Abstract
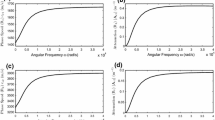
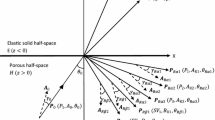
Time harmonic waves in a swelling porous elastic medium of infinite extent and consisting of solid, liquid and gas phases have been studied. Employing Eringen’s theory of swelling porous media, it has been shown that there exist three dilatational and two shear waves propagating with distinct velocities. The velocities of these waves are found to be frequency dependent and complex valued, showing that the waves are attenuating in nature. Here, the appearance of an additional shear wave is new and arises due to swelling phenomena of the medium, which disappears in the absence of swelling. The reflection phenomenon of an incident dilatational wave from a stress-free plane boundary of a porous elastic half-space has been investigated for two types of boundary surfaces: (i) surface having open pores and (ii) surface having sealed pores. Using appropriate boundary conditions for these boundary surfaces, the equations giving the reflection coefficients corresponding to various reflected waves are presented. Numerical computations are performed for a specific model consisting of sandstone, water and carbon dioxide as solid, liquid and gas phases, respectively, of the porous medium. The variations of phase speeds and their corresponding attenuation coefficients are depicted against frequency parameter for all the existing waves. The variations of reflection coefficients and corresponding energy ratios against the angle of incidence are also computed and depicted graphically. It has been shown that in a limiting case, Eringen’s theory of swelling porous media reduces to Tuncay and Corapcioglu theory of porous media containing two immiscible fluids. The various numerical results under these two theories have been compared graphically.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, J.D.: Wave Propagation in Elastic Solids, 1st edn. North Holland, Amsterdam (1973)
Ainslie, M.A., Burns, P.W.: Energy-conserving reflection and transmission coefficients for a solid–solid boundary. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 98, 2836–2840 (1995)
Atkin, R.J., Craine, R.E.: Continuum theories of mixtures: applications. J. Inst. Math. Appl. 17, 153–207 (1976a)
Atkin, R.J., Craine, R.E.: Continuum theories of mixtures: basic theory and historical development. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 29, 209–245 (1976b)
Auriault, J.L.: Dynamic behaviour of a porous medium saturated by a Newtonian fluid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 18, 775–785 (1980)
Auriault, J.L., Borne, L., Chambon, R.: Dynamics of porous saturated media: checking of generalised law of Darcy. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 77, 1641–1650 (1985)
Bear, J., Corapcioglu, M.Y.: Wave propagation in porous media. A review. In: Transport Processes in Porous Media, pp. 373–469. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1991)
Bedford, A., Drumheller, D.S.: Theory of immiscible and structured mixtures. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 21, 863–960 (1983)
Berryman, J.G.: Confirmation of Biot’s theory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 37, 382–384 (1980)
Berryman, J.G.: Elastic waves propagation in fluid-saturared porous media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 69, 416–424 (1981)
Biot, M.A.: The theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low-frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 28, 168–178 (1956a)
Biot, M.A.: The theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. II. Higher-frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 28, 179–191 (1956b)
Boffil, F., Quintanilla, R.: Anti-plane shear deformations of swelling porous elastic soils. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 41, 801–816 (2003)
Borcherdt, R.D.: Energy and plane waves in linear viscoelastic media. J. Geophys. Res. 78, 2442–2453 (1973)
Borcherdt, R.D.: Reflection–refraction of general P- and type-I S-waves in elastic and anelastic solids. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 70, 621–638 (1982)
Borcherdt, R.D.: Viscoelastic Waves in Layered Media. Cambridge University Press, New York (2009)
