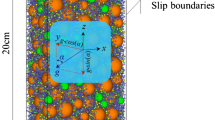
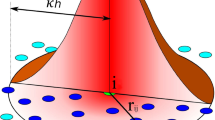
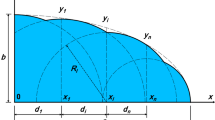
Abstract
Tortuosity quantitatively reflects the complexity of porous media. For the diffusion process in porous media, diffusive tortuosity is inevitably an important research topic. A simulation experimental method is proposed to study diffusive tortuosity in granular soil based on 3D pore-scale simulation by smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). On the basis of the simulation results, the relationships between diffusive tortuosity and microstructural parameters are discussed. Simulation experiments are implemented on 3D granular soil columns generated by PFC software and soil layers formed by periodic expansion of the soil columns. The accuracy of the pore-scale SPH diffusion model is verified by the analytic solution for the particular case of a pure water column. The results show that the dimensionality does affect the diffusive tortuosity. 2D profiles cannot represent the original 3D medium in terms of the diffusion characteristics. Within the limited range of the variation of porosity during soil compression, the relationship between porosity and diffusive tortuosity can be considered to be linear. In addition, for the case of uniform granule size, diffusive tortuosity is almost linearly related to the specific surface area. Tortuosity values for soil columns are larger than those for the soil layer, which denotes that the effect of the sidewall on diffusion cannot be overlooked for a centimeter-scale soil column.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Mass concentration of species in the solution
- C :
-
Total mass concentration of the species based on the total volume of soil
- c 0 :
-
Initial mass concentration of species in the solution
- D :
-
Effective diffusion coefficient in porous media
- D 0 :
-
Diffusion coefficient in pure water (usually molecular diffusion coefficient)
- f :
-
Field function
- h :
-
The smoothing length of the kernel function
- i :
-
Serial number of objective particle
- j :
-
Serial number of particle i’s adjacent particles
- J :
-
Diffusion flux through the representative volume of porous media
- k :
-
Summation series number of the analytic solution
- L :
-
Length of porous media
- L e :
-
The average length of diffusive pathway
- m :
-
Mass of particle
- n :
-
Porosity of porous media
- N :
-
The total number of particles within the influence area of particle i
- r* :
-
General term representing chemical or biological reactions
- r :
-
Particle distance
- R :
-
Ratio of r to h
- R f :
-
Structural parameter (ratio of D0 to D)
- S :
-
Specific surface area
- t :
-
Time
- T v :
-
Dimensionless time, Tv = D0t/L2
- x, x′, xi, xj :
-
Distance vector of particle
- x :
-
x axe of Cartesian coordinates
- y :
-
y axe of Cartesian coordinates
- z :
-
z axe of Cartesian coordinates, direction of macroscopic concentration gradient
- Z :
-
Characteristic length, Z = z/L
- W :
-
Kernel function
- \(\nabla\) :
-
Vector gradient operator
- α d :
-
Normalized constant in kernel function
- λ :
-
Rate constant
- τ :
-
Tortuosity factor, τ = (Le/L)2
- Δx, Δy, Δz :
-
Particle spacing
- ρ :
-
Density of particle
- Ω :
-
Integral domain
References
Adler, P.M., Jacquin, C.G., Thovert, J.F.: The formation factor of reconstructed porous media. Water Resour. Res. 28, 1571–1576 (1992)
Akanni, K.A., Evans, J.W., Abramson, I.S.: Effective transport coefficients in heterogeneous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 42, 1945–1954 (1987)
Allen, R., Sun, S.: Computing and comparing effective properties for flow and transport in computer-generated porous media. Geofluids 2017, 1–24 (2017)
Bai, B., Rao, D., Xu, T., Chen, P.: SPH–FDM boundary for the analysis of thermal process in homogeneous media with a discontinuous interface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 117, 517–526 (2018)
Bai, B., Rao, D., Chang, T., Guo, Z.: A nonlinear attachment–detachment model with adsorption hysteresis for suspension-colloidal transport in porous media. J. Hydrol. 578(11), 124080 (2019)
Bayesteh, H., Mirghasemi, A.A.: Numerical simulation of porosity and tortuosity effect on the permeability in clay: microstructural approach. Soils Found. 55, 1158–1170 (2015)
Bezzar, A., Ghomari, F.: Monitoring of pollutant diffusion into clay liners by electrical methods. Transp. Porous Media 97, 147–159 (2013)
Boudreau, B.P.: The diffusive tortuosity of fine-grained unlithified sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, 3139–3142 (1996)
