analysis. Water Resour Res (2012). https://doi.org/10.1029/2012WR011877
Gunstensen, A.K., Rothman, D.H., Zaleski, S., Zanetti, G.: Lattice boltzmann model of immiscible fluids. Phys. Rev. A 43(8), 4320–4327 (1991)
Guo, Z., Zheng, C.: Analysis of lattice boltzmann equation for microscale gas flows: relaxation times, boundary conditions and the knudsen layer. Int J Comput Fluid Dyn 22(7), 465–473 (2008)
Guo, Z.L., Zheng, C.G., Shi, B.C.: An extrapolation method for boundary conditions in lattice boltzmann method. Phys. Fluids 14(6), 2007–2010 (2002)
Guo, Y., He, X., Huang, W., Wang, M.: Microstructure effects on effective gas diffusion coefficient of nanoporous materials. Transp. Porous Media 126(2), 431–453 (2019)
Ha, J., Kim, H.Y.: Capillarity in soft porous solids. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 52, 263–284 (2020)
Hughes, R.G., Blunt, M.J.: Pore scale modeling of rate effects in imbibition. Transp. Porous Media 40(3), 295–322 (2000)
Huppert, H.E., Neufeld, J.A.: The fluid mechanics of carbon dioxide sequestration. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 46, 255–272 (2014)
Jiang, F., Tsuji, T.: Estimation of three-phase relative permeability by simulating fluid dynamics directly on rock-microstructure images. Water Resour. Res. 53(1), 11–32 (2017)
Kang, Q.J., Lichtner, P.C., Viswanathan, H.S., Abdel-Fattah, A.I.: Pore scale modeling of reactive transport involved in geologic CO2 sequestration. Transp. Porous Media 82(1), 197–213 (2010)
Krevor, S.C.M., Pini, R., Zuo, L., Benson, S.M.: Relative permeability and trapping of CO2 and water in sandstone rocks at reservoir conditions. Water Resour Res (2012). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR010859
Latva-Kokko, M., Rothman, D.H.: Diffusion properties of gradient-based lattice boltzmann models of immiscible fluids. Phys. Rev. E 71(5), 056702 (2005)
Liu, H., Valocchi, A.J., Werth, C., Kang, Q., Oostrom, M.: Pore-scale simulation of liquid CO2 displacement of water using a two-phase lattice Boltzmann model. Adv. Water Resour. 73, 144–158 (2014)
Liu, T., Jin, X., Wang, M.: Critical resolution and sample size of digital rock analysis for unconventional reservoirs. Energies 11(7), 1798 (2018)
Liu, T., Zhang, S., Wang, M.: Does rheology of Bingham fluid influence upscaling of flow through tight porous media? Energies 14(3), 680 (2021)
Mehmani, A., Kelly, S., Torres-Verdín, C.: Leveraging digital rock physics workflows in unconventional petrophysics: A review of opportunities, challenges, and benchmarking. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 190, (2020)
Mostaghimi, P., Blunt, M.J., Bijeljic, B.: Computations of absolute permeability on micro-CT images. Math. Geosci. 45(1), 103–125 (2013)
Pan, C., Luo, L.-S., Miller, C.T.: An evaluation of lattice Boltzmann schemes for porous medium flow simulation. Comput. Fluids 35(8–9), 898–909 (2006)
Parlange, J.Y.: Water transport in soils. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 12, 77–102 (1980)
Shi, Y., Tang, G.H.: Relative permeability of two-phase flow in three-dimensional porous media using the lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 73, 101–113 (2018)
Sukop, M.C., Or, D.: Lattice boltzmann method for modeling liquid-vapor interface configurations in porous media. Water Resour Res (2004). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003WR002333
Vilarrasa, V., Bolster, D., Dentz, M., Olivella, S., Carrera, J.: Effects of CO2 compressibility on CO2 storage in deep saline aquifers. Transp. Porous Media 85(2), 619–639 (2010)
Wang, J., Wang, M., Li, Z.: A lattice boltzmann algorithm for fluid-solid conjugate heat transfer. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 46(3), 228–234 (2007a)
Wang, M., Wang, J., Chen, S.: Roughness and cavitations effects on electro-osmotic flows in rough microchannels using the lattice poisson-boltzmann methods. J. Comput. Phys. 226(1), 836–851 (2007b)
Wang, F., Liu, T., Lei, W., Zhao, Y., Li, B., Yang, G., Liu, Y., Wang, M.: Dynamic analysis of deformation and start-up process of residual-oil droplet on wall under shear flow. J Petr Sci Eng 199, 108335 (2021)
Xie, C., Lei, W., Wang, M.: Lattice Boltzmann model for three-phase viscoelastic fluid flow. Phys. Rev. E 97(2), 023312 (2018a)
Xie, C., Lv, W., Wang, M.: Shear-thinning or shear-thickening fluid for better EOR? - A direct pore-scale study. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 161, 683–691 (2018b)
Xu, Z., Liu, H., Valocchi, A.J.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of immiscible two-phase flow with capillary valve effect in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 53(5), 3770–3790 (2017)
Yi, J., Xing, H., Wang, J., Xia, Z., Jing, Y.: Pore-scale study of the effects of surface roughness on relative permeability of rock fractures using lattice boltzmann method. Chem Eng Sci 209, 115178 (2019)
Yiotis, A.G., Psihogios, J., Kainourgiakis, M.E., Papaioannou, A., Stubos, A.K.: A lattice Boltzmann study of viscous coupling effects in immiscible two-phase flow in porous media. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspect 300(1–2), 35–49 (2007)
Yoon, H., Dewers, T.A.: Nanopore structures, statistically representative elementary volumes, and transport properties of chalk. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40(16), 4294–4298 (2013)
Yu, Z., Fan, L.S.: Multirelaxation-time interaction-potential-based lattice boltzmann model for two-phase flow. Phys Rev E 82(4), 046708 (2010)
Zhao, H., Ning, Z., Kang, Q., Chen, L., Zhao, T.: Relative permeability of two immiscible fluids flowing through porous media determined by lattice boltzmann method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 85, 53–61 (2017)
Zhao, J., Kang, Q., Yao, J., Viswanathan, H., Pawar, R., Zhang, L., Sun, H.: The effect of wettability heterogeneity on relative permeability of two-phase flow in porous media: a lattice boltzmann study. Water Resour. Res. 54(2), 1295–1311 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFA0708704) and NSF grant of China (No. U1837602). Our simulations are run on the “Explorer 100” cluster of Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL performed simulation and analysis of data and wrote the paper. MW provided guidance and critical review of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Wang, M. Critical REV Size of Multiphase Flow in Porous Media for Upscaling by Pore-Scale Modeling. Transp Porous Med 144, 111–132 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01621-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01621-2