Bowen, R.M.: Theory of mixtures. In: Eringen, A.C. (ed.) Continuum Physics, vol. III. Academic Press, New York (1976)
Bowen, R.M.: Compressible porous media models by use of the theory of mixtures. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 20, 697–735 (1982)
Brutsaert, W.: The propagation of elastic waves in unconsolidated unsaturated granular medium. J. Geophys. Res. 69, 243–257 (1964)
Burridge, R., Keller, J.B.: Poroelasticity equations derived from microstructure. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 70, 1140–1146 (1981)
Carcione, J.M.: Wave Fields in Real Media—Wave Propagation in Anisotropic, Anelastic, Porous and Electromagnetic Media, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2007)
Carcione, J.M., Santos, J.E., Ravazzoli, C.L., Helle, H.B.: Wave simulation in partially frozen porous media with fractal freezing conditions. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7839–7847 (2003)
Ciarletta, M., Straughan, B.: Poroacoustic acceleration waves. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 462, 3493–3499 (2006)
Corapcioglu, M.Y., Tuncay, K.: Propagation of waves in porous media. In: Advances in Porous Media, vol. III, pp. 361–440. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (1996)
Cox, D.A.: Galois Theory, Chap. 1. Wieley, Hoboken (2004)
de la Cruz, V., Hube, J., Spanos, T.J.T.: Reflection and transmission of seismic waves at the boundaries of porous media. Wave Motion 16(4), 323–338 (1992)
de la Cruz, V., Spanos, T.J.T.: Seismic wave propagation in a porous medium. Geophysics 50, 1556–1565 (1985)
Deresiewicz, H.: The effect of boundaries on wave propagation in a liquid-filled porous solid: I. Reflection of plane waves at a free plane boundary (non-dissipative case). Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 50(4):599–607 (1960)
Deresiewicz, H., Rice, J.T.: The effect of boundaries on wave propagation in a liquid-filled porous solid: III. Reflection of plane waves at a free plane boundary (general case). Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 52(3):595–625 (1962)
Deresiewicz, H., Skalak, R.: On uniqueness in dynamic poroelasticity. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 53(4), 783–788 (1963)
Dutta, N.C., Ode, H.: Seismic reflections from a gas–water contact. Geophysics 48, 148–162 (1983)
Eringen, A.C.: A continuum theory of swelling porous elastic soils. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 32, 1337–1349 (1994) [Corrigendum, ibid, 42, 949–949 (2004)]
Gales, C.: On the special behaviour in the theory of swelling porous elastic soils. Int. J. Solid. Struct. 39, 4151–4165 (2002a)
Gales, C.: Some uniqueness and continuous dependence results in the theory of swelling porous elastic soils. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 40, 1211–1231 (2002b)
Gales, C.: On the asymptotic partition of energy in the theory of swelling porous elastic soils. Arch. Mech. 55, 91–107 (2003)
Gales, C.: Waves and vibrations in the theory of swelling porous elastic soils. Eur. J. Mech. A 23, 345–357 (2004)
Garg, S.K.: Wave propagation effects in a fluid-saturated porous solid. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 7947–7962 (1971)
Garg, S.K., Nayfeh, A.H.: Compressional wave propagation in liquid and/or gas saturated elastic porous media. J. Appl. Phys. 60, 3045–3055 (1986)
Geertsma, J., Smit, D.C.: Some aspects of elastic wave propagation in fluid saturated porous solids. Geophysics 26, 169–181 (1961)
Hassanzadeh, S.: Acoustic modeling in fluid-saturated porous media. Geophysics 56, 424–435 (1991)
Jones, J.: Pulse propagation in a poroelastic solid. J. Appl. Mech. 36, 878–880 (1969)
Krebes, E.S.: Discrepancies in energy calculations for inhomogeneous waves. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 75, 839–846 (1983)
Leclaire, P., Cohen-Tenoudji, F., Puente, J.A.: Extension of Biot’s theory of wave propagation to frozen porous media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 96, 3753–3768 (1994)
Lin, C.-H., Lee, V.W., Trifunac, M.D.: The reflection of plane waves in a poroelastic half-space saturated with inviscid fluid. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 25, 205–223 (2005)
