Abstract
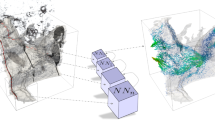
Direct numerical simulations of flow on micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) images are extensively used in many disciplines of science and engineering. Recently, we have developed a pore-scale finite volume solver (PFVS) to directly solve for flow on micro-CT images and predict permeability of digital cores. The solver assigns a local conductivity to each voxel based on geometrical and topological constraints. The local conductivity term in PFVS is conventionally calculated by an iterative local scanning algorithm, where the number of iterations depends on the size of the largest flow channel. This can increase the computation time of PFVS significantly if the largest flow channel is reasonably large. In this paper, we apply convolutional neural networks (CNN) to predict local conductivity for each voxel, thus bypassing the iterative algorithm while also preserving the mass conservation in the system by still solving for flow using conventional methods. The network is trained to convert segmented binary images of rocks into a numerical map required for flow simulation by the use of paired image-to-image translation using a ResNet-Style architecture. Comparison of the generated and original coefficient maps shows that the average error is within 1% over the 3D pore geometries used in this study. Then, we compare the absolute permeability results obtained from the original PFVS and the CNN-PFVS and the errors are within 20% with the average of 13.8%. Machine learning improves the computation time significantly especially on the images with large domain size and flow channels. On the samples tested, the speedup factor is 10 times using CNN compared to iterative calculations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarnes, J., et al.: Geometrical Modeling, Numerical Simulation, and Optimization: Industrial Mathematics at SINTEF, chapter An introduction to the numerics of flow in porous media using Matlab. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Al-Dhahli, A.R., et al.: Three-phase pore-network modeling for reservoirs with arbitrary wettability. SPE J. 18(02), 285–295 (2012)
Alpak, F., et al.: Prediction of fluid topology and relative permeability in imbibition in sandstone rock by direct numerical simulation. Adv. Water Resour. 122, 49–59 (2018)
Alqahtani, N., et al.: Machine learning for predicting properties of porous media from 2d X-ray images. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 184, 106514 (2020)
Armstrong, R.T., et al.: Modeling the velocity field during Haines jumps in porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 77, 57–68 (2015)
Armstrong, R., et al.: Modeling of pore-scale two-phase phenomena using density functional hydrodynamics. Transp. Porous Media 112(3), 577–607 (2016a)
Armstrong, R.T., et al.: Beyond Darcy's law: The role of phase topology and ganglion dynamics for two-fluid flow. Phys. Rev. E 94(4), 043113 (2016b)
Bakke, S., Øren, P.-E.: 3-D pore-scale modelling of sandstones and flow simulations in the pore networks. SPE J. 2(02), 136–149 (1997)
Berg, C.F.: Permeability description by characteristic length, tortuosity, constriction and porosity. Transp. Porous Media 103(3), 381–400 (2014)
Berg, S., et al.: Connected pathway relative permeability from pore-scale imaging of imbibition. Adv. Water Resour. 90, 24–35 (2016)
Bijeljic, B., Blunt, M.J.: Pore-scale modeling and continuous time random walk analysis of dispersion in porous media. Water Resour. Res. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004578
Bijeljic, B., et al.: Predictions of non-Fickian solute transport in different classes of porous media using direct simulation on pore-scale images. Phys. Rev. E 87(1), 013011 (2013)
Blunt, M.J.: Flow in porous media—pore-network models and multiphase flow. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 6(3), 197–207 (2001)
Blunt, M.J.: Multiphase Flow in Permeable Media: A Pore-Scale Perspective. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2017)
Blunt, M., King, P.: Macroscopic parameters from simulations of pore scale flow. Phys. Rev. A 42(8), 4780 (1990)
Blunt, M., King, P.: Relative permeabilities from two-and three-dimensional pore-scale network modelling. Transp. Porous Media 6(4), 407–433 (1991)
