Abstract
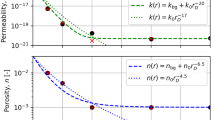
Quantitative in situ monitoring of oil recovery from sedimentary rock is demonstrated for the first time using advanced two-dimensional (2D) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) correlation measurements on a low field spectrometer. The laboratory-scale NMR system was chosen to provide a common physics of measurement with NMR well-logging tools. The NMR protocols are used to monitor recovery of a heavy Middle East crude oil from high permeability sandstone plugs using a brine (water) flood followed by chemical enhanced oil recovery agents: polymer and alkaline–surfactant–polymer solutions. 2D correlations between relaxation time (T 1, T 2) and apparent self-diffusion coefficient D app are used to obtain simultaneously a volumetric determination of the oil and aqueous fluid-phase saturations present in the porous material. The T 1 − T 2 and D app − T 2 correlations are bulk measurements of the entire rock core-plug; excellent agreement is shown between the measures of remaining oil (from NMR) and recovered oil (from gravimetric assay of the effluent). Furthermore, we introduce the capability to measure spatially resolved T 2 distributions on a low field spectrometer using a rapid frequency-encoded y − T 2 map. A non-uniform distribution of remaining oil is observed due to viscous instabilities in the flowing liquids; the final oil saturation ranges from \({S_{\rm o}^{\rm{(final)}} \approx 0}\) to 20 % along the direction of flow. These results highlight the quantitative nature of the NMR data obtainable in low field NMR core analysis and also the importance of spatially resolved measurements when studying short core-plugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora, S., Horstmann, D., Cherukupalli, P., Edwards, J., Ramamoorthy, R., McDonald, T., Bradley, D., Ayan, C., Zaggas, J., Cig, K.: Single-Well In-Situ Measurement of Residual Oil Saturation After an EOR Chemical Flood. SPE 129069 (2010)
Baldwin B.A., Spinler E.A.: A direct method for simultaneously determining positive and negative capillary pressure curves in reservoir rock. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 20, 161–165 (1998)
Baldwin B.A., Yamanashi W.S.: Detecting fluid movement and isolation in reservoir core with medical NMR imaging techniques. SPE Reserv. Eng. 4, 207–212 (1989)
Baldwin B.A., Yamanashi W.S.: Capillary-pressure determinations from NMR images of centrifuged core plugs: Berea sandstone. Log Anal. 32, 550–556 (1991a)
Baldwin B.A., Yamanashi W.S.: NMR imaging of fluid saturation distributions in cores. Log Anal. 32, 536–549 (1991b)
Blackband S., Mansfield P., Barnes J.R., Clague A.D.H., Rice S.A.: Discrimination of crude oil and water in sand and in bore cores with NMR imaging. SPE Form. Eval. 1, 31–34 (1986)
Borgia G.C., Brancolini A., Camanzi A., Maddinelli G.: Capillary water determination in core plugs: A combined study based on imaging techniques and relaxation analysis. Magn. Reson. Imaging 12, 221–224 (1994)
Borgia, G.C., Bortolotti, V., Fantazzini, P.: Magnetic resonance relaxation-tomography to assess fractures induced in vugular carbonate cores. SPE 56787. In: ATC, Houston, Texas, 3–6 October 1999
Bortolotti, V., Macini, P., Mesini, E., Srisuriyachai, F., Fantazzini, P., Gombia, M.: Combined spatially resolved and non-resolved 1H-NMR relaxation analysis to assess and monitor wettability reversal in carbonate rocks. IPTC 13443. In: IPTC, Doha, Qatar, 7–9 December 2009
Bouwmeester, R., Faber, R.: Shell Global Solutions International BV. Private communication (2012)
Brautaset, A., Ersland, G., Graue, A., Stevens, J., Howard, J.: Using MRI to Study In Situ Oil Recovery During CO2 Injection in Carbonates. SCA 2008-41 (2008)
Brown, L.D.: NMR Imaging: Principles and Recent Progress. SCA88-12 (1988)
Butler J.P., Reeds J.A., Dawson S.V.: Estimating solutions of 1st kind integral-equations with nonnegative constraints and optimal smoothing. SIAM J Num. Anal. 18(3), 381–397 (1981)
Callaghan P.: Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Microscopy. Clarendon, Oxford (1991)
Carr H., Purcell E.: Effects of diffusion on free precession in NMR experiments. Phys. Rev. 94, 630–638 (1954)
Chardaire-Rivière, C., Roussel, J.C.: Use of a High Magnetic Field to Visualize Fluids in Porous Media by MRI. SCA91-12 (1991)
Chen Q., Balcom B.J.: Measurement of rock-core capillary pressure curves using a single-speed centrifuge and one-dimensional magnetic-resonance imaging. J. Chem. Phys. 122, 214–720 (2005)
Chen Q., Gingras M.K., Balcom B.J.: A magnetic resonance study of pore filling processes during spontaneous imbibition in Berea sandstone. J. Chem. Phys. 119, 9609–9616 (2003)
