Abstract
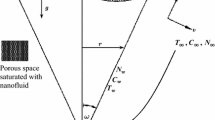
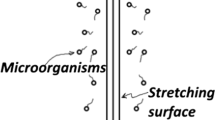
The free convection of non-Newtonian nanofluids along a vertical plate in porous medium is investigated numerically. It is assumed that the medium contains gyrotactic microorganisms along with nanoparticles and the plate is subjected to prescribed temperature, concentration of nanoparticles and density of motile microorganisms. It is further assumed that the plate is impermeable. The governing partial differential equations are reduced to nonlinear ordinary differential equations using similarity transformations. The nonlinear ordinary differential equations are then solved by a finite difference numerical method. The effects of controlling parameters on several dimensionless quantities and numbers of our interest are investigated. The numerical results are compared with the published data and an excellent agreement has been found. It is found that nanofluid and bioconvection parameters have strong effects on local Nusselt, Sherwood and density numbers.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(b\) :
-
Chemotaxis constant
- \(\bar{{C}}\) :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction (\(\text{ kg}\, \text{ m}^{-3})\)
- \(\bar{{C}}_\mathrm{w}\) :
-
Wall nanoparticle volume fraction (\(\text{ kg}\, \text{ m}^{-3})\)
- \(\bar{{C}}_\infty \) :
-
Ambient nanoparticle volume fraction (\(\text{ kg}\, \text{ m}^{-3})\)
- \(D_\mathrm{B}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient (\(\text{ m}^{2}\,\text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(D_n \) :
-
Diffusivity of microorganisms (\(\text{ m}^{2}\,\text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(D_\mathrm{T} \) :
-
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient (\(\text{ m}^{2}\,\text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(Ec\) :
-
Eckert number
- \(f(\eta )\) :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- \(g\) :
-
Acceleration due to gravity (\(\text{ m}\,{\text{ s}}^{-2})\)
- \(k\) :
-
Thermal conductivity (\(\text{ m}^{2}\,\text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(K\) :
-
Consistency coefficient (\(\text{ kg}\,{\text{ m}}^{-1}\text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(K_0\) :
-
Permeability of the porous medium (\(\text{ m}^{2})\)
- \(L\) :
-
Characteristic length (\(\text{ m}^{2})\)
- \(Lb\) :
-
Bioconvection Lewis number
- \(Le\) :
-
Lewis number
- \(m\) :
-
Power law index
- \(\bar{{n}}_n \) :
-
Volume fraction of motile microorganisms (\(\text{ kg}\, \text{ m}^{-3})\)
- \(Nb\) :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- \(Nn_{\bar{{x}}} \) :
-
Local density number of the motile microorganisms
- \(Nt\) :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- \(Nu_{\bar{{x}}} \) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \(Pe\) :
-
Bioconvection Péclet number
- \(Pr \) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(\bar{p}\) :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- \(\bar{q}_\mathrm{m} \) :
-
Wall mass flux (\(\text{ kg}\,\text{ m}^{-2}\, \text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(\bar{{q}}_n \) :
-
Wall motile microorganisms flux (\(\text{ kg}\,{\text{ m}}^{-2} \,\text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(\bar{q}_\mathrm{w} \) :
-
Wall heat flux (\(\text{ J}\,{\text{ m}}^{-2}\, \text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(Ra\) :
-
Rayleigh number for the porous medium
- \(Ra_{\bar{{x}}} \) :
-
Local Rayleigh number for the porous medium
- \(Rb\) :
-
Bioconvection Rayliegh number
- \(Sh_{\bar{{x}}} \) :
-
Local Sherwood number
- \(\bar{{T}}\) :
-
Nanofluid temperature (K)
- \(\bar{{T}}_\mathrm{w} \) :
-
Wall temperature (K)
- \(\bar{{T}}_\infty \) :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- \(\bar{u},\;\bar{v}\) :
-
Velocity components along \(\bar{x}\)- and \(y\)-axes (\(\text{ m}\,{\text{ s}}^{-1})\)
- \(\tilde{\bar{u}},\;\tilde{\bar{v}}\) :
-
Average directional swimming velocity of microorganisms along \(\bar{x}\)- and \(y\)-axes (m s\(^{-1})\)
- \(W_\mathrm{c}\) :
-
Constant maximum cell swimming speed (\(\text{ m}\, \text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(\bar{x}, \bar{y}\) :
-
