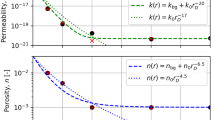
Abstract
Fractures serve as primary conduits having a great impact on the migration of injected fluid into fractured permeable media. Appropriate transport properties such as relative permeability and capillary pressure are essential for successful simulation and prediction of multi-phase flow in such systems. However, the lack of a thorough understanding of the dynamics governing immiscible displacement in fractured media, limits our ability to properly represent their macroscopic transport properties. Previous experimental observations of imbibition front evolution in fractured rocks are examined in the present study using an automated history-matching approach to obtain representative relative permeability and capillary pressure curves. Predicted imbibition front evolution under different flow conditions resulted in an excellent agreement with experimental observations. Sensitivity analyses, in combination with direct experimental observation, allowed exploring the competing effects of relative permeability and capillary pressure on the development of saturation distribution and imbibing front evolution in fractured porous media. Results show that residual saturations are most sensitive to matrix relative permeability to oil, while the ratio of oil and water relative permeability, rock heterogeneity, boundary condition, and matrix–fracture capillary pressure contrast, affect displacement shape, speed, and geometry of the imbibing front.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alajmi, A.F.: The influence of a fracture tip on two-phase flow displacement processes. PhD, The Pennsylvania State University (2003)
Alajmi, A.F., Grader, A.S.: Analysis of fracture–matrix fluid flow interactions using X-ray CT. In: SPE Eastern Meeting, Morgantown, West Virginia, 17–19 Oct 2000
Anderson T.W., Darling D.A.: Asymptotic theory of certain goodness of fit criteria based on stochastic processes. Ann. Math. Stat. 23(2), 193–212 (1952)
Angeles, R., Torres-Verdín, C., Hadibeik, A., Sepehrnoori, K.: Estimation of capillary pressure and relative permeability from formation-tester measurements using design of experiment and data-weighing inversion: synthetic and field examples. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2010.10.006
Archer J.S., Wong S.W.: Use of a reservoir simulator to interpret laboratory waterflood. Data SPE J. 13(6), 5 (1973)
Al-Wadahi, M., Grader, A.S., Ertekin, T.: An investigation of three-phase counter-current flow Using X-ray computerized tomography and neuro-simulation modeling. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, USA, 1–4 Oct 2000
Babadagli, T.: Injection rate controlled capillary imbibition transfer in fractured systems. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 Sep 1994
Babadagli T.: Efficiency of capillary imbibition dominated displacement of nonwetting phase by wetting phase in fractured porous media. Transp. Porous Media 40(3), 323–344 (2000)
Basbug B., Karpyn Z.T.: Estimation of fracture–matrix transport properties from saturation profiles using a multivariate automatic history matching method. Pet. Sci. Technol. 29(9), 11 (2011)
Belayneh M., Geiger S., Matthai S.K.: Numerical simulation of water injection into layered fractured carbonate reservoir analogs. AAPG Bull. 90(10), 1473–1493 (2006). doi:10.1306/05090605153
Bertels S.P., DiCarlo D.A., Blunt M.J.: Measurement of aperture distribution, capillary pressure, relative permeability, and in situ saturation in a rock fracture using computed tomography scanning. Water Resour. Res. 37(3), 649–662 (2001)
Bogdanov I.I., Mourzenko V.V., Thovert J.-F., Adler P.M.: Two-phase flow through fractured porous media. Phys. Rev. E 68(2), 1–24 (2003)
Bourbiaux B.J., Kalaydjian F.J.: Experimental study of cocurrent and countercurrent flows in natural porous media. SPE Reserv. Eng. 5(3), 361–368 (1990)
Brooks R.H., Corey A.T.: Hydraulic properties of porous media: hydrology papers. Colorado State University, Fort Collins (1964)
Chavent, G., Cohen, G., Espy, M.: Determination of relative permeability and capillary pressure by automatic adjustment method. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, USA, 21–24 Sep 1980
Chen, S., Li, G., Peres, A., Reynolds, A.C.: A well test for in-situ determination of relative permeability curves. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, USA, 9–12 Oct 2005
De la Porte, J.J., Kossack, C.A., Zimmerman, R.W.: The effect of fracture relative permeabilities and capillary pressures on the numerical simulation of naturally fractured reservoirs. Paper presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, Dallas, Texas, USA, 9–12 Oct 2005
Donato G., Lu H.Y., Tavassoli Z., Blunt M.J.: Multirate-transfer dual-porosity modeling of gravity drainage and imbibition. SPE J. 12(1), 77–88 (2007)
El-Khatib, N.: Development of a modified capillary pressure J-function In: Middle East Oil Show, Bahrain, 11–14 March 1995
Ertekin, T., Abou-Kassem, J.H., King, G.R.: Basic applied reservoir simulation. SPE Textbook Series, vol. 7. Society of Petroleum Engineers Publications Department, Dallas (2001)
Ewing R.P., Berkowitz B.: A generalized growth model for simulating initial migration of dense non-aqueous phase liquids. Water Resour. Res. 34(4), 611–622 (1998)
Firoozabadi A., Hauge J.: Capillary-pressure in fractured porous-media. J. Pet. Technol. 42(6), 784–791 (1990)
Firoozabadi, A., Markeset, T.: An experimental study of capillary and gravity crossflow fractured porous media. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Washington, DC, 4–7 Oct 1992
Hatiboglu C.U., Babadagli T.: Oil recovery by counter-current spontaneous imbibition: Effects of matrix shape factor, gravity, IFT, oil viscosity, wettability, and rock type. J. Pet. Sci. and Eng 59(1-2), 106–122 (2007)