Cotts R.M., Hoch M.J.R., Sun T., Markert J.T.: Pulsed field gradient stimulated echo methods for improved NMR diffusion measurements in heterogeneous systems. J. Magn. Reson. 83, 252–266 (1989)
Davies S., Packer K.J.: Pore-size distributions from nuclear magnetic resonance spin-lattice relaxation measurements of fluid-saturated porous solids. I. Theory and simulation. J. Appl. Phys. 67(6), 3163–3170 (1990a)
Davies S., Packer K.J.: Pore-size distributions from nuclear magnetic resonance spin-lattice relaxation measurements of fluid-saturated porous solids. II. Applications to reservoir core samples. J. Appl. Phys. 67(6), 3171–3176 (1990b)
Doughty D.A., Maerefat N.L.: Preliminary transformation of an NMR spectrometer into an NMR imager for evaluating fluid content and rock properties of core samples. Log Anal. 30, 78–84 (1989)
Doughty D.A., Tomutsa L.: Multinuclear NMR microscopy of two-phase fluid systems in porous rock. Magn. Reson. Imaging 14, 869–873 (1996)
Edelstein, W.A., Vinegar, H.J., Tutunjian, P.N., Roemer, P.B., Mueller, O.M.: NMR imaging for core analysis, pp. 101–112. SPE 18272. In: 63rd ATC, Houston, Texas, 2–5 October 1988
Enwere, M.P., Archer, J.S.: NMR imaging for water/oil displacement in cores under viscous-capillary force control. SPE/DOE 24166, pp. 99–104. In: SPE/DOE 8th Symposium on EOR, Tulsa, Oklahomo, 22–24 April 1992
Fernø, M.A., Ersland, G., Haugen, Å, Graue, A., Stevens, J., Howard, J.J.: Visualizing Fluid Flow with MRI in Oil-Wet Fractured Carbonate Rock. SCA2007-12 (2007)
Fordham E.J., Horsfield M.A., Hall L.D., Maitland G.C.: Depth filtration of clay in rock cores observed by one-dimensional 1H NMR imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 156, 253–255 (1993)
Fordham E.J., Sezginer A., Hall L.D.: Imaging multiexponential relaxation in the (y, log_e T 1) plane, with application to clay filtration in rock cores. J. Magn. Reson. A 113, 139–150 (1995)
Gladden L.F., Mitchell J.: Measuring adsorption, diffusion and flow in chemical engineering: applications of magnetic resonance to porous media. New J. Phys. 13, 035,001 (2011)
Gleeson J.W., Woessner D.E., Jordan C.F. Jr.: NMR imaging of pore structures in limestones. SPE Form. Eval. 8, 123–127 (1993)
Green, D.P., Dick, J.R., McAloon, M., Cano-Barrita, P.F.d.J., Burger, J., Balcom, B.: Oil/Water Imbibition and Drainage Capillary Pressure Determined by MRI on a Wide Sampling of Rocks. SCA2008-01 (2008)
Haacke E.M., Brown R.W., Thompson M.R., Venkatesan R.: Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles and Sequence Design. Wiley, New York (1999)
Hahn E.L.: Spin echoes. Phys. Rev. 80(4), 580–594 (1950)
Heaton, N.J.: Multi-Measurement NMR Analysis Based on Maximum Entropy. US patent 6,960,913 B2 (2005)
Hilfer R., Øren P.E.: Dimensional analysis of pore scale and field scale immiscible displacement. Transp. Porous Media 22, 53–72 (1996)
Howard J.J., Spinler E.A.: Nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of wettability and fluid saturations in chalk. SPE Adv. Tech. Ser. 3, 60–65 (1995)
Hürlimann M.D.: Effective gradients in porous media due to susceptibility differences. J. Magn. Reson. 131, 232–240 (1998)
Hürlimann M.D., Griffin D.D.: Spin dynamics of Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill-like sequences in grossly inhomogeneous B 0 and B 1 fields and application to NMR well logging. J. Magn. Reson. 143(1), 120–135 (2000)
Hürlimann M.D., Venkataramanan L.: Quantitative measurement of two-dimensional distribution functions of diffusion and relaxation in grossly inhomogeneous fields. J. Magn. Reson. 157, 31–42 (2002)
Hürlimann M.D., Venkataramanan L., Flaum C.: The diffusion-spin relaxation time distribution function as an experimental probe to characterize fluid mixtures in porous media. J. Chem. Phys. 117, 10223–10232 (2002)
Kenyon W.E.: Petrophysical principles of applications of NMR logging. Log Anal. 38, 21–43 (1997)
Li L., Han H., Balcom B.J.: Spin echo SPI methods for quantitative analysis of fluids in porous media. J. Magn. Reson. 198, 252–260 (2009)
Mahmoud S., Doughty D.A., Tomutsa L., Honarpour M.M.: Pore Level Fluid Imaging Using High Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Thin Slab Micromodels. SCA90-24 (1990)
Marle C.M.: Multiphase Flow in Porous Media. Editions Technip, Paris (1981)
Mattiello, D., Balzarini, M., Ferraccioli, L., Brancolini, A.: Calculation of Constituent Porosity in a Dual-Porosity Matrix: MRI and Image Analysis Integration. SCA-9706 (1997)
McDonald P.J., Korb J.P., Mitchell J., Monteilhet L.: Surface relaxation and chemical exchange in hydrating cement pastes: a two-dimensional NMR relaxation study. Phys. Rev. E 72, 011409 (2005)
