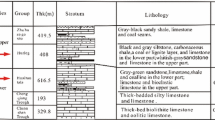
Abstract
Permeability is the most important parameter that describes gas flow characteristics in shale. Water saturation and effective pressure have a considerable effect on shale permeability. This paper presents the results of a laboratory study of the effects of water saturation and effective pressure on gas permeability in Carboniferous shales of the Qaidam Basin, China. The permeability of shale samples with varying water saturation (0–33 wt%) was measured at effective pressure of 6.9 to 27.59 MPa and at low mean pore pressure (< 6.89 MPa) at room temperature, using a pressure pulse decay permeameter. The results indicate that the water saturation and the effective pressure are the main factors affecting the shale permeability. Permeability of sample C034, which has a high clay content and is dominated by nanoscale slit-shaped pores, shows a large decrease (up to 90%) with increasing water saturation (from 0 to 31.7 wt%), depending on the effective pressure. A much larger permeability reduction with increasing water saturation fraction is associated with the swelling of clay minerals. For each sample with varying water saturation, our analyses revealed a consistent line relationship between log permeability and effective pressure variation. The impact of effective pressure on the measured permeability becomes more significant as water saturation increases. With increasing water saturation, the gas slippage factor decreases and calculated effective pore size increases, and gas–water flow in the shale samples occurs as channel flow. This study provides practical information for further studies of stress-dependent permeability of shale with water and the gas slippage effect in two-phase, gas–water flow.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernabe, Y.: The effective pressure law for permeability in Chelmsford granite and Barre granite. Int. J. Rock Mech. Mining Sci. Geomech. Abstr. Pergam. 23(3), 267–275 (1986)
Bowker, K.A.: Recent developments of the Barnett play. In: Fort Worth basin: Innovative Gas Exploration Concepts Symposium. Rocky Mountain Association of Geologists and Petroleum Technology Transfer Council (2002)
Bustin, A. M. M., Bustin, R. M., Cui, X. Importance of fabric on the production of gas shales. In: SPE Unconventional reservoirs conference. Society of Petroleum Engineers, (2008)
Byrnes, A.P., Sampath K, Randolph P L.: Effect of pressure and moisture content on permeability of western tight sandstones. In: Fifth Annual DOE Symposium on Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery and Improved Drilling Technology. 22–24 (1979)
Chalmers, G.R.L., Bustin, R.M.: Lower cretaceous gas shales in northeastern British Columbia, Part I: geological controls on methane sorption capacity. Bull. Can. Pet. Geol. 56(1), 1–21 (2008)
Chalmers, G.R.L., Ross, D.J.K., Bustin, R.M.: Geological controls on matrix permeability of Devonian gas Shales in the Horn River and Liard basins, northeastern British Columbia Canada. Int. J. Coal Geol. 103, 120–131 (2012)
Chang, C., Zhou, Q., Xia, L., Li, X.Y., Yu, Q.C.: Dynamic displacement and non-equilibrium dissolution of supercritical CO2 in low-permeability sandstone: an experimental study. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 14(5), 1–14 (2013)
China National Petroleum Company: SY/T 5163–2010: Analysis method for clay minerals and ordinary non-clay minerals in sedimentary rocks by the X-ray diffraction. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (2010)
Cui, X., Bustin, A.M.M., Bustin, R.M.: Measurements of gas permeability and diffusivity of tight reservoir rocks: different approaches and their applications. Geofluids 9(3), 208–223 (2009)
Curtis, J.B.: Fractured shale-gas systems. AAPG Bull. 86(11), 1921–1938 (2002)
Denney, D.: Evaluating implications of hydraulic fracturing in shale-gas reservoirs. J. Pet. Technol. 61(8), 53–54 (2009)
Estes, R.K., Fulton, P.F.: Gas slippage and permeability measurements. J. Pet. Technol. 8(10), 69–73 (1956)
Fathi, E., Tinni, A., Akkutlu, I.Y.: Correction to Klinkenberg slip theory for gas flow in nano-capillaries. Int. J. Coal Geol. 103(23), 51–59 (2012)
Faulkner, D.R., Rutter, E.H.: The effect of temperature, the nature of the pore fluid, and subyield differential stress on the permeability of phyllosilicate-rich fault gouge. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 108, 2227–2239 (2003)
