Abstract
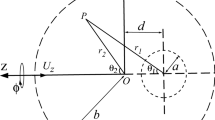
The flow past an impermeable sphere embedded in a fluid-saturated porous medium was investigated numerically. The flow is considered viscous, laminar, axisymmetric, steady and incompressible. The generalized model for fluid flow through an isotropic, rigid and homogeneous porous medium was used. The stream function–vorticity equations were solved numerically in spherical coordinates system by a defect correction multigrid method. The computations were focused on the influence of the Darcy number (Da) and Forchheimer constant on the flow field for two boundary conditions on the surface of the sphere: slip and no-slip. The conditions when the macroscopic inertial terms of the generalized model can be neglected are presented. For high-porosity porous media, the macroscopic inertial terms of the generalized model can be neglected if Da \(Re< 1\) (Re is the sphere Reynolds number).















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(a\) :
-
Radius of the sphere
- \(C_{D}\) :
-
Total drag coefficient
- \(C_{D,F}\) :
-
Friction drag coefficient
- \(C_{D,P}\) :
-
Pressure drag coefficient
- \(C_{F}\) :
-
Forchheimer constant
- \(d\) :
-
Diameter of the sphere, \(d = 2a\)
- Da :
-
Darcy number, \(K / d^{2}\)
- \(K\) :
-
Permeability of the porous medium
- \(p\) :
-
Dimensionless local average pressure
- \(r\) :
-
Dimensionless radial coordinate, \(r^{*} / a\), in spherical coordinate system
- \(r^{*}\) :
-
Radial coordinate in spherical coordinate system
- Re :
-
Reynolds number based on the diameter of the sphere, \(Re = U_{0}d\rho / \mu \)
- \(U_{0}\) :
-
Darcy free-stream velocity
- \(V_{R}\) :
-
Darcy dimensionless radial velocity component
- \(V_{\theta }\) :
-
Darcy dimensionless tangential velocity component
- \(x\) :
-
Transformed dimensionless radial coordinate
- \(\beta \) :
-
Dimensionless slip coefficient
- \(\varepsilon \) :
-
Porosity of the porous medium
- \(\mu \) :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the fluid
- \(\theta \) :
-
Polar angle in spherical coordinate system
- \(\rho \) :
-
Density of the fluid
- \(\psi \) :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- \(\zeta \) :
-
Dimensionless vorticity
- \(s\) :
-
Refers to the surface of the sphere
References
Bagchi, P., Ha, M.Y., Balachandar, S.: Direct numerical simulation of flow and heat transfer from a sphere in a uniform cross-flow. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 123, 347–358 (2001)
Bear, J., Bachmat, Y.: Introduction to Modeling of Transport Phenomena in Porous Media. Kluiwer Academic, Dordrecht (1990)
Berman, B.: Flow of a Newtonian fluid past an impervious sphere embedded in a porous medium. Indian J. Pure Appl. Math 27, 1249–1256 (1996)
Brabston, D.C.: Numerical solution of steady viscous flow past spheres and gas bubbles. Ph. D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology (1974)
Brabston, D.C., Keller, H.B.: Viscous flow past spherical gas bubbles. J. Fluid Mech. 69, 179–189 (1975)
Brinkman, H.C.: A calculation of the viscous force exerted by a flowing fluid on a dense swarm of particles. Appl. Sci. Res. 1, 27–34 (1947)
Charya, D.S., Murthy, J.V.R.: Flow past an axisymmetric body embedded in a saturated porous medium. C. R. Mec. 330, 417–423 (2002)
Cherepanov, G.P.: Two-dimensional convective heat/mass transfer for low Prandtl and any Peclet numbers. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 58, 942–960 (1998)
Clift, R., Grace, J.R., Weber, M.E.: Bubbles, Drops and Particles. Academic Press, New York (1978)
Coulaud, O., Morel, P., Caltagirone, J.P.: Numerical modeling of nonlinear effects in laminar flow through a porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 190, 393–407 (1988)
Cvetkovic, V.D.: A continuum approach to high velocity flow in a porous medium. Transp. Porous Media 1, 63–97 (1986)
Darcy, H.P.G.: Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon. Victor Dalmont, Paris (1856)
Ene, H.I., Polisevski, D.: Thermal Flow in Porous Media. Rudel, Dordrecht (1987)
Feng, Z.-G., Michaelides, E.E.: Unsteady mass transport from a sphere immersed in a porous medium at finite Peclet numbers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 42, 535–546 (1999)
Ganapathy, R.: Creeping flow past a solid sphere in a porous medium. ZAMM 77, 871–875 (1997)
Hassanizadeh, S.M., Gray, W.C.: High velocity flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 2, 521–531 (1987)
