Abstract
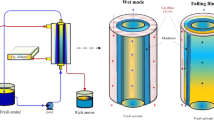
Simulation of transport phenomena in capture of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) from air was carried out in this work. Separation of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) as an air pollutant from nitrogen using porous membranes is simulated to optimize the process. Computational fluid dynamics approach is utilized for numerical simulation of process aiming to predict the concentration of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) in the membrane module. 2-Amino-2-methyl-1-propanol as chemical absorbent was considered in the simulations. Hydrodynamics and mass transfer of system were investigated by the developed numerical procedure. The simulation results were validated through comparing with experimental data, and good agreement was achieved. The simulation results revealed that \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) removal rate increases with an enhancement of absorbent flow rate, and decreases with the increasing gas flow rate. This simulation procedure can predict \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) capture from air using porous membranes.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(C_{0}\) :
-
Inlet concentration \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C\) :
-
Concentration \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_{\mathrm{CO_{2}{\text {-}}shell}}\) :
-
\(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) concentration in the shell \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_{\mathrm{CO_{2}{\text {-}}tube}}\) :
-
\(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) concentration in the tube \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_\mathrm{i}\) :
-
Concentration of any species \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_{\mathrm{i{\text {-}}tube}}\) :
-
Concentration of any species in the tube \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_{\mathrm{in}}\) :
-
Absorbent concentration at the inlet \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_{\mathrm{inlet}}\) :
-
Inlet concentration of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) in the shell \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_{\mathrm{outlet}}\) :
-
Outlet concentration of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) in the shell \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_\mathrm{AMP{\text {-}}tube}\) :
-
AMP (amine) concentration \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(C_{\mathrm{M0}}\) :
-
Inlet AMP concentration \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3})\)
- \(D\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient \((\hbox {m}^{2}/\hbox {s})\)
- \(D_{\mathrm{i{\text {-}}membrane}}\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient of any species in the membrane \((\hbox {m}^{2}/\hbox {s})\)
- \(D_{\mathrm{i{\text {-}}tube}}\) :
-
Diffusion coefficient of any species in the tube \((\hbox {m}^{2}/\hbox {s})\)
- \(k\) :
-
Reaction rate coefficient of \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\) with absorbent \((\hbox {m}^{3}/\hbox {mol s})\)
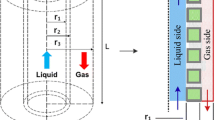
- \(L\) :
-
Length of a fiber (m)
- \(m\) :
-
Partition coefficient (–)
- \(n\) :
-
Number of fibers
- \(p\) :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- \(Q_{\mathrm{g}}\) :
-
Gas flow rate (L/h)
- \(Q_{\mathrm{l}}\) :
-
Liquid flow rate (L/h)
- \(r_{1}\) :
-
Tube inner radius (m)
- \(r_{2}\) :
-
Tube outer radius (m)
- \(r_{3}\) :
-
Inner shell radius (m)
- \(r\) :
-
Radial coordinate (m)
- \(\mathfrak {R}\) :
-
Module inner radius (m)
- \(R_{\mathrm{i}}\) :
-
Overall reaction rate of any species \((\hbox {mol/m}^{3} \hbox {s})\)
- \(t\) :
-
Time (s)
- \(T\) :
-
Temperature (K)
- \(u\) :
-
Average velocity (m/s)
- \(V\) :
-
Velocity in the module (m/s)
- \(V_{z{\text {-}}\mathrm{shell}}\) :