Firouzi, M., Alnoaimi, K., Kovscek, A., Wilcox, J.: Klinkenberg effect on predicting and measuring helium permeability in gas shales. Int. J. Coal Geol. 123(2), 62–68 (2014)
Franquet, M., Ibrahim, M., Wattenbarger, R.A., Maggard J.B.: Effect of pressure-dependent permeability in tight gas reservoirs, transient radial flow. In: Canadian International Petroleum Conference, Petroleum Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum, Calgary, Alberta, Canada, 2004–089, 1–10 (2004)
Fulton, P.F.: The effect of gas slippage on relative permeability measurements. Producers Mon. 15(12), 14–19 (1951)
Gao, H., Li, H.A.: Pore structure characterization, permeability evaluation and enhanced gas recovery techniques of tight gas sandstones. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 28, 536–547 (2015)
Gao, J., Yu, Q., Lu, X.: Apparent permeability and gas flow behavior in carboniferous shale from the Qaidam Basin, China: an experimental study. Transp. Porous Media 116(2), 585–611 (2017)
Ghanizadeh, A., Gasparik, M., Amann-Hildenbrand, A., Gensterblum, Y., Krooss, B.M.: Experimental study of fluid transport processes in the matrix system of the European organic-rich shales: I. Scandinavian Alum Shale. Marine Pet. Geol. 51, 79–99 (2014)
Gutierrez, M., Øinob, L.E., Nygård, R.: Stress-dependent permeability of a de-mineralised fracture in shale. Marine Pet. Geol. 17, 895–907 (2000)
Heller, R., Vermylen, J., Zoback, M.: Experimental investigation of matrix permeability of gas shales. AAPG Bull. 98(5), 975–995 (2014)
Hildenbrand, A., Schlömer, S., Krooss, B.M.: Gas breakthrough experiments on fine-grained sedimentary rocks. Geofluids 2(1), 3–23 (2002)
Hildenbrand, A., Schlömer, S., Krooss, B., Littke, R.: Gas breakthrough experiments on pelitic rocks: comparative study with N2, CO2 and CH4. Geofluids 4, 61–80 (2004)
Hougen, O.A., Watson, K.M.: Chemical process principles. Wiley, Inc Chapman And Hall, Limited, London (1947)
Javadpour, F.: Nanopores and apparent permeability of gas flow in mudrocks (shales and siltstone). J. Can. Pet. Technol. 48(8), 16–21 (2009)
Jiang, Y.Q., Dong, D.Z., Qi, L., Shen, Y.F., Jiang, C., He, P.W.: The basic characteristics and evaluation of shale gas reservoirs. Geol. Exploration 30(10), 7–12 (2010)
Jones, F.O., Owens, W.W.: A laboratory study of low-permeability gas sands. J. Pet. Technol. 32(9), 1631–1640 (1980)
Jones, S.C.: A technique for faster pulse-decay permeability measurements in tight rocks. SPE Formation Eval. 12(1), 19–26 (1997)
Kestin, J., Leidenfrost, W.: The viscosity of helium. Physic 25(1–6), 537–555 (1959)
Klaver, J., Desbois, G., Urai, J.L., Littke, R.: BIB-SEM study of the pore space morphology in early mature Posidonia Shale from the Hils area. Germany. Int. J. Coal Geol. 103, 12–25 (2012)
Klinkenberg, L.J.: The permeability of porous media to liquids and gases. In: Drilling and production practice. American Petroleum Institute(1941)
Kuila, U., Prasad, M.: Specific surface area and pore-size distribution in clays and shales. Geophys. Prospecting 61(2), 341–362 (2013)
Kwon, O., Kronenberg, A.K., Gangi, A.F., Johnson, B.: Permeability of Wilcox shale and its effective pressure law. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 106(B9), 19339–19353 (2001)
Kwon, O., Kronenberg, A.K., Gangi, A.F., Johnson, B., Herbert, B. E.: Permeability of illite-bearing shale: 1. Anisotropy and effects of clay content and loading. J. Geophys. Res. 109(B10205) (2004)
Letham, E.A., Bustin, R.M.: Klinkenberg gas slippage measurements as a means for shale pore structure characterization. Geofluids 16(2), 264–278 (2016)
Li, K.W., Horne, R.N.: Experimental Study of Gas Slippage in Two-Phase Flow. SPE Res. Eval. Eng. 7(6), 409–415 (2004)
Li, M., Xiao, W.L., Bernabé, Y., Zhao, J.Z.: Nonlinear effective pressure law for permeability. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 119(1), 302–318 (2014)
Li, Y.J., Sun, Y.L., Chang, C., Zhao, Y., Yu, Q.C., Ma, Y.S.: Prospects of carboniferous shale Gas exploitation in the eastern qaidam Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition) 88, 620–634 (2015)
Liu, Q., J., Liu, B.H., Li, X.B., Yan, S.G.: The effect of water saturation on gas slip factor by pore scale network modeling. In: SCA Symposium. Monterey, California (2002)