Carslaw, H., Jaeger, J.: Conduction of Heat in Solids. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1959)
Cleary, P.W.: Modelling confined multi-material heat and mass flows using SPH. Appl. Math. Model. 22, 981–993 (1998)
Cleary, P.W., Monaghan, J.J.: Conduction modelling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 148, 227–264 (1999)
Cundall, P.A., Strack, O.D.L.: A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies. Géotechnique 29, 47–65 (1979)
Davarzani, H., Marcoux, M., Costeseque, P., et al.: Experimental measurement of the effective diffusion and thermodiffusion coefficients for binary gas mixture in porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 65, 5092–5104 (2010)
Elwinger, F., Pourmand, P., István, F.: Diffusive transport in pores. Tortuosity and molecular interaction with the pore wall. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 13757–13764 (2017)
Esmaili, M.A., Nikseresht, A.H.: Neumann and Robin boundary conditions for heat conduction modeling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 198, 1–11 (2016)
Ghanbarian, B., Hunt, A.G., Ewing, R.P., et al.: Tortuosity in porous media: a critical review. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 77, 1461–1477 (2013)
Ghassemi, A., Pak, A.: Pore scale study of permeability and tortuosity for flow through particulate media using Lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 35, 886–901 (2011)
Li, Z., Dong, M.: Experimental study of diffusive tortuosity of liquid-saturated consolidated porous media. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49, 6231–6237 (2010)
Liu, M.B., Liu, G.R.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH): an overview and recent developments. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 17, 25–76 (2010)
Monaghan, J.J.: Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 110, 399–406 (1994)
Niya, S.M.R., Selvadurai, A.P.S.: A statistical correlation between permeability, porosity, tortuosity and conductance. Transp. Porous Media 121, 741–752 (2018)
Olsen, H.W.: Hydraulic flow through saturated clays. Clays Clay Miner. 11, 131–161 (1962)
Price, D.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 759–794 (2012)
Ryan, E.M., Tartakovsky, A.M., Amon, C.: Pore-scale modeling of competitive adsorption in porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 120–121, 56–78 (2011)
Saomoto, H., Katagiri, J.: Direct comparison of hydraulic tortuosity and electric tortuosity based on finite element analysis. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 5, 177–180 (2015)
Scholes, O.N., Clayton, S.A., Hoadley, A.F.A., et al.: Permeability anisotropy due to consolidation of compressible porous media. Transp. Porous Media 68, 365–387 (2007)
Shackelford, C.D.: Laboratory diffusion testing for waste disposal—a review. J. Contam. Hydrol. 7, 177–217 (1991)
Shen, L., Chen, Z.: Critical review of the impact of tortuosity on diffusion. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 3748–3755 (2007)
Tartakovsky, A.M., Trask, N., Pan, K., et al.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications for multiphase flow and reactive transport in porous media. Comput. Geosci. 20, 807–834 (2016)
Trinh, S., Arce, P., Locke, B.R.: Effective diffusivities of point-like molecules in isotropic porous media by Monte Carlo simulation. Transp. Porous Media 38, 241–259 (2000)
Valdés-Parada, F.J., Porter, M.L., Wood, B.D.: The role of tortuosity in upscaling. Transp. Porous Media 88, 1–30 (2011)
Wang, P.: Lattice Boltzmann simulation of permeability and tortuosity for flow through dense porous media. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 1–7 (2014)
Yang, X., Mehmani, Y., Perkins, W.A., et al.: Intercomparison of 3D pore-scale flow and solute transport simulation methods. Adv. Water Resour. 95, 176–189 (2016)
Zheng, J.H., Soe, M.M., Zhang, C., et al.: Numerical wave flume with improved smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Hydrodyn. 22, 773–781 (2010)
Zhu, Y., Fox, P.J.: Simulation of pore-scale dispersion in periodic porous media using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 182, 622–645 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51678043, 51878035), and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (8182046). The authors would like to thank the reviewers and editors for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, D., Bai, B. Study of the Factors Influencing Diffusive Tortuosity Based on Pore-Scale SPH Simulation of Granular Soil. Transp Porous Med 132, 333–353 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01394-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-020-01394-0