-
\(z\)-velocity in the shell (m/s)
- \(V_{z{\text {-}}\mathrm{tube}}\) :
-
\(z\)-velocity in the tube (m/s)
- \(z\) :
-
Axial coordinate (m)
References
Asimakopoulou, A.G., Karabelas, A.J.: Mass transfer in liquid–liquid membrane based extraction at small fiber packing fractions. J. Membr. Sci. 271, 151–162 (2006)
Bird, R.B., Stewart, W.E., Lightfoot, E.N.: Transport Phenomena, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1960)
Chun, M.S., Lee, K.H.: Analysis on a hydrophobic hollow fiber membrane absorber and experimental observations of \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) removal by enhanced absorption. Sep. Sci. Technol. 32(15), 2445–2466 (1997)
Esato, K., Eiseman, B.: Experimental evaluation of Gore-Tex membrane oxygenator. J. Thorac. Cardiovas. Surg. 69, 690–697 (1975)
Feron, P.H.M., Jansen, A.E.: Membrane technology in carbon dioxide removal. Energy Convers. Manag. 23, 421–428 (1992)
Feron, P.H.M., Jansen, A.E.: Capture of carbon dioxide using membrane gas absorption and reuse in the horticultural industry. Energy Convers. Manag. 36, 411–414 (1995)
Feron, P.H.M., Jansen, A.E.: The production of carbon dioxide from flue gas by membrane gas absorption. Energy Convers. Manag. 38, S93–S98 (1997)
Happel.: Viscous flow relative to arrays of cylinders. AIChE J. 5, 174–177 (1959)
Karror, S., Sirkar, K.K.: Gas absorption study in micro porous hollow fiber membrane modules. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 32, 674–684 (1993)
Kieffer, R., Charcosset, C., Puel, F., Mangin, D.: Numerical simulation of mass transfer in a liquid–liquid membrane contactor for laminar flow conditions. Comput. Chem. Eng. 32, 1325–1333 (2008)
Kim, Y., Yang, S.: Absorption of carbon dioxide through hollow fiber membranes using various aqueous absorbents. Sep. Purif. Technol 21, 101–109 (2000)
Kreulen, H., Versteeg, G.F., Smolders, C.A., Van Swaaij, W.P.M.: Selective removal of \(\text{ H }_{2}\text{ S }\) from sour gas with micro porous membranes Part 1. Application in a gas-liquid system. J. Membr. Sci. 73, 293–304 (1992)
Kreulen, H., Smolders, C.A., van Versteeg, G.F., Swaaij, W.P.M.: Micro porous hollow fiber membrane modules as gas-liquid contactors. Part 2. Mass transfer with chemical reaction. J. Membr. Sci. 78, 217 (1993a)
Kreulen, H., Smolders, C.A., van Versteeg, G.F., Swaaij, W.P.M.: Micro porous hollow fiber membrane modules as gas–liquid contactors. Part 1. Physical mass transfer processes: a specific application: mass transfer in highly viscous liquids. J. Membr. Sci. 78, 197–216 (1993b)
Lee, H.K., Jo, H.D., Choi, W.K., Park, H.H., Lim, C.W., Lee, Y.T.: Absorption of \(\text{ SO }_{2}\) in hollow fiber membrane contactors using various aqueous absorbents. Desalination 200, 604–605 (2006)
Li, M.H., Lie, Y.C.: Densities and viscosities of solutions mono ethylamine N-methyldiethanolamine water and mono ethanolamine 2-Amino -2-methyl-1-propanol water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 39, 444 (1994)
Li, K., Dongliang, W., Koe, C.C., Teo, W.K.: Use of asymmetric hollow fiber modules for elimination of \(\text{ H }_{2}\text{ S }\) from gas streams via a membrane absorption method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 53, 1111–1119 (1998)
Li, K., Kong, J.F., Wang, D., Teo, W.K.: Tailor-made asymmetric PVDF hollow fiber for soluble gas removal. AIChE J. 45, 1211–1219 (1999)
Mansourizadeh, A., Ismail, A.F.: Hollow fiber gas-liquid membrane contactors for acid gas capture: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 171, 38–53 (2009)
Miramini, S.A., Razavi, S.M.R., Ghadiri, M., Mahdavi, S.Z., Moradi, S.: CFD simulation of acetone separation from an aqueous solution using supercritical fluid in a hollow-fiber membrane contactor. Chem. Eng. Process. 72, 130–136 (2013)
Nii, S., Takeuchi, H.: Removal \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) and/or \(\text{ SO }_{2}\) from gas streams by a membrane absorption method. Gas Sep. Purif. 8, 107–114 (1994)