Liu, Z., Zhao, J., Liu, H., et al.: Experimental simulation of gas seepage characteristics of a low-permeability volcanic rock gas reservoir under different water saturations. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 51(2), 199–206 (2015)
Mbia, E.N., Fabricius, I.L., Krogsboll, A., Frykman, P., Dalhoff, F.: Permeability, compressibility and porosity of Jurassic shale from the Norwegian-Danish Badin. Pet. Geosci. 20, 257–281 (2014)
McKernan, R., Mecklenburgh, J., Rutter, E. & Taylor, K.: Microstructural controls on the pressure dependent permeability of Whitby mudstone. In: Rutter, E.H., Mecklenburgh, J. & Taylor, K.G. (eds) Geomechanical and Petrophysical Properties of Mudrocks. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 454. First published online May 31, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1144/SP454.15
Metwally, Y.M., Sondergeld, C.H.: Measuring low permeabilities of gas-sands and shales using a pressure transmission technique. Int. J. Rock Mech. Mining Sci. 48(7), 1135–1144 (2011)
Randolph, P.L, Soeder, D. J., Chowdiah, P.: Porosity and permeability of tight sands. In: SPE Unconventional Gas Recovery Symposium, Society of Petroleum Engineers (1984)
Rose, W.D.: Permeability and gas-slippage phenomena. In: 28th Annual Mtg, Topical Committee on Production Technology (1948)
Rouquerol, J., Avnir, D., Fairbridge, C.W., Everett, D.H., Haynes, J.H., Pernicone, N., Ramsay, J.D.F., Sing, K.S.W., Unger, K.K.: Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 66(8), 1739–1758 (1994)
Rushing, J.A., Newsham, K.E., Fraassen, K.C.: Measurement of the Two-Phase Gas Slippage Phenomenon and Its Effect on Gas Relative Permeability in Tight Gas Sands. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Society of Petroleum Engineers (2003)
Rutter, E.H., McKernan, R.E., Mecklenburgh, J., May, S.E.: Permeability of stress sensitive formations: its importance for shale gas reservoir simulation and evaluation. Petro-Industry N. 2013(September), 44–45 (2013)
Smith, D.H., Jikich, S.A.: Effects of fluid, confining, and effective pressure on the helium permeability of upper freeport bituminous coal: measurements and interpretation. National Energy Technology Laboratory, US Department of Energy(2009)
Tanikawa, W., Shimamoto, T.: Comparison of Klinkenberg-corrected gas permeability and water permeability in sedimentary rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Mining Sci. 46(2), 229–238 (2009)
Thomas, R.D., Ward, D.C.: Effect of overburden pressure and water saturation on gas permeability of tight sandstone cores. J. Pet. Technol. 24(2), 120–124 (1972)
Walls, J.D., Nur, A.M., Bourbie, T.: Effects of pressure and partial water saturation on gas permeability in tight sands: experimental results. J. Pet. Technol. 34(4), 930–936 (1982)
Warlick, D.: Gas shale and CBM development in North America. Oil Gas Financial J. 3(11), 1–5 (2006)
Wei, K.K., Morrow, N.R., Brower, K.R.: Effect of fluid, confining pressure, and temperature on absolute permeabilities of low-permeability sandstones. SPE Formation Eval. 1(4), 413–423 (1986)
Wu, Y.S., Pruess, K., Persoff, P.: Gas flow in porous media with Klinkenberg effects. Transp. Porous Media 32(1), 117–137 (1998)
Yin, G.Z., Jiang, C.B., Jiang, X., Guo, L.S., Peng, S.J., Li, W.P.: An experimental study on the effects of water saturation on coalbed gas permeability in ground stress fields. Transp. Porous Media 94(1), 87–99 (2012)
Zhang, R., Ning, Z., Yang, F., Zhao, H.W., Wang, Q.: A laboratory study of the porosity-permeability relationships of shale and sandstone under effective stress. Int. J. Rock Mech. Mining Sci. 81, 19–27 (2016)
Zhang, R., Ning, Z.F., Yang, F., Wang, X., Zhao, H.W., Wang, Q.: Impacts of nanopore structure and elastic properties on stress-dependent permeability of gas shales. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 26, 1663–1672 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 40772208 and 41272387), and the China Geological Survey program (Nos. 20120113040000-3 and 1212011120964) is gratefully acknowledged. Our special thanks are extended to Professor E. Rutter, Editor Martin Julian Blunt, as well as one anonymous reviewer, for many critical and constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Yu, Q. Effect of Water Saturation on Pressure-Dependent Permeability of Carboniferous Shale of the Qaidam Basin, China. Transp Porous Med 123, 147–172 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1029-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1029-y