Meiboom S., Gill D.: Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 29, 668–691 (1958)
Mitchell J., Fordham E.J.: Emulation of petroleum well-logging D − T 2 correlations on a standard benchtop spectrometer. J. Magn. Reson. 212, 394–401 (2011)
Mitchell J., Blumler P., McDonald P.J.: Spatially resolved nuclear magnetic resonance studies of planar samples. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 48(4), 161–181 (2006)
Mitchell J., Graf von der Schulenburg D.A., Holland D.J., Fordham E.J., Johns M.L., Gladden L.F.: Determining NMR flow propagator moments in porous rocks without the influence of relaxation. J. Magn. Reson. 193, 218–225 (2008a)
Mitchell J., Sederman A.J., Fordham E.J., Johns M.L., Gladden L.F.: A rapid measurement of flow propagators in porous rocks. J. Magn. Reson. 191, 267–272 (2008b)
Mitchell J., Hürlimann M.D., Fordham E.J.: A rapid measurement of T 1/T 2: the DECPMG sequence. J. Magn. Reson. 200, 198–206 (2009)
Mitchell J., Chandrasekera T.C., Johns M.L., Gladden L.F., Fordham E.J.: Nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation and diffusion in the presence of internal gradients: the effect of magnetic field strength. Phys. Rev. E 81, 26–101 (2010)
Mitchell J., Chandrasekera T.C., Gladden L.F.: Numerical estimation of relaxation and diffusion distributions in two dimensions. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 62, 34–50 (2012)
Nørgaard, J.V., Olsen, D., Springer, N., Reffstrup, J.: Capillary pressure curves for low permeability chalk obtained by NMR imaging of core saturation profiles, pp. 807–816. SPE 30605. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, 22–25 October 1995
Petrov O.V., Ersland G., Balcom B.J.: T 2 distribution mapping profiles with phase-encode MRI. J. Magn. Reson. 209, 39–46 (2011)
Saraf D.N., Fatt I.: Three-phase relative permeability measurement using a nuclear magnetic resonance technique for estimating fluid saturation. SPE J. 1760, 235–242 (1967)
Singer P.M., Leu G., Fordham E.J., Sen P.N.: Low magnetic fields for flow propagators in permeable rocks. J. Magn. Reson. 183, 167–177 (2006)
Song Y.Q., Venkataramanan L., Hürlimann M.D., Flaum M., Frulla P., Straley C.: T 1 − T 2 correlation spectra obtained using a fast two-dimensional Laplace inversion. J. Magn. Reson. 154(2), 261–268 (2002)
Song K.M., Mitchell J., Jaffel H., Gladden L.F.: Simultaneous monitoring of hydration kinetics, microstructural evolution, and surface interactions in hydrating gypsum plaster in the presence of additives. J. Mater. Sci 45, 5282–5290 (2010)
Stejskal E.D., Tanner J.E.: Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of a time-dependent field gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 42, 288–292 (1965)
van Duijn C.J., Molenaar J., de Neef M.J.: The effect of capillary forces on immiscible two-phase flow in heterogeneous porous media. Transp. Porous Media 21, 71–93 (1995)
van Duijn C.J., Mikelić A., Pop I.S.: Effective equations for two-phase flow with trapping on the micro scale. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 62, 1531–1563 (2002)
Venkataramanan L., Song Y.Q., Hürlimann M.D.: Solving Fredholm integrals of the first kind with tensor product structure in 2 and 2.5 dimensions. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 50, 1017–1026 (2002)
Wahba G.: Practical approximate solutions to linear operator equations when data are noisy. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 14, 651–667 (1977)
Washburn K.E., Eccles C.D., Callaghan P.T.: The dependence on magnetic field strength of correlated internal gradient relaxation time distributions in heterogeneous materials. J. Magn. Reson. 194, 33–40 (2008)
Watson A.T., Chang C.T.P.: Characterizing porous media with NMR methods. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 31, 343–386 (1997)
Wilson J.D.: Statistical approach to the solution of 1st kind integral-equations arising in the study of materials and their properties. J. Mater. Sci. 27(14), 3911–3924 (1992)
Yortsos Y.C., Chang J.: Capillary effects in steady-state flow in heterogeneous cores. Transp. Porous Media 5, 399–420 (1990)
Yortsos Y.C., Xu B., Salin D.: Delineation of microscale regimes of fully-developed drainage and implications for continuum models. Comp. Geosci. 5, 257–278 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, J., Staniland, J., Chassagne, R. et al. Quantitative In Situ Enhanced Oil Recovery Monitoring Using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Transp Porous Med 94, 683–706 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-0019-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-0019-8