Nishikawa, N., Ishibashi, M., Ohata, H., Akutsu, N.: \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) removal by hollow fibers gas-liquid contactor. Energy Convers. Manag. 36, 415–418 (1995)
Park, H.H., Deshwal, B.R., Kim, I.W., Lee, H.K.: Absorption of \(\text{ SO }_{2}\) from flue gas using PVDF hollow fiber membranes in a gas–liquid contactor. J. Membr. Sci. 319, 29–37 (2008)
Poddar, T.K., Majumdar, S., Sirkar, K.K.: Membrane based absorption of VOCs from a gas stream. AIChE J. 42, 3267–3282 (1996)
Qi, Z., Cussler, E.L.: Micro porous hollow fibers for gas absorption. Part 1. Mass transfer in the liquid. J. Membr. Sci. 23, 321–332 (1985a)
Qi, Z., Cussler, E.L.: Micro-porous hollow fibers for gas absorption. Part 2. Mass transfer across the membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 23, 333–345 (1985b)
Rangwala, H.A.: Absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous solutions using hollow fiber membrane contactors. J. Membr. Sci. 112, 229–240 (1996)
Razavi, S.M.R., Shirazian, S., Najafabadi, M.S.: Investigations on the ability of di-isopropanol amine solution for removal of \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) from natural gas in porous polymeric membranes. Polym. Eng. Sci. (2014). doi:10.1002/pen.23924
Razavi, S.M.R., Razavi, S.M.J., Miri, T., Shirazian, S.: CFD simulation of \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) capture from gas mixtures in nanoporous membranes by solution of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol and piperazine. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 15, 142–149 (2013)
Saha, A.K., Bandyopadhyay, S.S.: Kinetics of absorption of \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) into aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-metyl-1-propanol. Chem. Eng. Sci. 50(22), 3587–3598 (1995)
Shirazian, S., Moghadassi, A., Moradi, S.: Numerical simulation of mass transfer in gas–liquid hollow fiber membrane contactors for laminar flow conditions. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 17, 708–718 (2009)
Sohrabi, M.R., Marjani, A., Moradi, S., Davallo, M., Shirazian, S.: Mathematical modeling and numerical simulation of \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) transport through hollow-fiber membranes. Appl. Math. Model. 35, 174–188 (2011)
Song, J.H., Park, S.B., Yoon, J.H., Lee, H.: Densities and viscosities of mono ethanolamine + ethylene glycol + water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 41, 1152 (1996)
Versteeg, G.F., van Swaaij, W.P.M.: Solubility and diffusivity of acid gases (\(\text{ CO }_{2},\,\text{ N }_{2}\text{ O }\)) in aqueous alkanol amine solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 33, 29 (1988)
Wang, D., Teo, W.K., Li, K.: Removal of \(\text{ H }_{2}\text{ S }\) to ultra-low concentrations using an asymmetric hollow fiber membrane module. Sep. Purif. Technol. 27, 33–40 (2002)
Wang, D., Teo, W.K., Li, K.: Selective removal of traces \(\text{ H }_{2}\text{ S }\) from gas streams containing \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) using hollow fiber modules/contactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 35, 125–131 (2004)
Zaidiza, D.A., Billaud, J., Belaissaoui, B., Rode, S., Roizard, D., Favre, E.: Modeling of \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) post-combustion capture using membrane contactors, comparison between one- and two-dimensional approaches. J. Membr. Sci. 455, 64–74 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razavi, S.M.R., Marjani, A. & Shirazian, S. \(\mathrm{{CO}}_{2}\) Capture from Gas Mixtures by Alkanol Amine Solutions in Porous Membranes. Transp Porous Med 106, 323–338 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-014-0403-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-014-0403-7