Blunt, M.J., et al.: Detailed physics, predictive capabilities and macroscopic consequences for pore-network models of multiphase flow. Adv. Water Resour. 25(8–12), 1069–1089 (2002)
Blunt, M.J., et al.: Pore-scale imaging and modelling. Adv. Water Resour. 51, 197–216 (2013)
Chhatre, S.S., et al.: A blind study of four digital rock physics vendor labs on porosity, absolute permeability, and primary drainage capillary pressure data on tight outcrop rocks. In: Annual Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts (2017)
Chung, T., et al.: Approximating permeability of microcomputed-tomography images using elliptic flow equations. SPE J. 24, 1–154 (2019)
Chung, T., et al.: Voxel agglomeration for accelerated estimation of permeability from micro-CT images. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 184, 106577 (2020)
Coenen, J., et al.: Measurement parameters and resolution aspects of micro X-ray tomography for advanced core analysis. In: Proceedings of International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts (2004)
Dong, H., Blunt, M.J.: Pore-network extraction from micro-computerized-tomography images. Phys. Rev. E 80(3), 036307 (2009)
Erofeev, A., et al.: Prediction of porosity and permeability alteration based on machine learning algorithms. Transp. Porous Media 128(2), 677–700 (2019)
Flannery, B.P., et al.: Three-dimensional X-ray microtomography. Science 237(4821), 1439–1444 (1987)
Hazlett, R.: Simulation of capillary-dominated displacements in microtomographic images of reservoir rocks. Multiphase Flow Porous Media 20, 21–35 (1995)
Hughes, R.G., Blunt, M.J.: Pore scale modeling of rate effects in imbibition. Transp. Porous Media 40(3), 295–322 (2000)
Hurley, N. F., et al.: Multiscale digital rock modeling for reservoir simulation, Google Patents (2015)
Huynh-Thu, Q., Ghanbari, M.J.E.I.: Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment. Electron. Lett. 44(13), 800–801 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20080522
Kamrava, S., et al.: Linking morphology of porous media to their macroscopic permeability by deep learning. Transp. Porous Media 131(2), 427–448 (2020)
Khayrat, K., Jenny, P.: A multi-scale network method for two-phase flow in porous media. J. Comput. Phys. 342, 194–210 (2017)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint http://arxiv.org/abs/05322 (2014)
Lie, K.A., et al.: Open-source MATLAB implementation of consistent discretisations on complex grids. Comput. Geosci. 16(2), 297–322 (2012)
Lindquist, W.B., et al.: Medial axis analysis of void structure in three-dimensional tomographic images of porous media. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 101(B4), 8297–8310 (1996)
Liu, M., Mostaghimi, P.: Characterisation of reactive transport in pore-scale correlated porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 173, 121–130 (2017a)
Liu, M., Mostaghimi, P.: Pore-scale simulation of dissolution-induced variations in rock mechanical properties. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 111, 842–851 (2017b)
Liu, M., et al.: Impact of mineralogical heterogeneity on reactive transport modelling. Comput. Geosci. 104, 12–19 (2017a)
Liu, Z., et al.: Pore-scale characterization of two-phase flow using integral geometry. Transp. Porous Media 118(1), 99–117 (2017b)
McClure, J.E., et al.: A novel heterogeneous algorithm to simulate multiphase flow in porous media on multicore CPU–GPU systems. Comput. Phys. Commun. 185(7), 1865–1874 (2014)
Meakin, P., Tartakovsky, A.M.: Modeling and simulation of pore-scale multiphase fluid flow and reactive transport in fractured and porous media. Rev. Geophys. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008RG000263
Menke, H.P., et al.: Dynamic three-dimensional pore-scale imaging of reaction in a carbonate at reservoir conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(7), 4407–4414 (2015)
Molins, S., et al.: An investigation of the effect of pore scale flow on average geochemical reaction rates using direct numerical simulation. Water Resour. Res. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR011404
Mostaghimi, P., et al.: Simulation of flow and dispersion on pore-space images. SPE J. 17(04), 1131–131141 (2012)
Mostaghimi, P., et al.: Computations of absolute permeability on micro-CT images. Math. Geosci. 45(1), 103–125 (2013)
Mostaghimi, P., et al.: Numerical simulation of reactive transport on micro-CT images. Math. Geosci. 48(8), 963–983 (2016)