Hsu, C.T., Cheng, P.: Thermal dispersion in a porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 33, 1587–1597 (1990)
Johnson, T.A., Patel, V.C.: Flow past a sphere up to a Reynolds number of 300. J. Fluid Mech. 378, 19–70 (1999)
Juncu, G.: Brinkman–Forchheimer–Darcy flow past an impermeable sphere embedded in a porous medium. Presented at Xth Workshop on Mathematical Modelling of Environmental and Life Sciences Problems, to appear in Anal. Univ. Ovidius Constanta, Seria Matematica (2015)
Juncu, G., Mihail, R.: Numerical solution of the steady incompressible Navier–Stokes equations for the flow past a sphere by a multigrid defect correction technique. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 11, 379–395 (1990)
Kaviany, M.: Principles of Heat Transfer in Porous Media, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1995)
Lage, J.L.: The fundamental theory of flow through permeable media: from Darcy to turbulence. In: Ingham, D.B., Pop, I. (eds.) Transport Phenomena in Porous Media, pp. 1–30. Elsevier, Oxford (1998)
Le Bars, M., Worster, M.G.: Interfacial conditions between a pure fluid and a porous medium: implications for binary alloy solidification. J. Fluid Mech. 550, 149–173 (2006)
Leont’ev, N.E.: Flow past a cylinder and a sphere in a porous medium within the framework of the Brinkman equation with the Navier boundary condition. Fluid Dyn. 49, 232–237 (2014)
Levy, A., Levi-Hevroni, D., Sorek, S., Ben-Dor, G.: Derivation of Forchheimer terms and their verification by application to waves propagation in porous media. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 25, 683–704 (1999)
Nield, D.A.: Closure statements on the Brinkman—Forchheimer—extended Darcy model. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 17, 34–35 (1996)
Nield, D.A., Bejan, A.: Convection in Porous Media, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Nithiarasu, P., Seetharamu, K.N., Sundararajan, T.: Finite element modeling of flow, heat and mass transfer in fluid saturated porous media. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 9, 3–42 (2002)
Oliver, D.L.R., Chung, J.N.: Steady flows inside and around a fluid sphere at low Reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 154, 215–230 (1985)
Pop, I., Ingham, D.B.: Flow past a sphere embedded in a porous medium based on the Brinkman model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 23, 865–874 (1996)
Romero, L.A.: Low or high Peclet number flow past a sphere in a saturated porous medium. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 54, 42–71 (1994)
Romero, L.A.: Low or high Peclet number flow past a prolate spheroid in a saturated porous medium. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 55, 952–974 (1995a)
Romero, L.A.: Forced convection past a slender body in a saturated porous medium. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 55, 975–985 (1995b)
Rudraiah, N., Shivakumaran, I.S., Palaniappan, D., Chandrashekar, D.V.: Flow past an impervious sphere embedded in a porous medium based on non-Darcy model. Adv. Fluid Mech. 2, 253–256 (2004)
Sorek, S., Levi-Hevroni, D., Levy, A., Ben-Dor, G.: Extensions to the macroscopic Navier–Stokes equation. Transp. Porous Media 61, 215–233 (2005)
Sorek, S., Ronen, D., Gitis, V.: Scale-dependent macroscopic balance equations governing transport through porous media. Transp. Porous Media 81, 61–72 (2010)
Straughan, B.: Structure of the dependence of Darcy and Forchheimer coefficients on porosity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 48, 1610–1621 (2010)
Vafai, K., Tien, C.L.: Boundary and inertia effects on flow and heat transfer in porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 24, 195–203 (1981)
Wang, C.Y.: Darcy–Brinkman flow with solid inclusions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 197, 261–274 (2009)
Yu, P., Zeng, Y., Lee, T.S., Chen, X.B., Low, H.T.: Numerical simulation on steady flow around and through a porous sphere. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 36, 142–152 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The author would like to express his sincere thanks to the two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juncu, G. A Numerical Study of the Flow Past an Impermeable Sphere Embedded in a Porous Medium. Transp Porous Med 108, 555–579 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0488-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0488-7