Liu, Q.R., Katsube, N.: The discovery of a second kind of rotational wave in a fluid-filled porous material. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 88(2), 1045–1053 (1990)
Morland, L.W.: A simple constitutive theory for a fluid saturated porous solid. J. Geophys. Res. 77, 890–900 (1972)
Morse, P.M., Feshback, H.: Methods of Theoretical Physics. McGraw-Hill Book, New York (1953)
Plona, T.J.: Observation of second bulk compressional wave in a porous medium at ultrasonic frequencies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 36, 259–261 (1980)
Pride, S.R., Gangi, A.F., Morgan, F.D.: Deriving equations of motion for isotropic media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 92, 3278–3290 (1992)
Quintanilla, R.: On the linear problem of swelling porous elastic soils. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 269, 50–72 (2002a)
Quintanilla, R.: On the linear problem of swelling porous elastic soils with incompressible fluid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 40, 1485–1494 (2002b)
Rajagopal, K.R., Tao, L.: Mechanics of Mixtures. Series on Advances in Mathematics for Applied Sciences. World Scientific, River Edge (1995)
Rubino, J.G., Ravazzoli, C.L., Santos, J.E.: Reflection and transmission of waves in composite porous media: a quantification of energy conservations involving slow waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120, 2425–2436 (2006)
Santos, J.E., Corbero, J.M., Douglas, J.J.: Static and dynamic behaviour of a porous solid saturated by a two-phase fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87, 1428–1438 (1990a)
Santos, J.E., Corbero, J.M., Douglas, J.J., Lovera, O.M.: A model for wave propagation in a porous medium saturated by a two-phase fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87, 1439–1448 (1990b)
Santos, J.E., Corbero, J.M., Ravazzoli, C.L., Hensley, J.L.: Reflection and transmission coefficients in fluid-saturated porous media. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 91, 1911–1923 (1992)
Santos, J.E., Ravazzoli, C.L., Carcione, J.M.: A model for wave propagation in a composite solid matrix saturated by a single-phase fluid. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115, 2749–2760 (2004)
Sharma, M.D.: Wave propagation in a dissipative poroelastic medium. IMA J. Appl. Math. 29, 1–11 (2011)
Sharma, M.D., Kumar, M.: Reflection of attenuated waves at the surface of a porous solid saturated with two immiscible viscous fluids. Geophys. J. Int. 184, 371–384 (2011)
Straughan, B.: Stability and Wave Motion in Porous Media. Springer, New York (2008)
Tomar, S.K., Arora, A.: Reflection and transmission of elastic waves at an elastic/porous solid saturated by two immiscible fluids. Int. J. Solid. Struc. 43(7–8), 1991–2013 (2006) [Erratum, ibid, 44(17), 5796–5800 (2007)]
Tuncay, K., Corapcioglu, M.Y.: Wave propagation in poroelastic media saturated by two fluids. J. Appl. Mech. 64, 313–320 (1997)
Wei, C., Muraleetharan, K.K.: A continuum theory of porous media saturated by multiphase immiscible fluids-I. Linear poroelasticity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 40, 1807–1833 (2002)
Yeh, C.-L., Lo, W.-C., Jan, C.-D., Yang, C.-C.: Reflection and refraction of obliquely incident elastic waves upon the interface between two porous elastic half-spaces saturated by different fluid mixtures. J. Hydrol. 395(1–2), 91–102 (2010)
Acknowledgments
One of the authors SG acknowledges the financial support provided by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, INDIA, in the form of JRF through the Grant No. 09/135(0623)/2010-EMR-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
The explicit expressions of the elements of matrices \(P\) and \(Q\) are given as
where \(i=1,2,3;\quad j=1,2;\quad J = j+3.\)
Appendix 2
The explicit expressions of the elements of matrices \(P^{\prime }\) and \(Q^{\prime }\) are given as
where \(i=1,2,3;\quad j=1,2;\quad J = j+3.\)
Appendix 3
The explicit expressions of the elements of the matrix \(F\) are given by
where \(i=1,2,3;\quad j=1,2;\quad J = j+3.\)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomar, S.K., Goyal, S. Elastic Waves in Swelling Porous Media. Transp Porous Med 100, 39–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0204-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-013-0204-4