Mostaghimi, P., et al.: Cleat-scale characterisation of coal: an overview. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 39, 143–160 (2017)
Notay, Y.: An aggregation-based algebraic multigrid method. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 37(6), 123–146 (2010)
Øren, P.-E., Bakke, S.: Reconstruction of Berea sandstone and pore-scale modelling of wettability effects. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 39(3–4), 177–199 (2003)
Ovaysi, S., Piri, M.: Direct pore-level modeling of incompressible fluid flow in porous media. J. Comput. Phys. 229(19), 7456–7476 (2010)
Ovaysi, S., Piri, M.: Multi-GPU acceleration of direct pore-scale modeling of fluid flow in natural porous media. Comput. Phys. Commun. 183(9), 1890–1898 (2012)
Rabbani, A., Babaei, M.J.: Hybrid pore-network and lattice-Boltzmann permeability modelling accelerated by machine learning. Adv. Water Resour. 126, 116–128 (2019)
Rabbani, A., et al.: Pore network extraction using geometrical domain decomposition. Adv. Water Resour. 123, 70–83 (2019)
Raeini, A.Q., et al.: Validating the generalized pore network model using micro-CT images of two-phase flow. Transp. Porous Media 130(2), 405–424 (2019)
Ramstad, T., et al.: Pore-scale simulations of single-and two-phase flow in porous media: approaches and applications. Transp. Porous Media 1–28 (2019)
Rassenfoss, S.: Digital rocks out to become a core technology. J. Petrol. Technol. 63(05), 36–41 (2011)
Salazar-Tio, R. (2014). System and method for multi-phase segmentation of density images representing porous media, Google Patents.
Schlüter, S., et al.: Image processing of multiphase images obtained via X-ray microtomography: a review. Water Resour. Res. 50(4), 3615–3639 (2014)
Shabro, V., et al.: Finite-difference approximation for fluid-flow simulation and calculation of permeability in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 94(3), 775–793 (2012)
Sorbie, K., Skauge, A.: Can network modeling predict two-phase flow functions? Petrophysics 53(06), 401–409 (2012)
Sudakov, O., et al.: Driving digital rock towards machine learning: predicting permeability with gradient boosting and deep neural networks. Comput. Geosci. 127, 91–98 (2019)
Szegedy, C., et al.: Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2017)
Valvatne, P.H., Blunt, M.J.: Predictive pore-scale modeling of two-phase flow in mixed wet media. Water Resour. Res. (2004). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003WR002627
Wang, Y., et al.: Computations of permeability of large rock images by dual grid domain decomposition. Adv Water Resour. Res. 126, 1–14 (2019a)
Wang, Y.D., et al.: Enhancing resolution of digital rock images with super resolution convolutional neural networks. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 182, 106261 (2019b)
Wang, Y., et al.: Accelerated computation of relative permeability by coupled morphological and direct multiphase flow simulation. J. Comput. Phys. 401, 108966 (2020a)
Wang, Y.D., et al.: Physical Accuracy of Deep Neural Networks for 2D and 3D Multi-Mineral Segmentation of Rock micro-CT Images. arXiv preprint http://arxiv.org/abs/05322 (2020b)
Wildenschild, D., Sheppard, A.P.: X-ray imaging and analysis techniques for quantifying pore-scale structure and processes in subsurface porous medium systems. Adv. Water Resour. 51, 217–246 (2013)
Yang, J.: Multi-scale simulation of multiphase multi-component flow in porous media using the Lattice Boltzmann Method, Imperial College London (2013). https://doi.org/10.25560/18928
Yang, X., et al.: Direct numerical simulation of pore-scale flow in a bead pack: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging observations. Adv. Water Resour. 54, 228–241 (2013)
Zacharoudiou, I., Boek, E.S.: Capillary filling and Haines jump dynamics using free energy Lattice Boltzmann simulations. Adv. Water Resour. 92, 43–56 (2016)
Zhang, Y., et al.: On the challenges of greyscale-based quantifications using X-ray computed microtomography. J. Microsc. 275(2), 82–96 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, T., Da Wang, Y., Armstrong, R.T. et al. CNN-PFVS: Integrating Neural Network and Finite Volume Models to Accelerate Flow Simulation on Pore Space Images. Transp Porous Med 135, 25–37 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01466-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01466-1