Heaviside, J., Black, C.J.J., Berry, J.F.: Fundamentals of relative permeability: experimental and theoretical considerations In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Francisco, California, USA, 5–8 Oct 1983
Hoteit H., Firoozabadi A.: An efficient numerical model for incompressible two-phase flow in fractured media. Adv. Water Resour. 31(6), 891–905 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.02.004
Hughes R.G., Blunt M.J.: Pore scale modeling of rate effects in imbibition. Transp. Porous Media 40(3), 295–322 (2000)
IMEX: Three-Phase Black Oil Simulator, User’s Guide. Computer Modeling Group (CMG), Calgary (2009)
Karimi-Fard M., Durlofsky L.J., Aziz K.: An efficient discrete-fracture model applicable for general-purpose reservoir simulators. SPE J. 9(2), 227–236 (2004)
Karpyn Z.T., Alajmi A., Radaelli F., Halleck P.M., Grader A.S.: X-ray CT and hydraulic evidence for a relationship between fracture conductivity and adjacent matrix porosity. Eng. Geol. 103(3–4), 139–145 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.06.017
Kruger W.D.: Determining areal permeability distribution by calculations. J. Pet. Technol. 13(7), 6 (1961)
Lee, C.H., Karpyn, Z.T.: Experimental investigation of rate effects on two-phase flow through fractured rocks using X-ray computed tomography. Paper presented at the 3rd international workshop on X-ray CT for geomaterials, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 1–3 March
Lenormand R., Touboul E., Zarcone C.: Numerical-nodels and experiments on immiscible displacements in porous-media. J. Fluid Mech. 189, 165–187 (1988)
Li, G.: History dependent modeling of countercurrent flow in porous media. PhD, The Pennsylvania State University (2003)
Li K.: A new method for calculating two-phase relative permeability from resistivity data in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 74(1), 21–33 (2008). doi:10.1007/s11242-007-9178-4
Li, K., Horne, R.N.: Correlation between resistivity index, capillary pressure and relative permeability. In: Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress 2010, Bali, Indonesia, 25–29 April 2010
Matthai S.K., Mezentsev A., Belayneh M.: Finite element-node-centered finite-volume two-phase-flow experiments with fractured rock represented by unstructured hybrid-element meshes. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 10(6), 740–756 (2007)
Melean Y., Broseta D., Blossey R.: Imbibition fronts in porous media: effects of initial wetting fluid saturation and flow rate. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 39(3–4), 327–336 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0920-4105(03)00072-X
Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N., Koederitz, L.F.: Two-phase steady-state and unsteady-state relative permeability prediction models. In: SPE Middle East Oil Show, Bahrain, 17–20 March 2001
Mowla A., Firoozabadi A., Borhani Haghighi A., Sahraian A.: Megadose clonazepam dependence: a case report. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 27(5), 542–543 (2007). doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181506e4e
Or D.: Scaling of capillary, gravity and viscous forces affecting flow morphology in unsaturated porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 31(9), 1129–1136 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2007.10.004
Prodanovic, M., Bryant, S.L., Karpyn, Z.T.: Investigating matrix–fracture transfer via a level set method for drainage and imbibition. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado, 21–24 Sep 2008
Rangel-German E.R., Kovscek A.R.: Experimental and analytical study of multidimensional imbibition in fractured porous media. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 36(1–2), 45–60 (2002)
Rangel-German E.R., Kovscek A.R.: Time-dependent matrix–fracture shape factors for partially and completely immersed fractures. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 54(3–4), 149–163 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2006.08.004
Rangel-German E.R., Akin S., Castanier L.: Multiphase-flow properties of fractured porous media. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 51(3–4), 197–213 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2005.12.010
Reichenberger V., Jakobs H., Bastian P., Helmig R.: A mixed-dimensional finite volume method for two-phase flow in fractured porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 29(7), 1020–1036 (2006)
Slough K.J., Sudicky E.A., Forsyth P.A.: Numerical simulation of multiphase flow and phase partitioning in discretely fractured geologic media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 40(2), 107–136 (1999)
Tavassoli Z., Zimmerman R.W., Blunt M.J.: Analysis of counter-current imbibition with gravity in weakly water-wet systems. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 48(1–2), 94–104 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2005.04.003
Tavassoli Z., Zimmerman R.W., Blunt M.J.: Analytic analysis for oil recovery during counter-current imbibition in strongly water-wet systems. Transp. Porous Media 58(1–2), 173–189 (2005). doi:10.1007/s11242-004-5474-4
Timur, A.: An investigation of permeability, porosity, and residual water saturation relationship for sandstone reservoirs. Paper presented at the SPWLA 9th annual logging symposium, 23–26 June
Trivedi J.J., Babadagli T.: Experimental and numerical modeling of the mass transfer between rock matrix and fracture. Chem. Eng. J. 146(2), 194–204 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.cej.2008.05.032
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CH., Karpyn, Z.T. Numerical Analysis of Imbibition Front Evolution in Fractured Sandstone under Capillary-Dominated Conditions. Transp Porous Med 94, 359–383 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-0009-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-012-0009-x