Cartesian coordinates (\(\bar{x}\)-axis is aligned along the stretching surface and \(y\)-axis is normal to it) (m)
- \(\alpha _\mathrm{m} \) :
-
Effective thermal diffusivity of the porous medium (\(\text{ m}^{2}\,\text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(\phi (\eta )\) :
-
Rescaled nanoparticle volume fraction
- \(\eta \) :
-
similarity variable
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Average volume of a microorganism (\(\text{ kg}\,\text{ m}^{-3})\)
- \(\theta (\eta )\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\nu \) :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the fluid (\(\text{ m}^{2}\, \text{ s}^{-1})\)
- \(\rho _\mathrm{f} \) :
-
Fluid density (\(\text{ kg}\,\text{ m}^{-3})\)
- \(\rho _\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Nanoparticle mass density (\(\text{ kg}\, \text{ m}^{-3}\))
- \(({\rho c})_\mathrm{f}\) :
-
Heat capacity of the fluid (\(\text{ J}\, \text{ kg}^{-3}\,\text{ K}^{-1}\))
- \(({\rho c})_\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Heat capacity of the nanoparticle material (\(\text{ J}\,\text{ kg}^{-3}\,\text{ K}^{-1})\)
- \(\tau \) :
-
Ratio between the effective heat capacity of the nanoparticle material and heat capacity of the fluid
- \(\sigma (\eta )\) :
-
Rescaled density of motile microorganisms
- \(\psi \) :
-
Stream function
References
Avramenko, A.A., Kuznetsov, A.V.: The onset of convection in a suspension of gyrotactic microorganisms in superimposed fluid and porous layers: effect of vertical throughflow. Transp. Porous. Med. 65, 159–176 (2006)
Avramenko, A.A., Kuznetsov, A.V.: Bio-thermal convection caused by combined effects of swimming of oxytactic bacteria and inclined temperature gradient in a shallow fluid layer. Int. J. Numer. Method. H. 20, 157–173 (2010)
Aziz, A., Khan, W.A., Pop, I.: Free convection boundary layer flow past a horizontal flat plate embedded in porous medium filled by nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 56, 48–57 (2012)
Cheng, P., Minkowycz, W.J.: Free convection about a vertical flat plate embedded in a porous medium with application to heat transfer from a dike. J. Geophys. Res. 82, 2040–2044 (1977)
Chen, H.T., Chen, C.K.: Free convection flow of non-Newtonian fluids along a vertical plate embedded in a porous medium. ASME J. Heat Transf. 110, 257–260 (1988)
Choi, S.U.S.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: The Proceedings of the 1995 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, San Francisco, USA, 1995; ASME, FED 231/MD 66, 99–105 (1995)
Das, S.: Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 125, 567–574 (2003)
Daungthongsuk, W., Wongwises, S.: A critical review of convective heat transfer nanofluids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 11, 797–817 (2007)
Eastman, J.A., Choi, S.U.S., Li, S., Yu, Y., Thompson, L.J.: Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(6), 718–720 (2001)
Geng, P., Kuznetsov, A.V.: Effect of small solid particles on the development of bioconvection plumes. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 31, 629–638 (2004)
Geng, P., Kuznetsov, A.V.: Settling of bidispersed small solid particles in a dilute suspension containing gyrotactic microorganisms. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 43, 992–1010 (2005a)
Geng, P., Kuznetsov, A.V.: Introducing the concept of effective diffusivity to evaluate the effect of bioconvection on small solid particles. Int. J. Transp. Phenom. 7, 321–338 (2005b)
Hady, F.M., Ibrahim, F.S., Abdel-Gaied, S.M., Eid, M.R.: Boundary-layer non-Newtonian flow over vertical plate in porous medium saturated with nanofluid. Appl. Math. Mech. Engl. Ed. 32(12), 1577–1586 (2011)
Hillesdon, A.J., Pedley, T.J.: Bioconvection in suspensions of oxytactic bacteria: linear theory. J. Fluid Mech. 324, 223–259 (1996)
Kakaç, S., Pramuanjaroenkij, A.: Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 3187–3196 (2009)
Kairi, R.R., Murthy, P.V.S.N.: Effect of melting on mixed convection heat and mass transfer in a non-newtonian fluid saturated non-darcy porous medium. ASME J. Heat Transf. 134, 042601–1 (2012)
Kuznetsov, A.V.: The onset of thermo-bioconvection in a shallow fluid saturated porous layer heated from below in a suspension of oxytactic microorganisms. Eur. J. Mech. B-Fluids. 25, 223–233 (2003).
Kuznetsov, A.V.: The onset of bioconvection in a suspension of gyrotactic microorganisms in a fluid layer of finite depth heated from below. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 32, 574–582 (2005a)
Kuznetsov, A.V.: Investigation of the onset of thermo-bioconvection in a suspension of oxytactic microorganisms in a shallow fluid layer heated from below. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 19, 287–299 (2005b)
Kuznetsov, A.V.: The onset of thermo-bioconvection in a shallow fluid saturated porous layer heated from below in a suspension of oxytactic microorganisms. Eur. J. Mech. B 25, 223–233 (2006)
Kuznetsov, A.V.: The onset of nanofluid bioconvection in a suspension containing both nanoparticles and gyrotactic microorganisms. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37, 1421–1425 (2010)
Kuznetsov, A.V.: Non-oscillatory and oscillatory nanofluid bio-thermal convection in a horizontal layer of finite depth. Eur. J. Mech. B 30(2), 156–165 (2011)
Kuznetsov, A.V., Avramenko, A.V.: Effect of small particles on the stability of bioconvection in a suspension of gyrotactic microorganisms in a layer of finite depth. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 31, 1–10 (2004)
Kuznetsov, A.V., Geng, P.: The interaction of bioconvection caused by gyrotactic micro-organisms and settling of small solid particles. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 15, 328–347 (2005)
Kuznetsov, A.V., Nield, D.A.: Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49, 243–247 (2010)
Masuda, H., Ebata, A., Teramea, K., Hishinuma, N.: Altering the thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles. Netsu Bussei 4(4), 227–233 (1993)
Minsta, H.A., Roy, G., Nguyen, C.T., Doucet, D.: New temperature dependent thermal conductivity data for water-based nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48, 363–371 (2009)
Nield, D.A., Bejan, A.: Convection in Porous Media, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Nield, D.A., Kuznetsov, A.V.: The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 5792–5795 (2009)
Pak, B.C., Cho, Y.: Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp. Heat Transf. 11, 151–170 (1988)
Pop, I., Ingham, D.B.: Convective Heat Transfer: Mathematical and Computational Modeling of Viscous Fluids and Porous Media. Pergamon, Oxford (2001)
Shenoy, A.V.: Non-Newtonian fluid heat transfer in porous media. Adv. Heat Transf. 24, 101–190 (1994)
Vafai, K.: Porous Media: Applications in Biological Systems and Biotechnology. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010)
Wang, X.Q., Mujumdar, A.S.: Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: a review. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 46, 1–19 (2007)
Wang, X.Q., Mujumdar, A.S.: A review on nanofluids—part I: theoretical and numerical investigations. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 25, 613–630 (2008a)
Wang, X.Q., Mujumdar, A.S.: A review on nanofluids—part II: experiments and applications. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 25, 631–648 (2008b)
Xuan, Y., Li, Q.: Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 125, 151–155 (2003)
Yih, K.H.: Uniform lateral mass flux effect on natural convection of non-Newtonian fluids over a cone in porous media. Int. Comm. Heat Mass Transf. 25, 959–968 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, W.A., Uddin, M.J. & Ismail, A.I.M. Free Convection of Non-Newtonian Nanofluids in Porous media with Gyrotactic Microorganisms. Transp Porous Med 97, 241–252 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-0120-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-0120-z